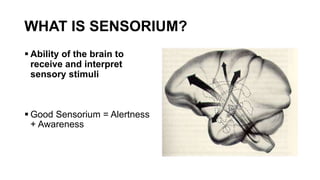
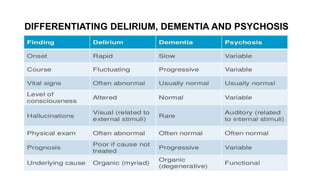
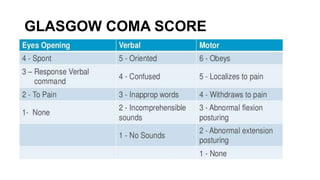
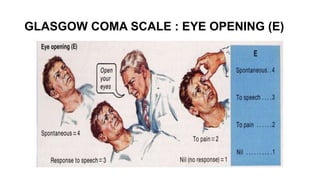
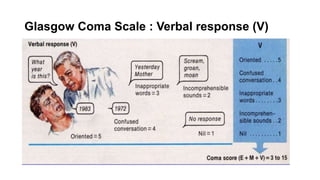
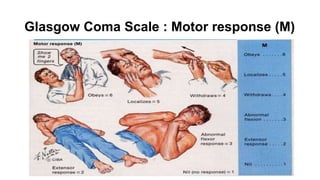
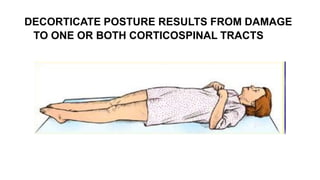
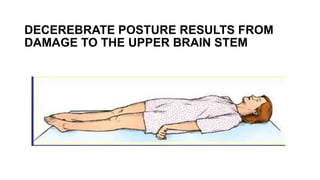
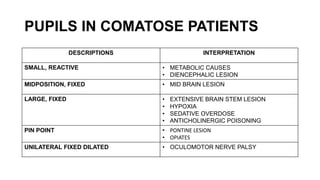
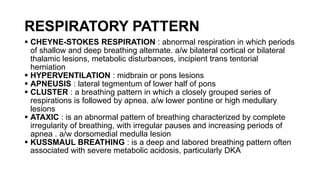
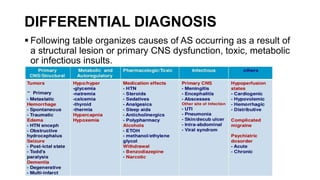
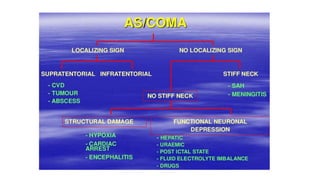
The document provides guidance on evaluating and managing a patient presenting with altered sensorium (AS). It defines sensorium and levels of consciousness. Common causes of AS include metabolic disturbances, infections, trauma, medications, and neurological conditions. The approach involves assessing ABCDE, obtaining history, performing a full physical exam including Glasgow Coma Scale, running diagnostic tests, considering various differential diagnoses, and treating reversible causes. The prognosis depends on the underlying etiology, with metabolic/toxic causes having a better outlook than structural injuries or hypoxia.