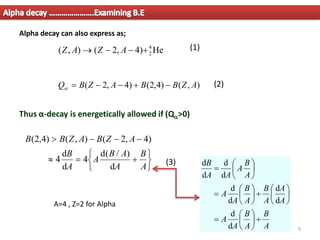
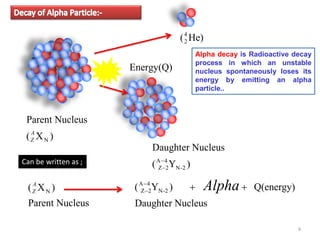
1. Alpha decay is a radioactive decay process where an unstable nucleus spontaneously emits an alpha particle, resulting in a daughter nucleus with a mass number 4 less and atomic number 2 less than the parent nucleus.
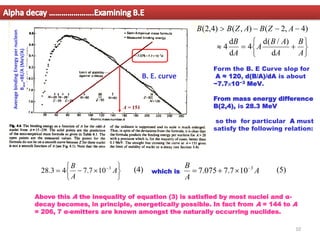
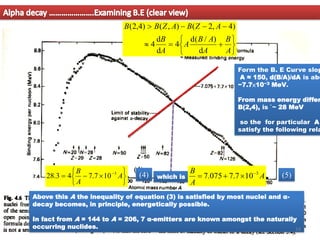
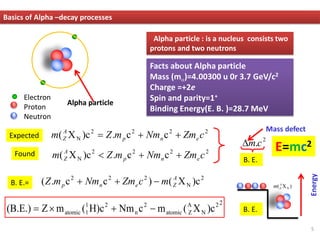
2. For alpha decay to be energetically possible, the Q-value or energy released must be positive. This can be determined by comparing the binding energies and masses of the parent and daughter nuclei based on the binding energy curve.
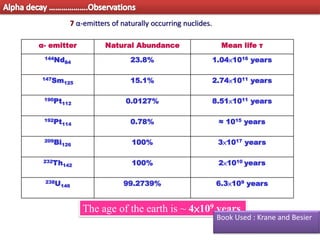
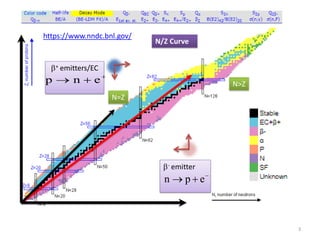
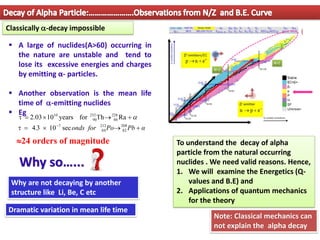
3. Between mass numbers 144-206, 7 naturally occurring alpha emitters are found, as the binding energy relationship in this range allows alpha decay to be energetically favorable. The lifetimes of these nuclei are long enough for them to remain from their origin in supern



![8
❑ An α- particle being kicked out from the unstable parent nucleus is due to
the effect of Coulomb repulsion.
❑ A heavy nucleus with too many protons can reduce some Coulomb
repulsion energy by emitting an α- particle.
❑ An α- particle is less massive and grater binding energy. (EB=28.3 MeV) than
parent nucleus.
❑ Q-Value is the energy available for the reaction i.e. given by the following
Alpha decay ………………….Examining Q-value
2
2
]c
Particle
Alpha
of
Mass
Nucleus
dauchter
of
Mass
Nucleus
Parent
of
[Mass
)]
4
,
2
(
)
4
,
2
(
)
,
(
[
−
−
=
−
−
−
−
=
Q
or
c
M
A
Z
M
A
Z
M
Q
The available energy Qα goes into the kinetic energies of the α-
particle and of the recoil of the daughter nucleus.
If Qα > 0, α-decay is energetically possible](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/alphadecay-1-upload-231225152328-5420bacd/85/alpha-decay-1-upload-pdf-8-320.jpg)