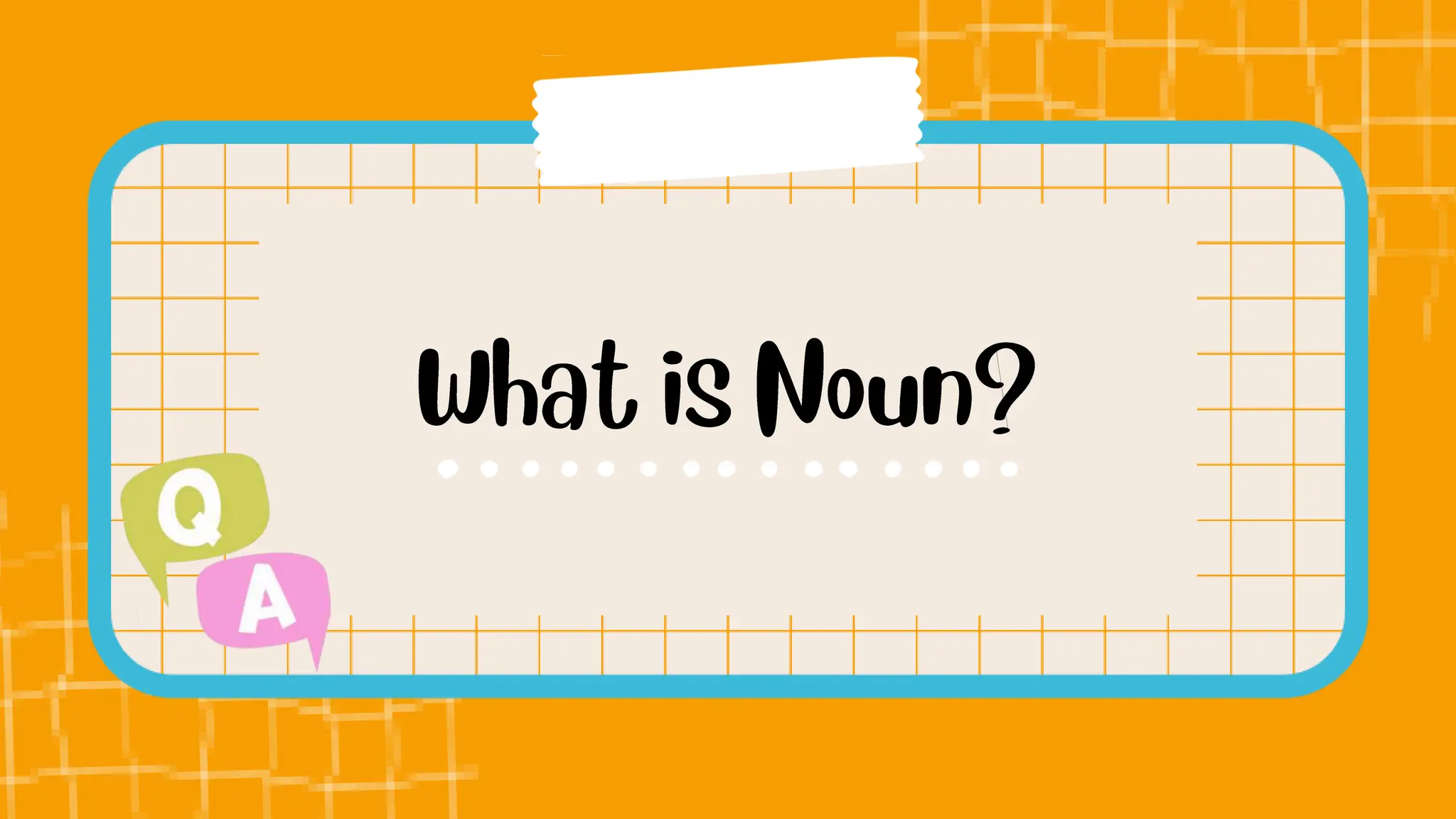
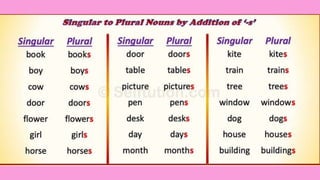
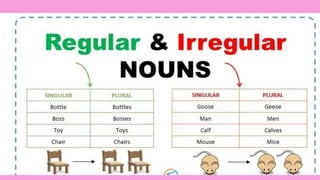
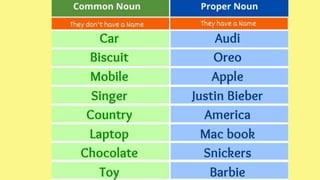
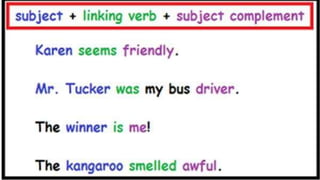
The document discusses different types of nouns including singular and plural nouns, possessive nouns, and how nouns function in a sentence as subjects, subject complements, direct objects, indirect objects, objects of preposition, and in direct address. It provides rules for forming regular plural nouns by adding suffixes like -s, -es depending on the ending of the singular noun. It also explains how to form possessive nouns and defines the different roles a noun can play within a sentence.