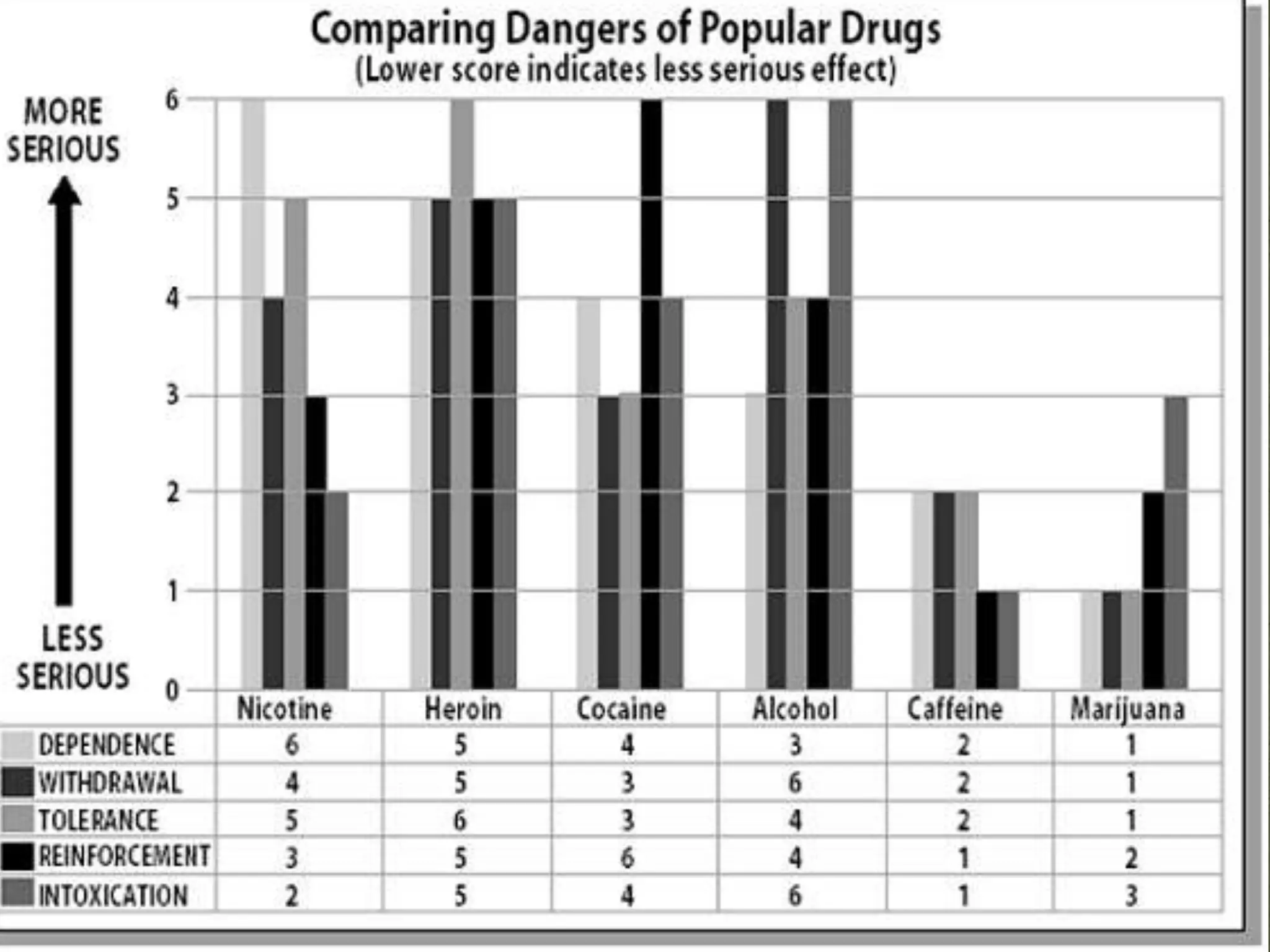
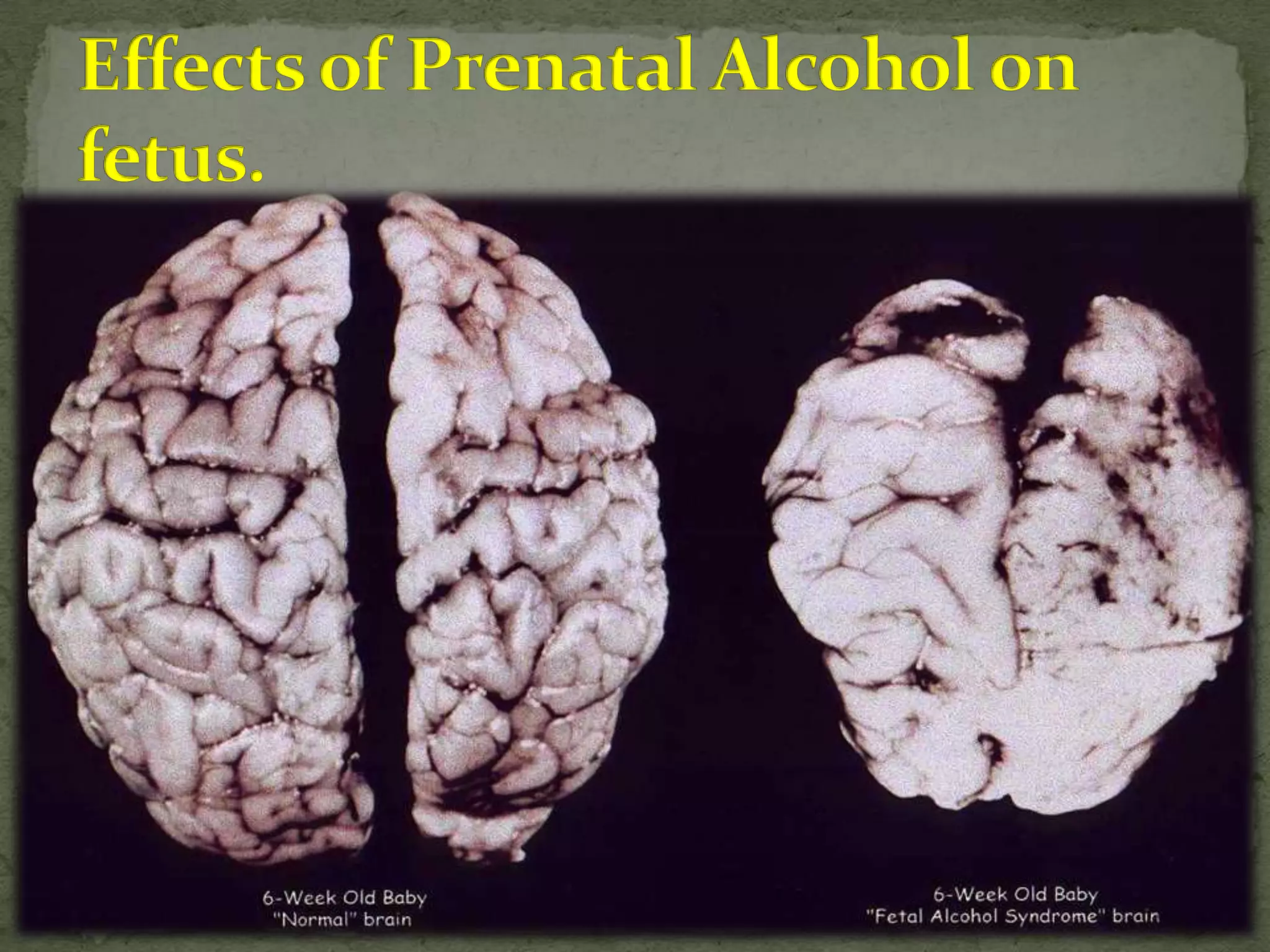
Alcohol is a depressant that is produced through fermentation and distillation. It is consumed for curiosity, socialization, and stress relief initially but can lead to addiction. Alcoholism is characterized by compulsive consumption that harms one's health, relationships, and standing. India has a large alcohol industry and consumption is increasing, especially among youth and women. Chronic alcohol abuse can damage organs and brain function while acute effects include impaired thinking and risk of alcohol poisoning. Treatment focuses on counseling and support groups to help people stop drinking.