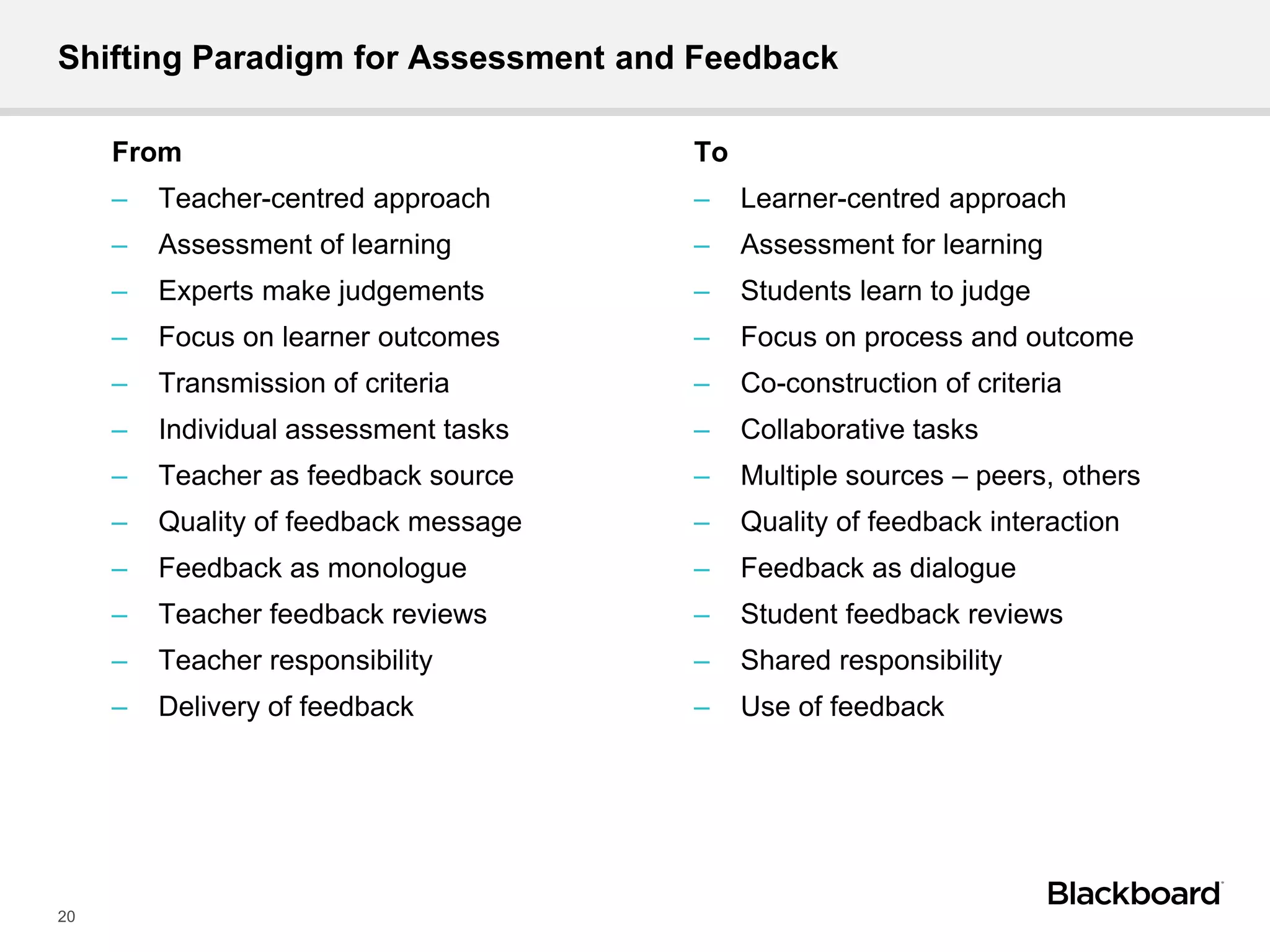
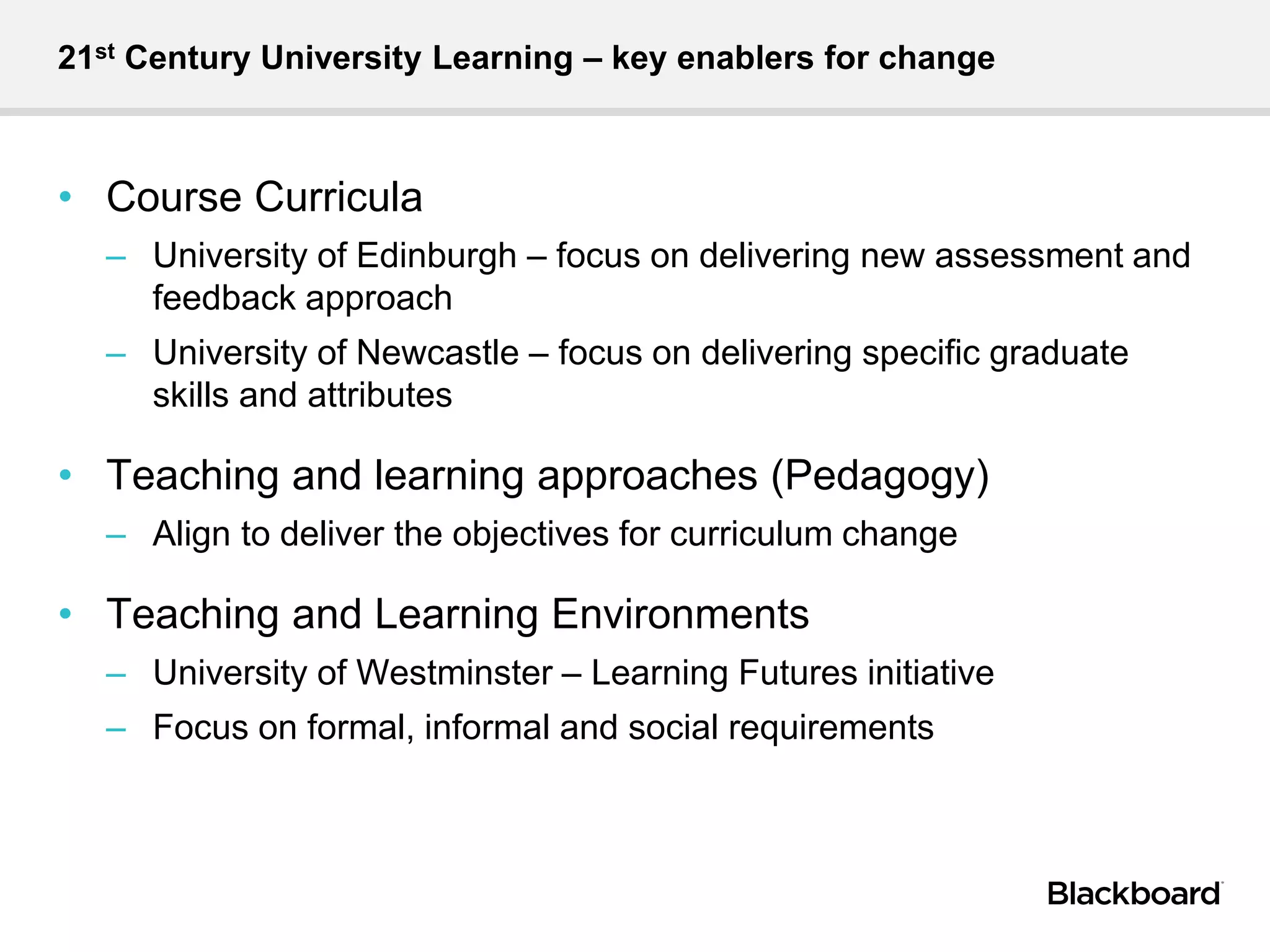
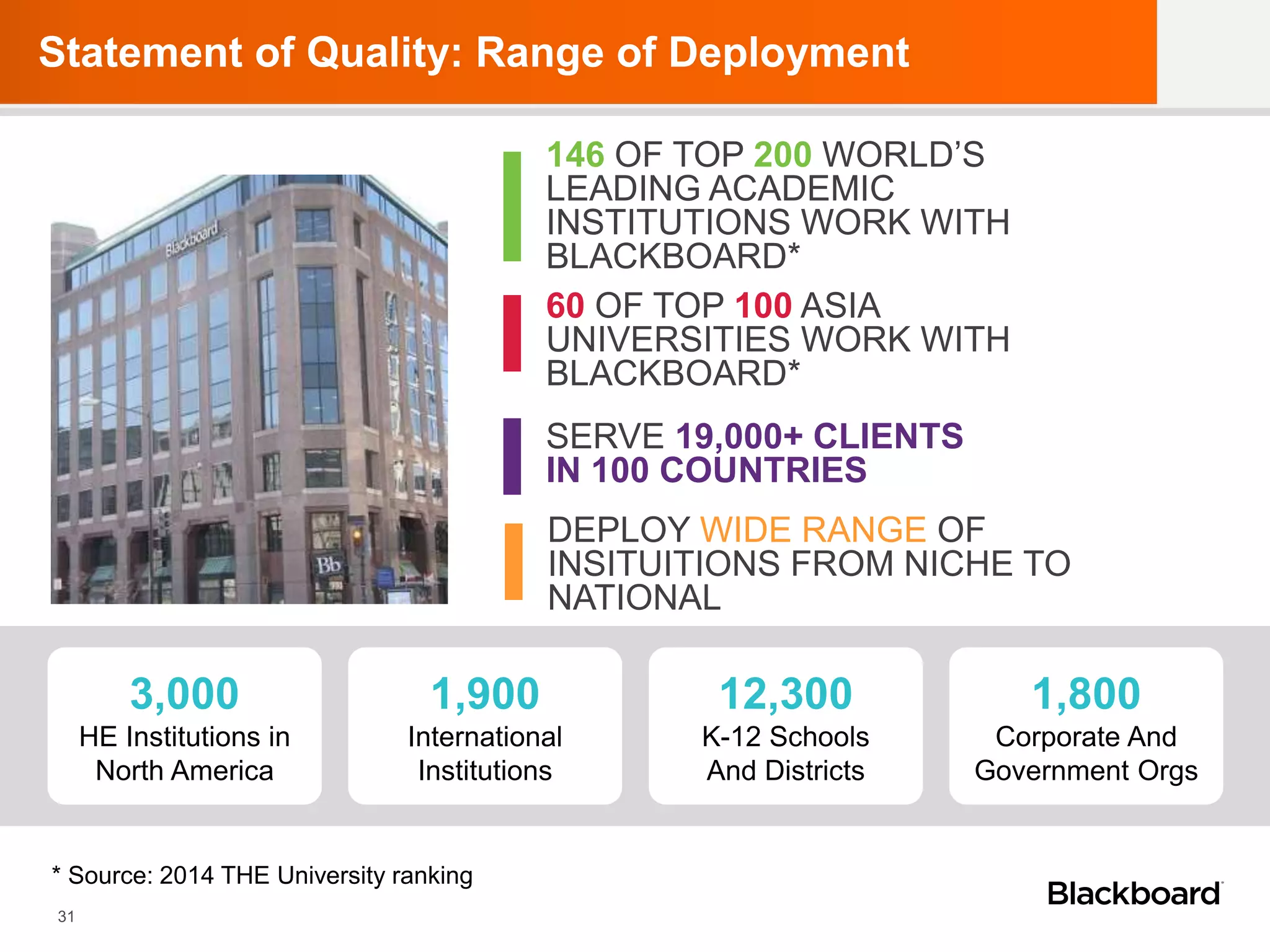
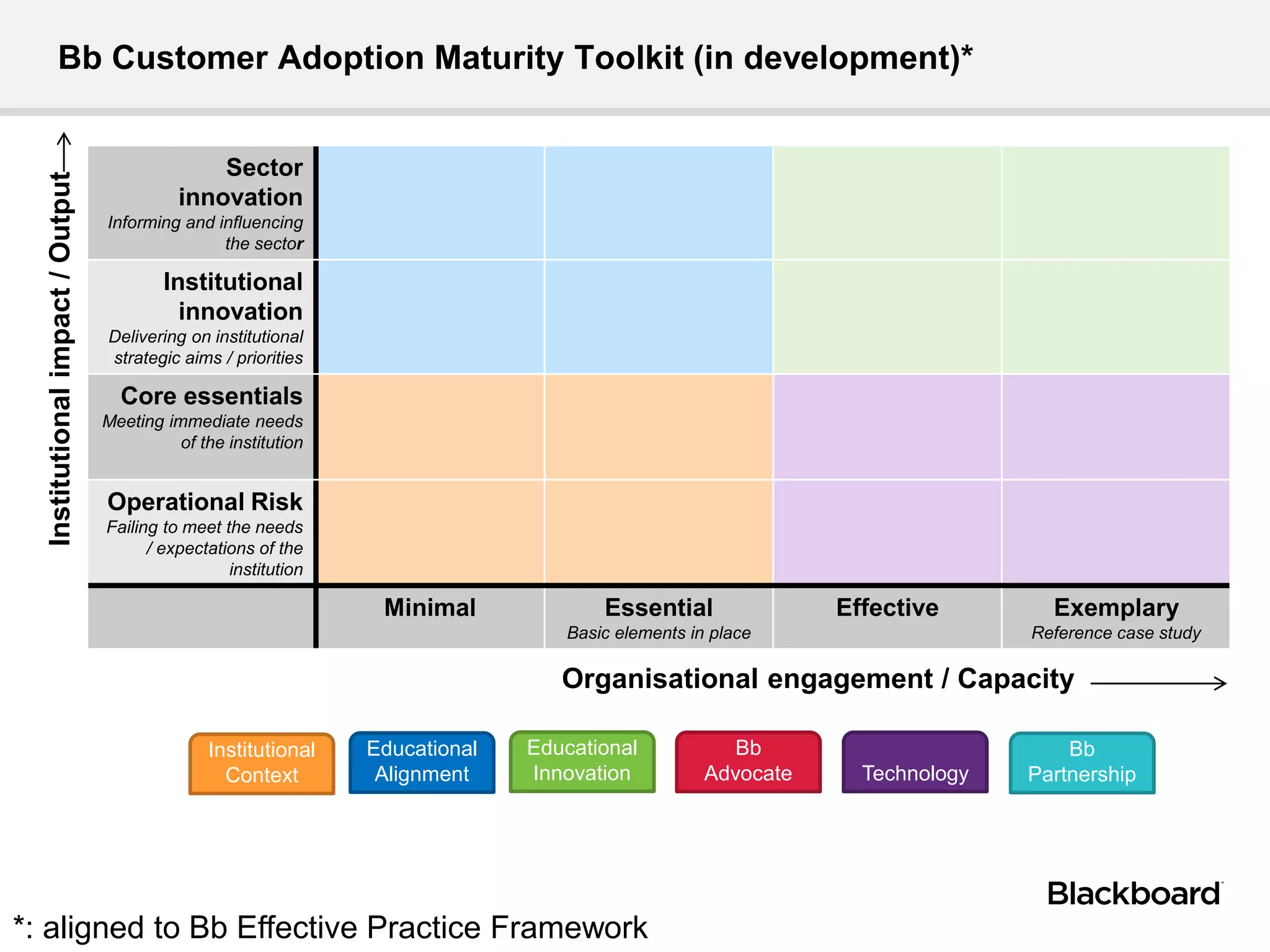
Dr. Alan Masson is the Head of International Customer Success at Blackboard. He has over 20 years of experience in academia and expertise in e-learning, curriculum innovation, and assessment. Blackboard's international customer success team provides expertise to help institutions maximize their use of technology to achieve strategic goals. Higher education faces challenges from global competition, government policies, and changing student expectations. Key characteristics of 21st century universities include talent, resources, governance, and agile processes. 21st century learning emphasizes enquiry-based learning, structured self-directed learning, and acquiring valuable skills through real-world experiences and interactions. Technology is a core element of the learning experience and can inform, inspire, and enable changes to curric