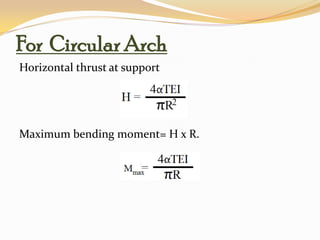
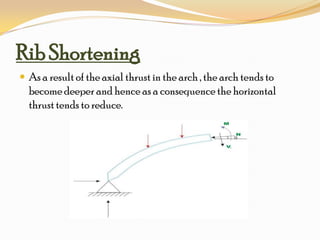
The document discusses temperature effects and rib shortening effects in arches. Due to temperature changes, arches develop a horizontal thrust without any loading, known as the temperature effect. For circular arches, the horizontal thrust at supports creates a maximum bending moment equal to the thrust multiplied by the radius. For parabolic arches, the maximum bending moment equals the horizontal thrust multiplied by the height. Rib shortening occurs as the arch tries to become deeper under axial thrust, reducing the horizontal thrust. The combined effects of temperature and rib shortening on an arch can be expressed through equations that calculate the net horizontal thrust.