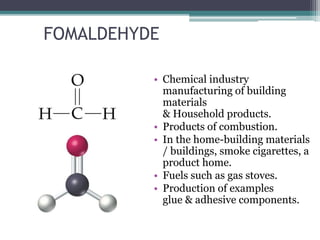
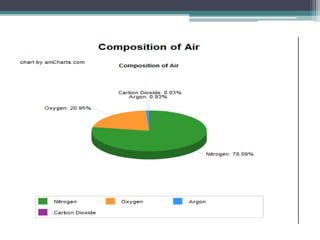
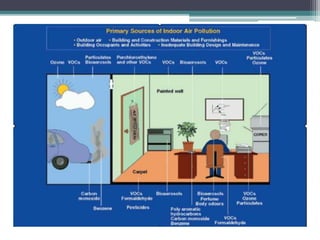
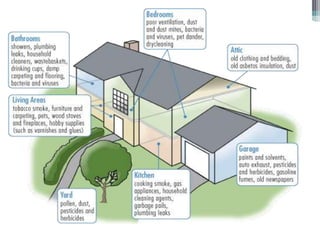
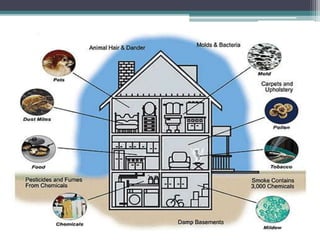
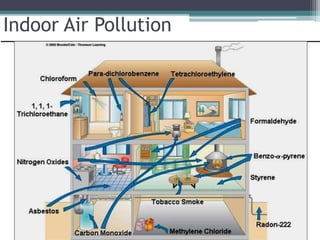
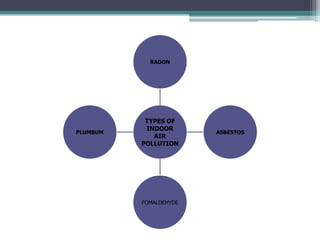
This document provides an overview of air pollution. It defines air pollution as any visible or invisible particle or gas found in the air that is not part of the original, normal composition, including natural sources like forest fires and dust storms, and unnatural man-made sources like emissions from cars, homes, and factories burning fuels like coal and wood. Pollutants are classified as either primary pollutants, which are directly emitted, or secondary pollutants, which form when primary pollutants react. Examples of indoor air pollutants discussed include radon, asbestos, formaldehyde, and lead. Radon is a radioactive gas that can accumulate in homes and cause lung cancer. Asbestos and formaldehyde are linked












![RADON
• Radon is a chemical element in the periodic table that
has the symbol Rn and atomic number 86.
• Noble gas that is formed by the disintegration of radium,
radon is the heaviest gases and is considered a health
hazard.
• The most stable isotope is Rn-222 which has a half life of
3.8 days and used in radiotherapy.
Radon gas can accumulate in homes and cause lung
cancer [1], causing potentially 20,000 deaths in Europe
alone each year.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/airpollution-230525110242-b3177d4f/85/AIR-POLLUTION-pptx-19-320.jpg)