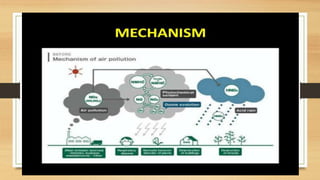
Air pollution occurs when harmful gases, dust, fumes or odors are present in the air. Heat trapping, also known as the greenhouse effect, refers to certain gases like carbon dioxide trapping heat in the lower atmosphere. Some key causes of air pollution and heat trapping include emissions from vehicles, power plants, wildfires, and household activities. This trapped heat leads to issues like rising global temperatures, sea level rise, and climate change. We can help address the problem through individual actions like conserving energy, limiting driving, and participating in conservation programs.