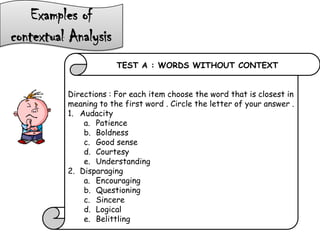
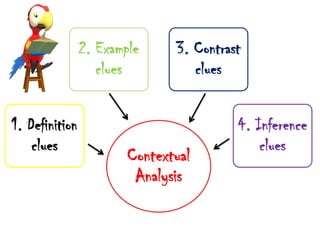
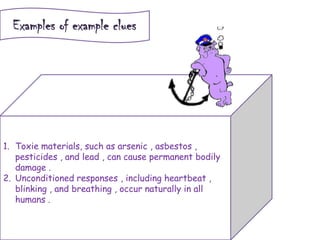
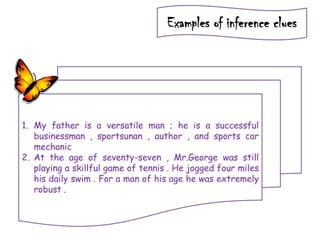
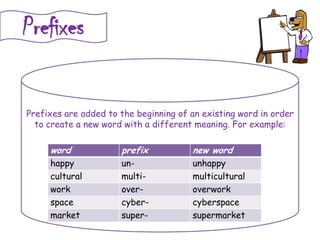
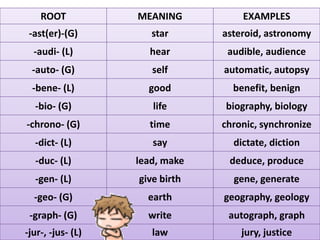
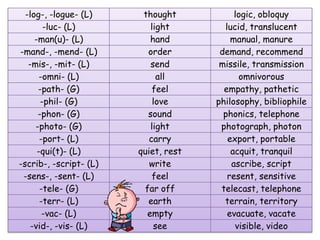
The document discusses different types of contextual clues that can help determine the meaning of unfamiliar words: definition clues, example clues, contrast clues, and inference clues. It provides examples of each type of clue, such as using a synonym or formal definition for definition clues, specific examples for example clues, contrasting words for contrast clues, and making inferences based on context for inference clues. The document also discusses analyzing word parts like prefixes, roots, and suffixes to determine a word's meaning.