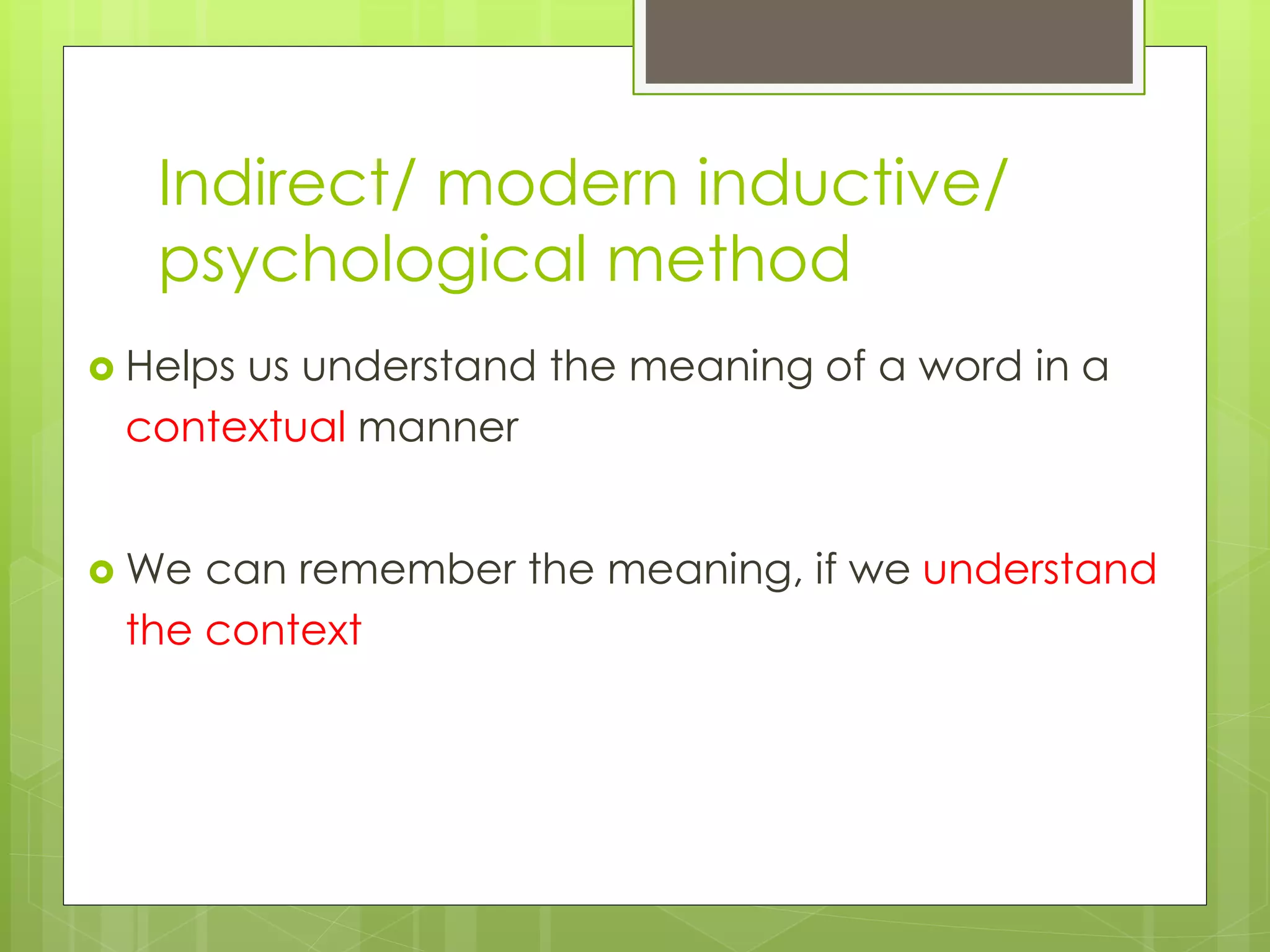
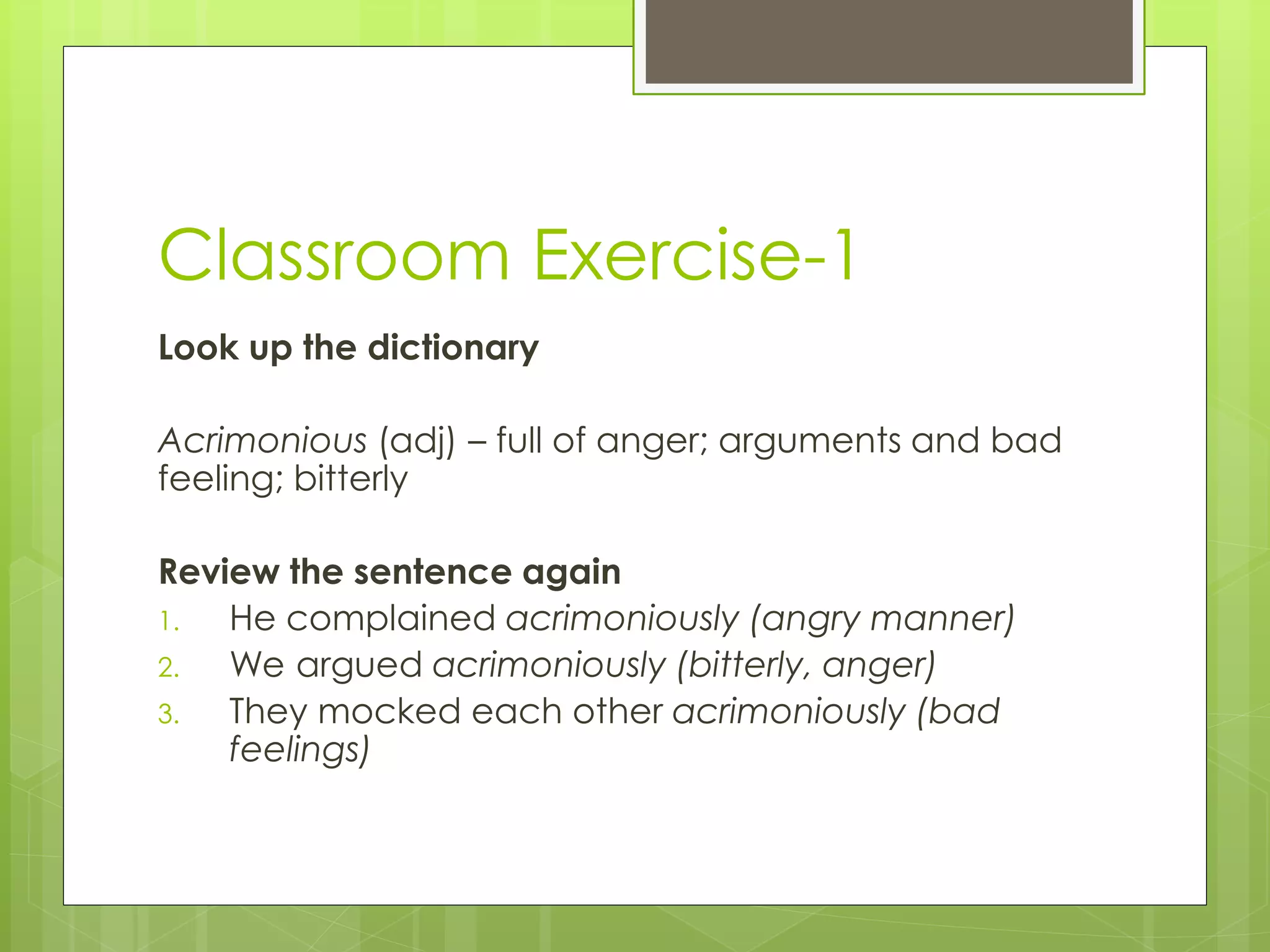
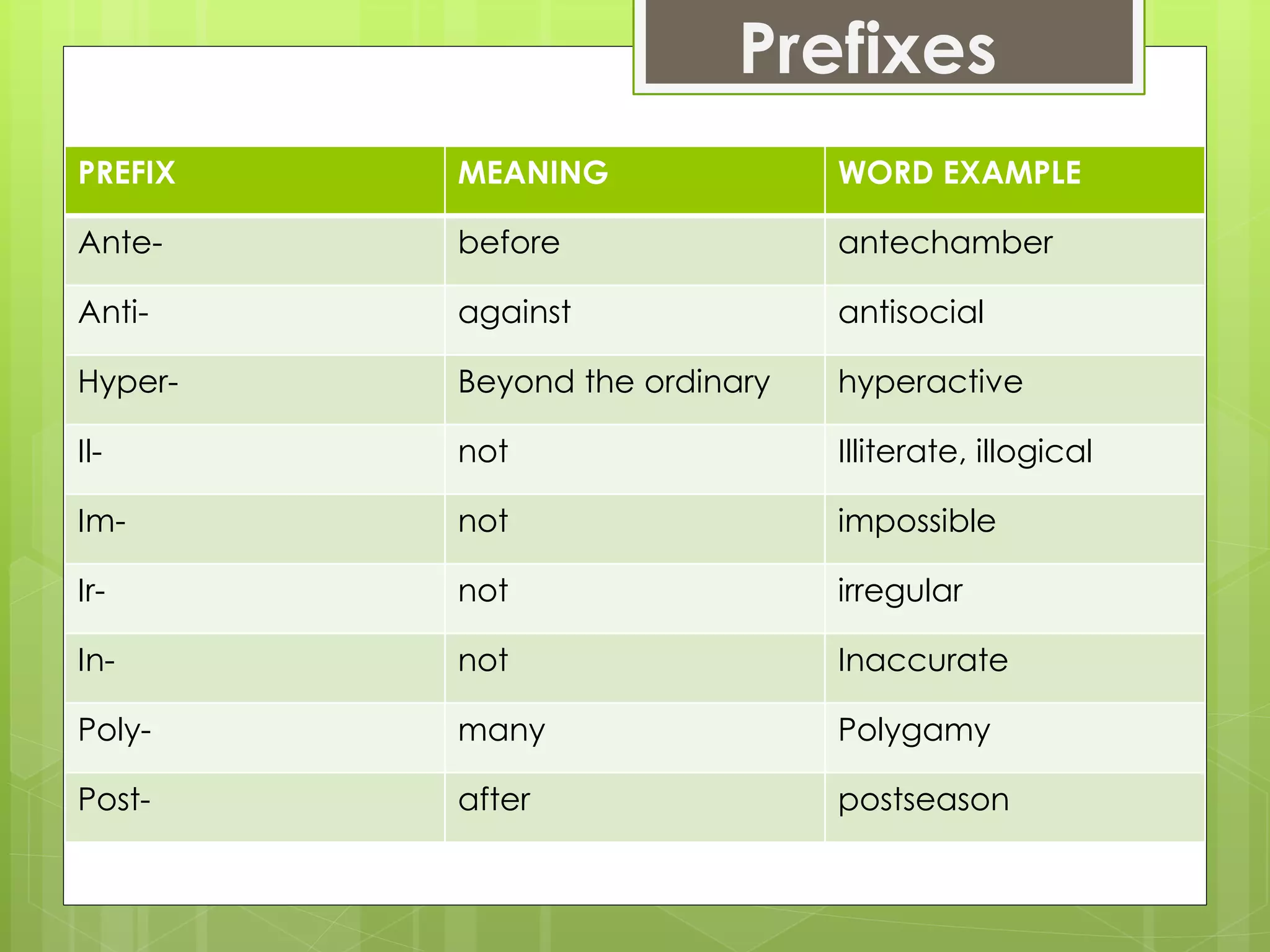
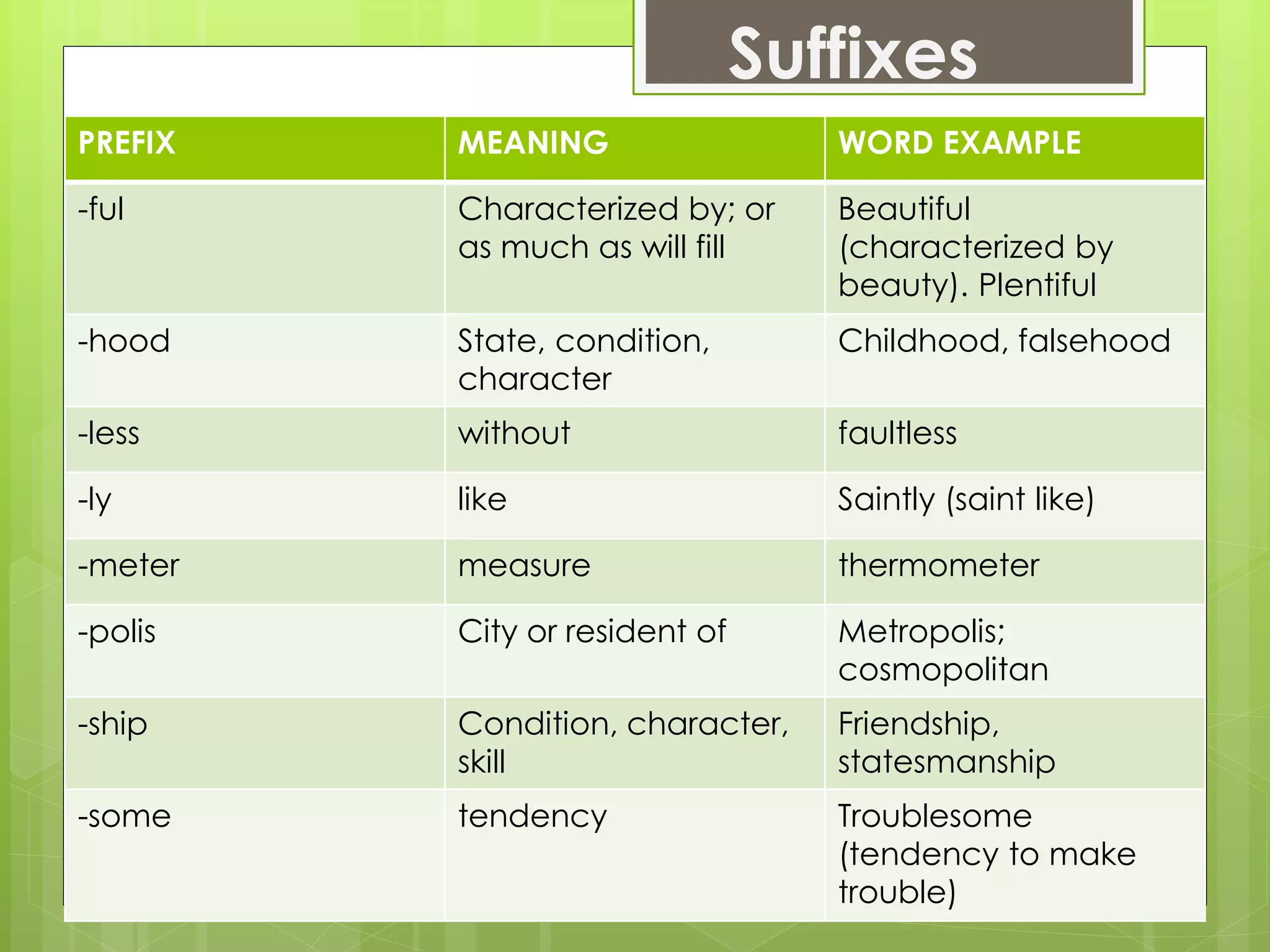
The document outlines an agenda for a training on building vocabulary, writing tips, and confidence. It discusses various vocabulary building techniques like using context clues, word forms, dictionaries, prefixes/suffixes. Examples are provided to demonstrate guessing meanings from context. Writing tips include being concise, using active voice and proofreading. Confidence topics include posture, etiquette, conversation skills. The goal is to improve English communication skills.