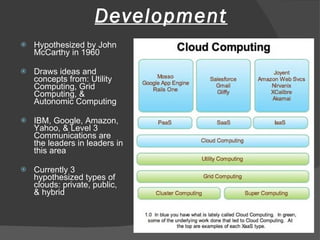
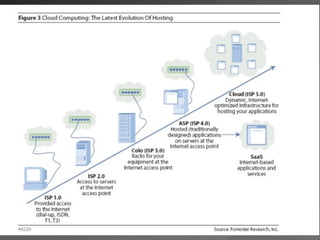
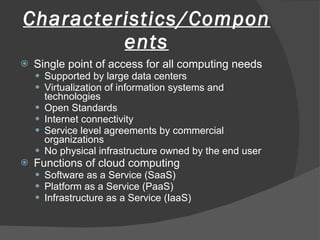
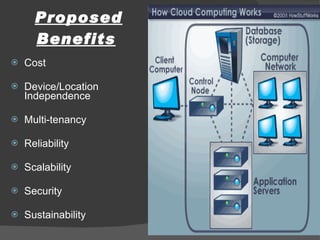
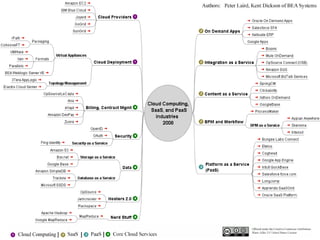
The document discusses cloud computing, including its history and types (private, public, hybrid clouds). It outlines the key characteristics and components of cloud computing like software, platform and infrastructure as a service. The proposed benefits include lower costs, flexibility, scalability, reliability and sustainability. However, concerns relate to privacy, security, regulation and long-term viability. The document recommends a hybrid cloud approach to balance cost savings with control over sensitive data.