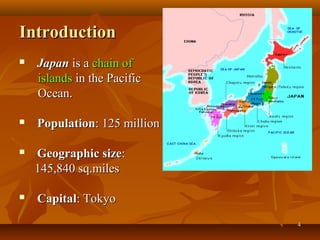
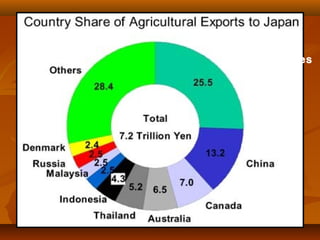
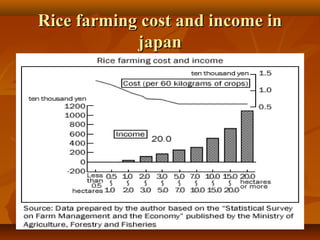
This document provides an overview of agriculture in Japan. It discusses the country's climate and economy, then focuses on different aspects of Japanese agriculture including crops, rice farming, livestock, problems facing farmers, and trends over time. The main crops grown are rice, vegetables, and fruit. Rice farming remains very important and has become more mechanized and productive. However, small family farms struggle with high costs and competition. Over the decades, fewer young people have entered farming as an occupation.