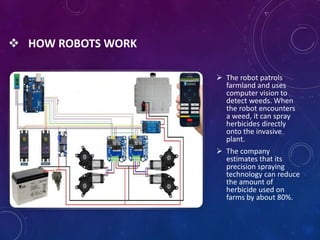
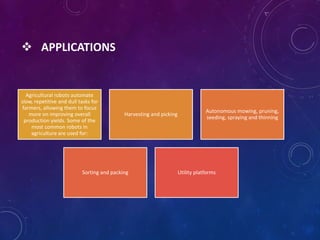
This document discusses the future of robotic agriculture. It begins with an introduction to robots and their ability to perform complex tasks automatically. It then outlines various types of agricultural robots, including those that can harvest crops, apply pesticides precisely via computer vision, and more. The document discusses the need for robotic agriculture to help with labor-intensive tasks. It explores applications like harvesting and utilities. Benefits include reduced pesticide use and focusing farmers on yields. Challenges involve jobs loss and high costs initially. The conclusion is that robotic opportunities in agriculture are vast and the technology can help overcome problems.