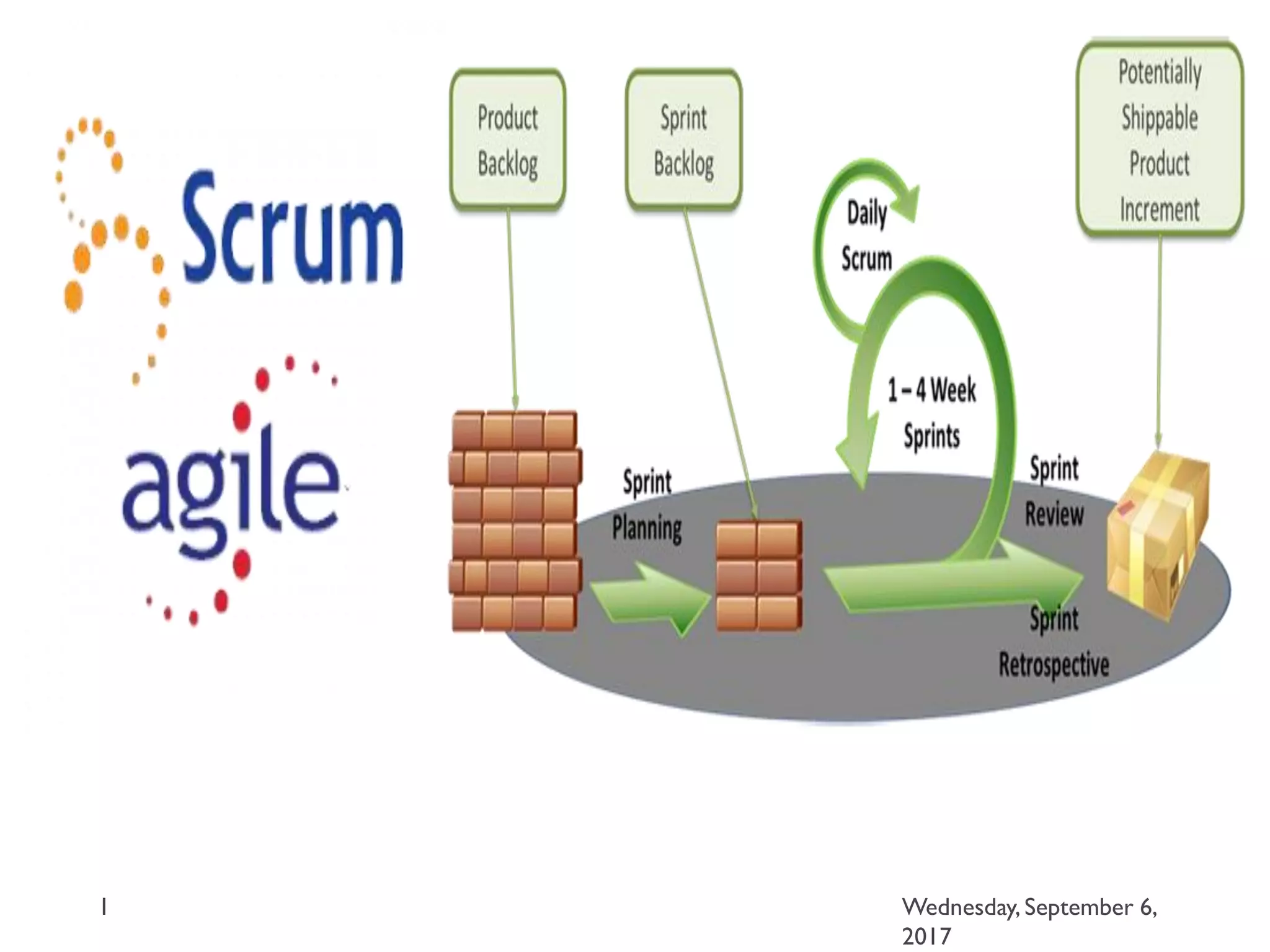
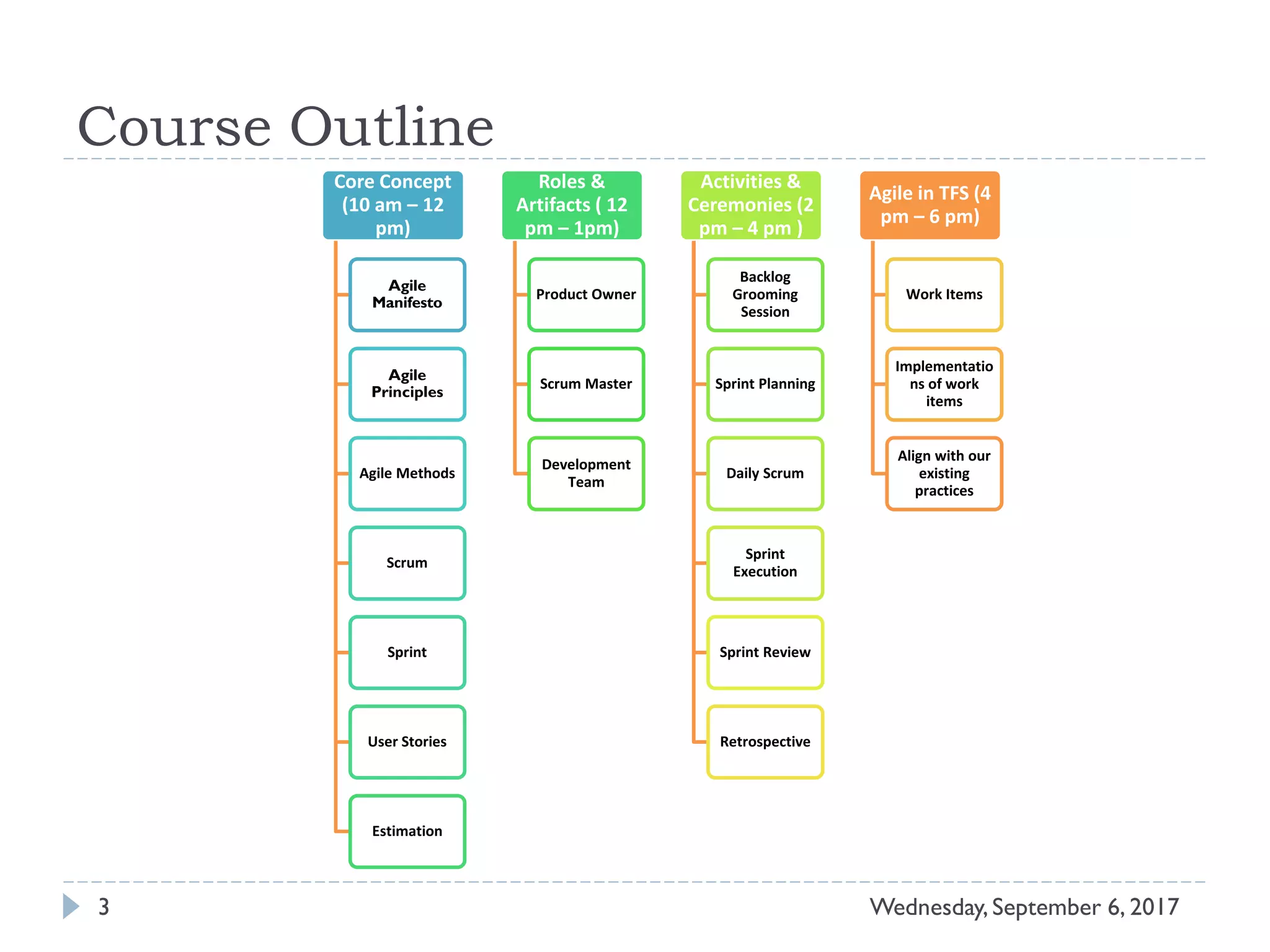
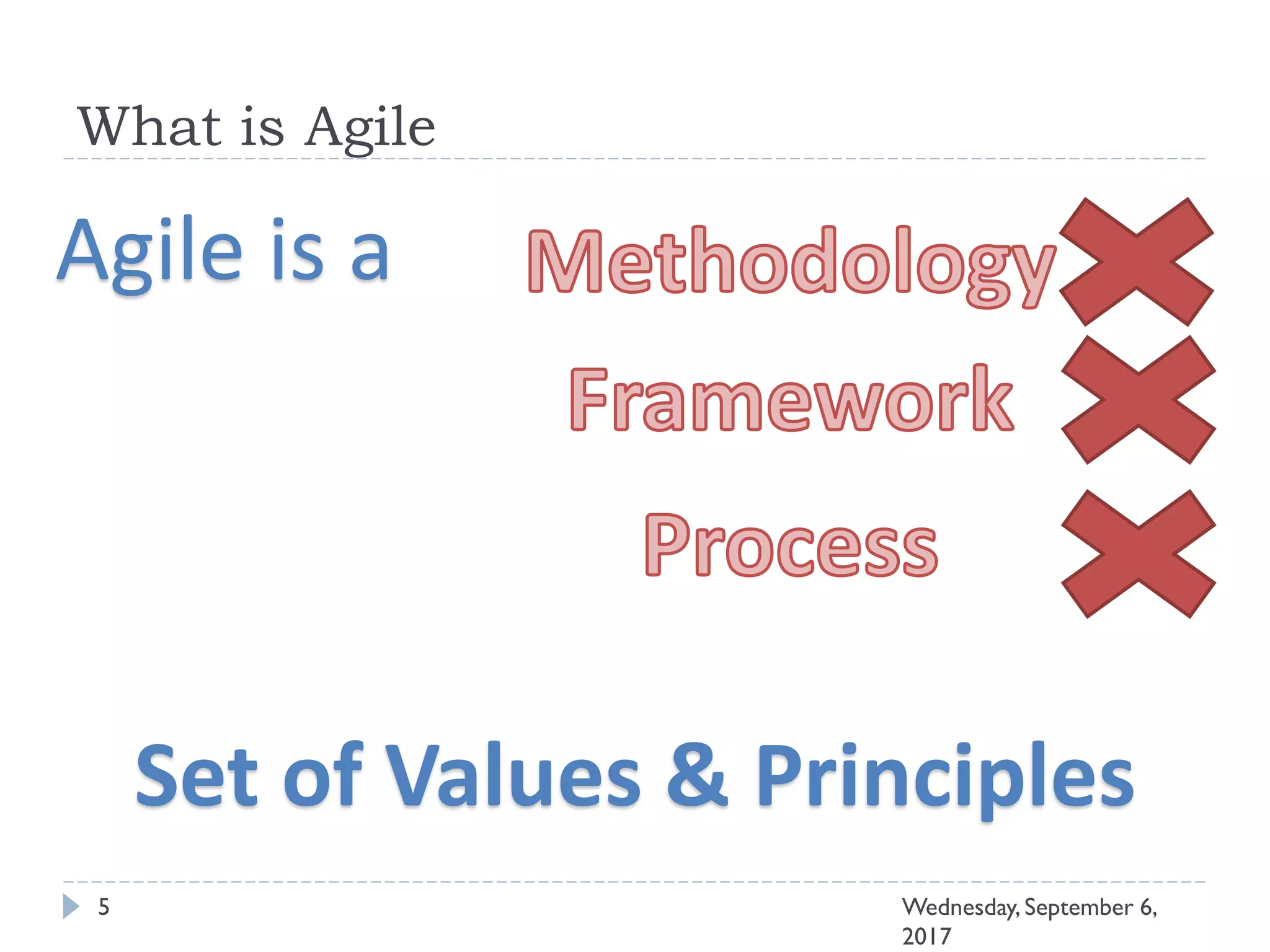
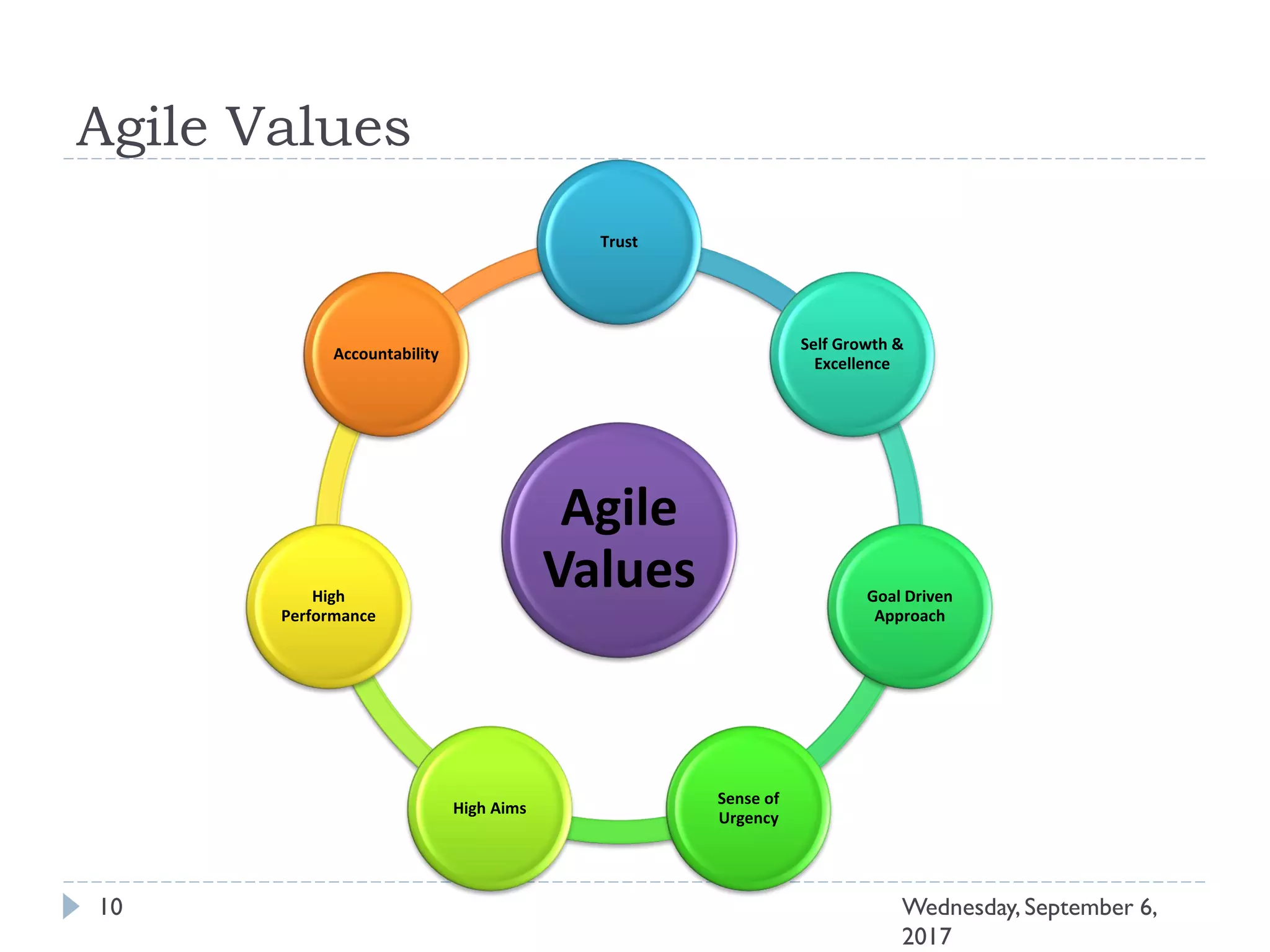
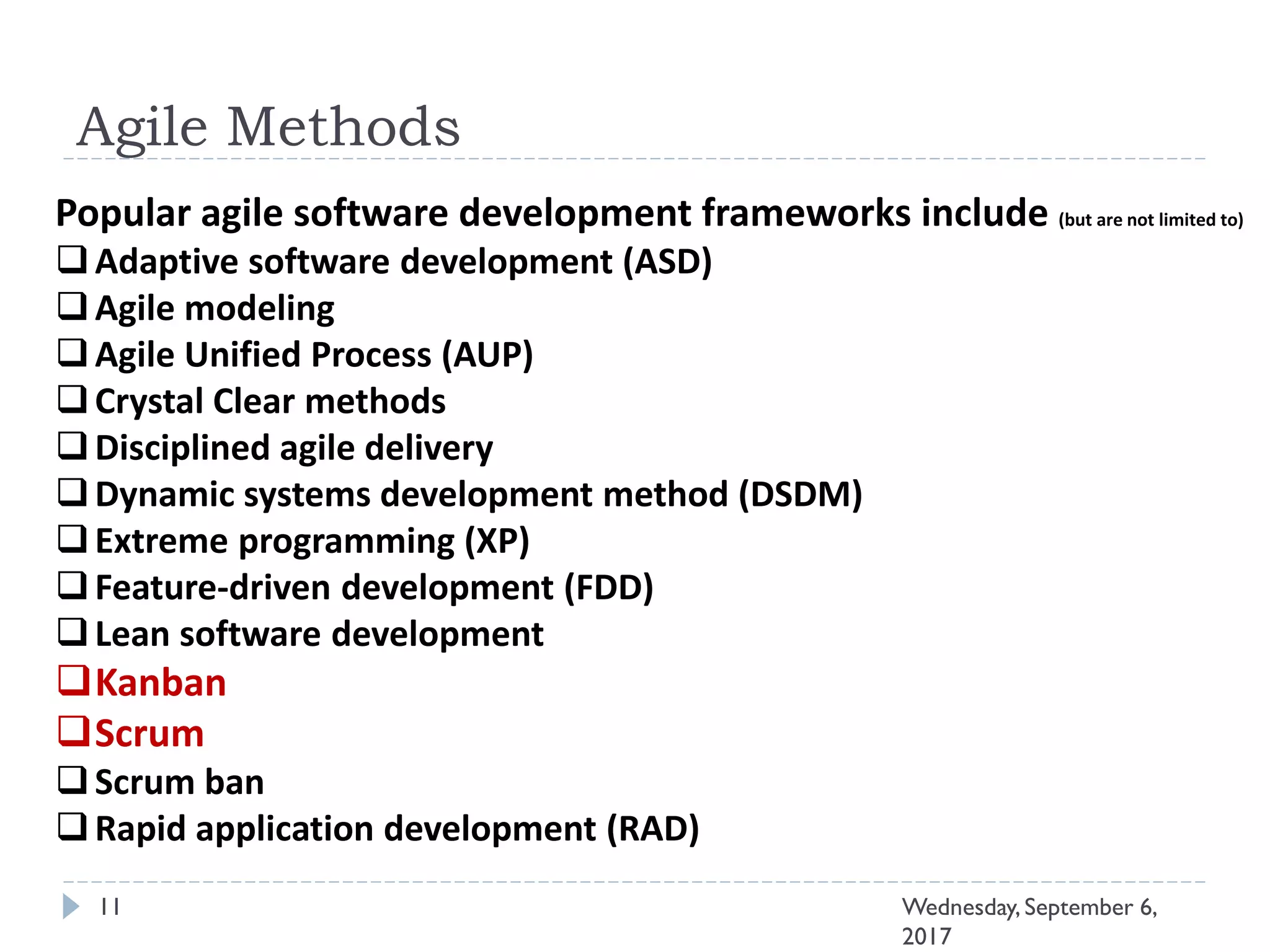
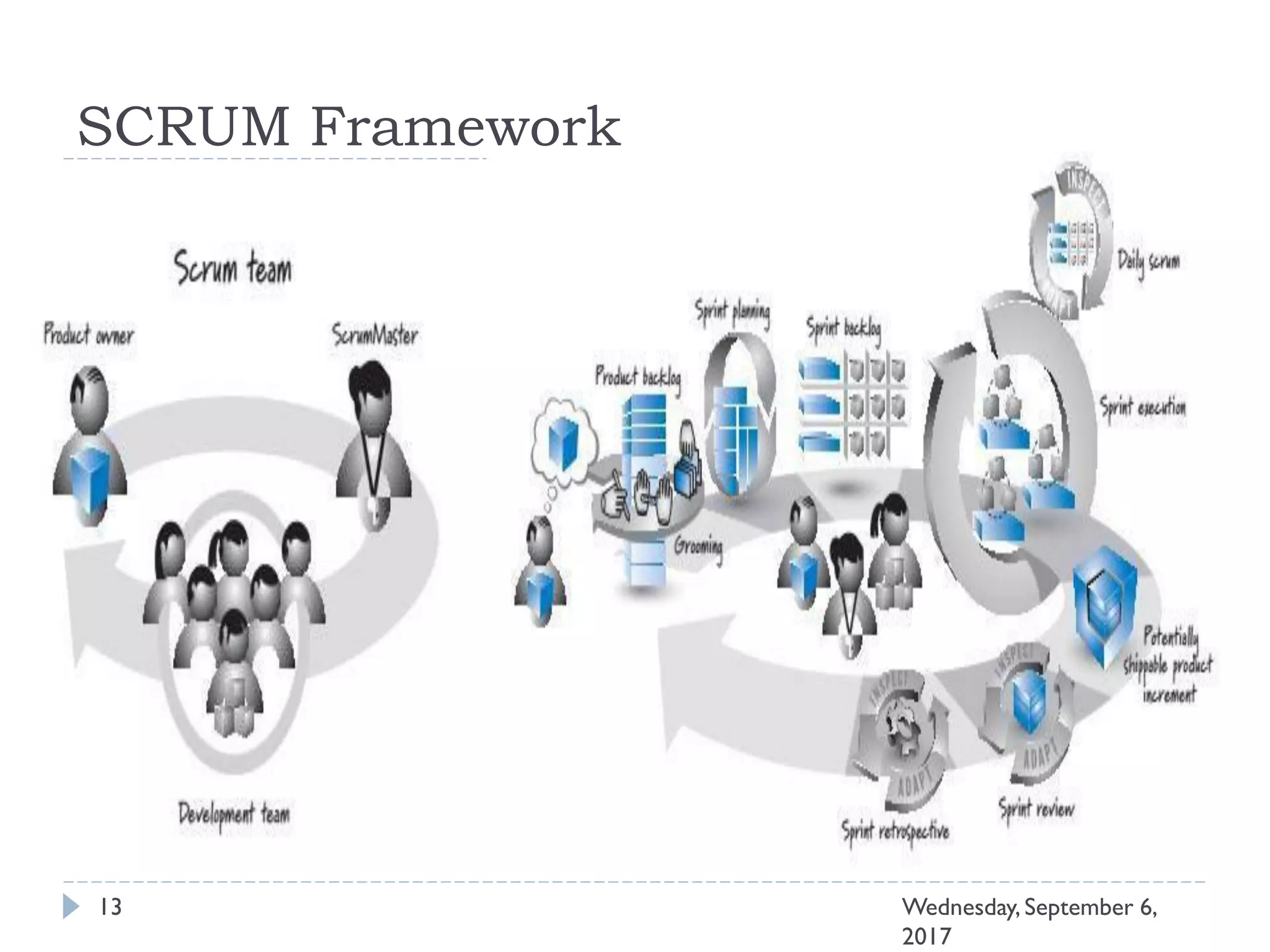
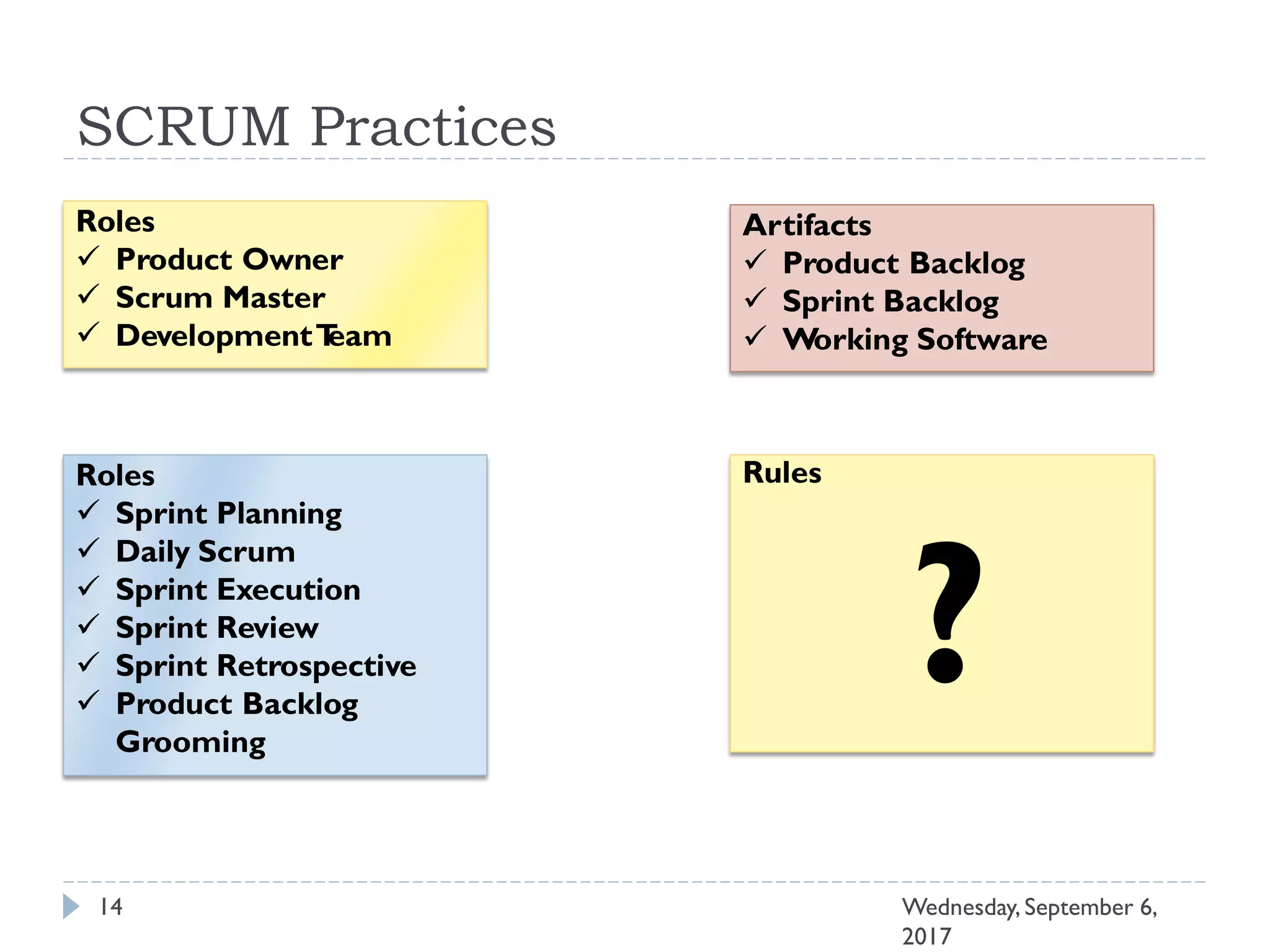
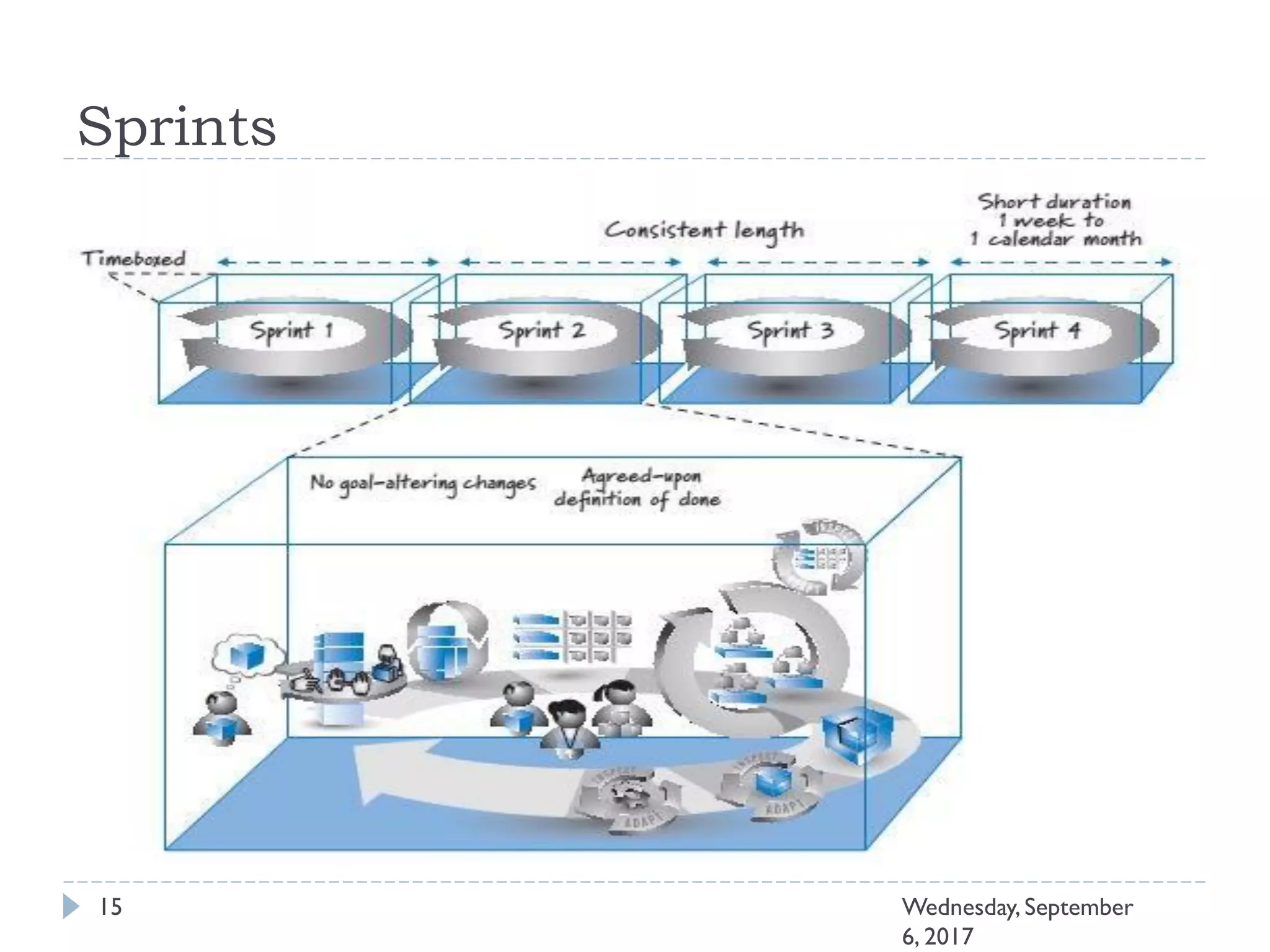
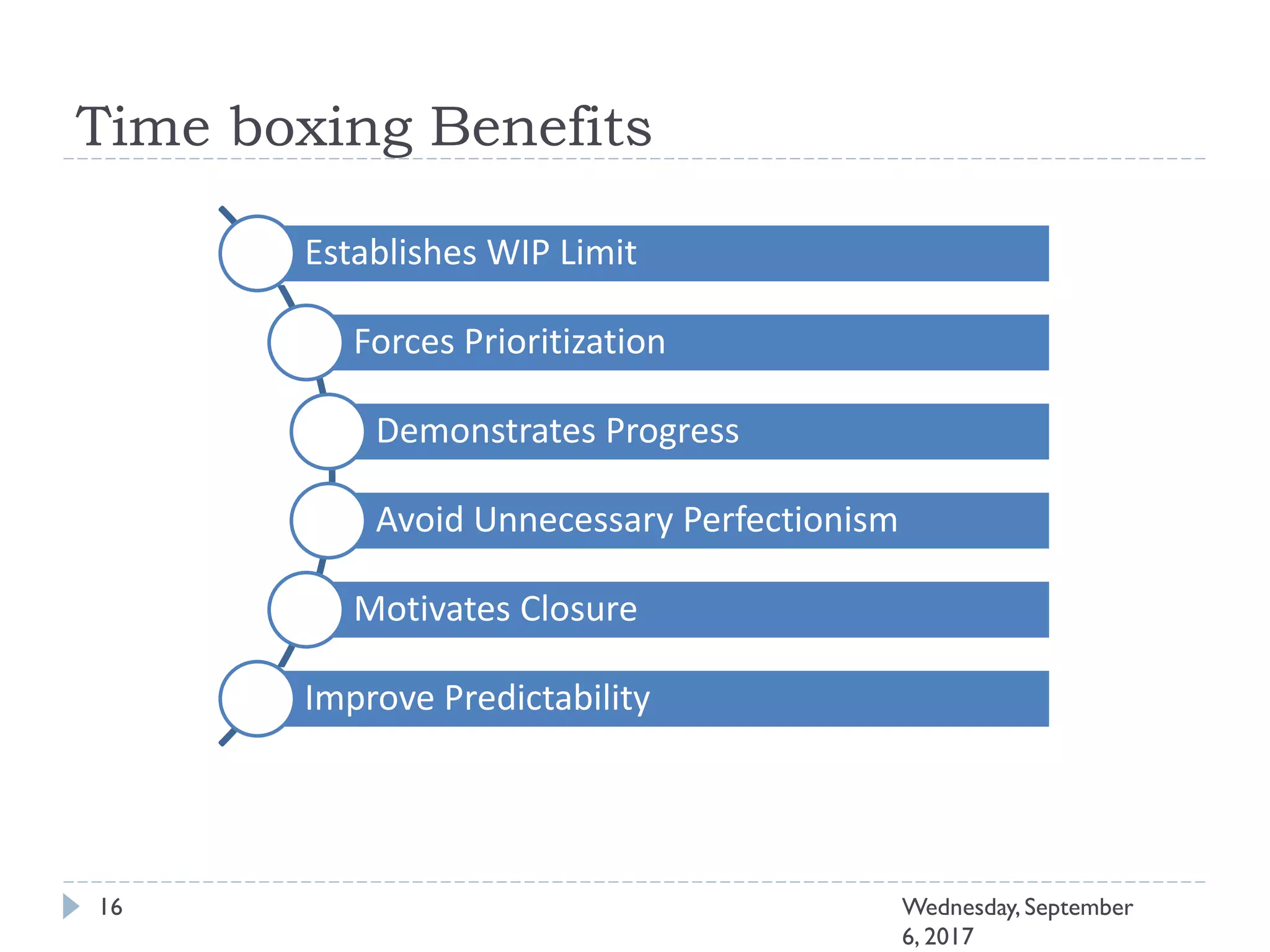
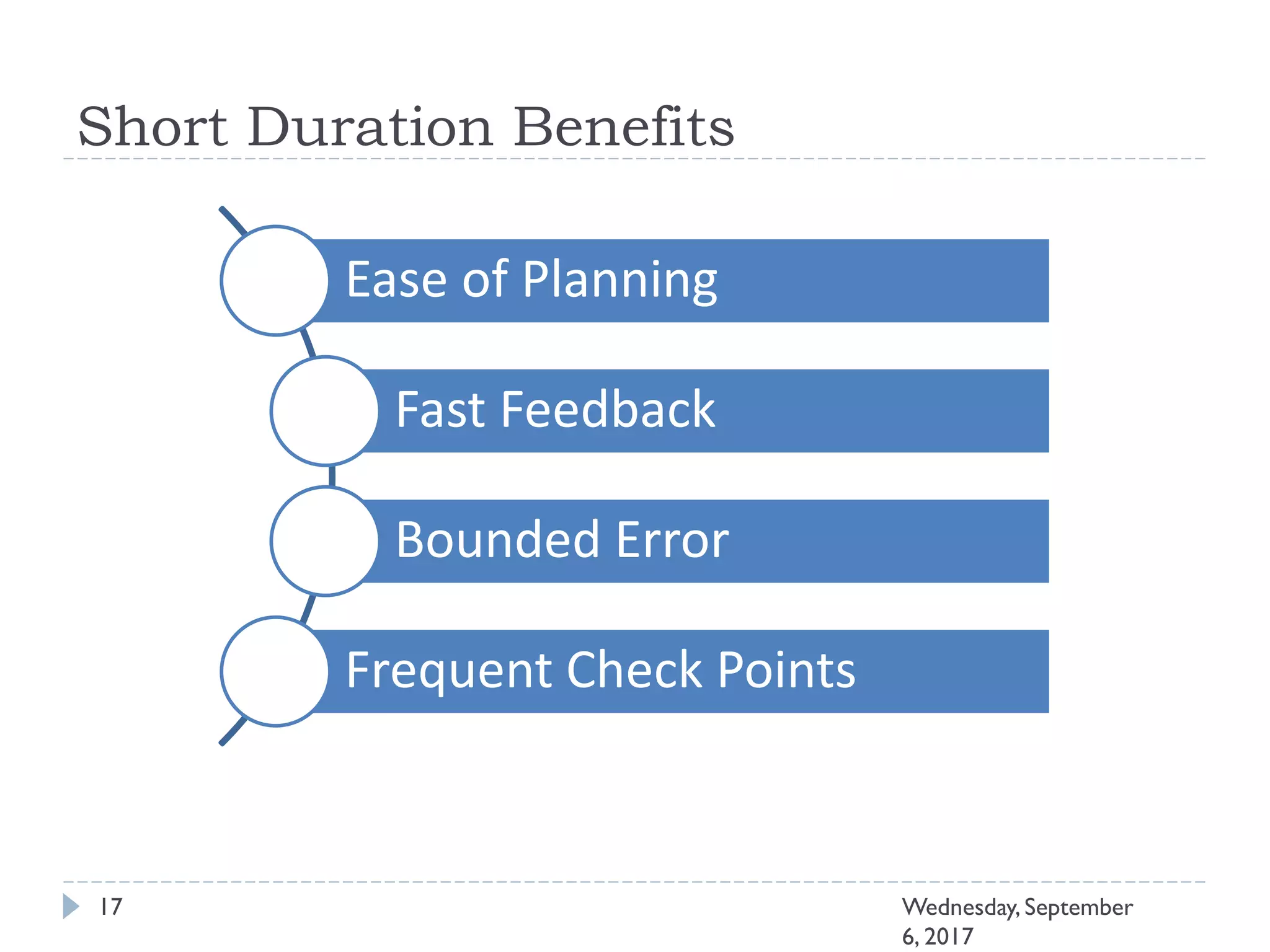
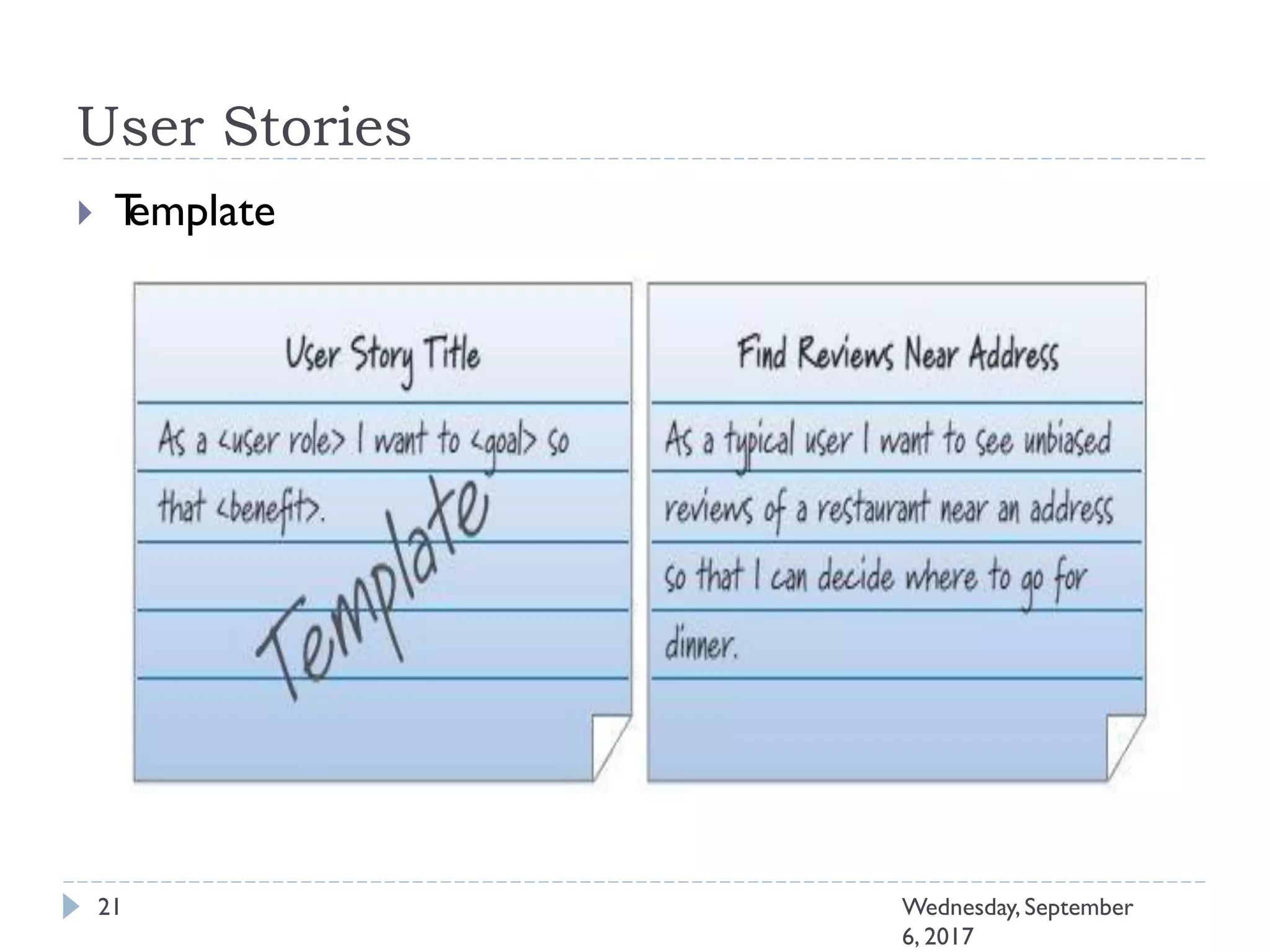
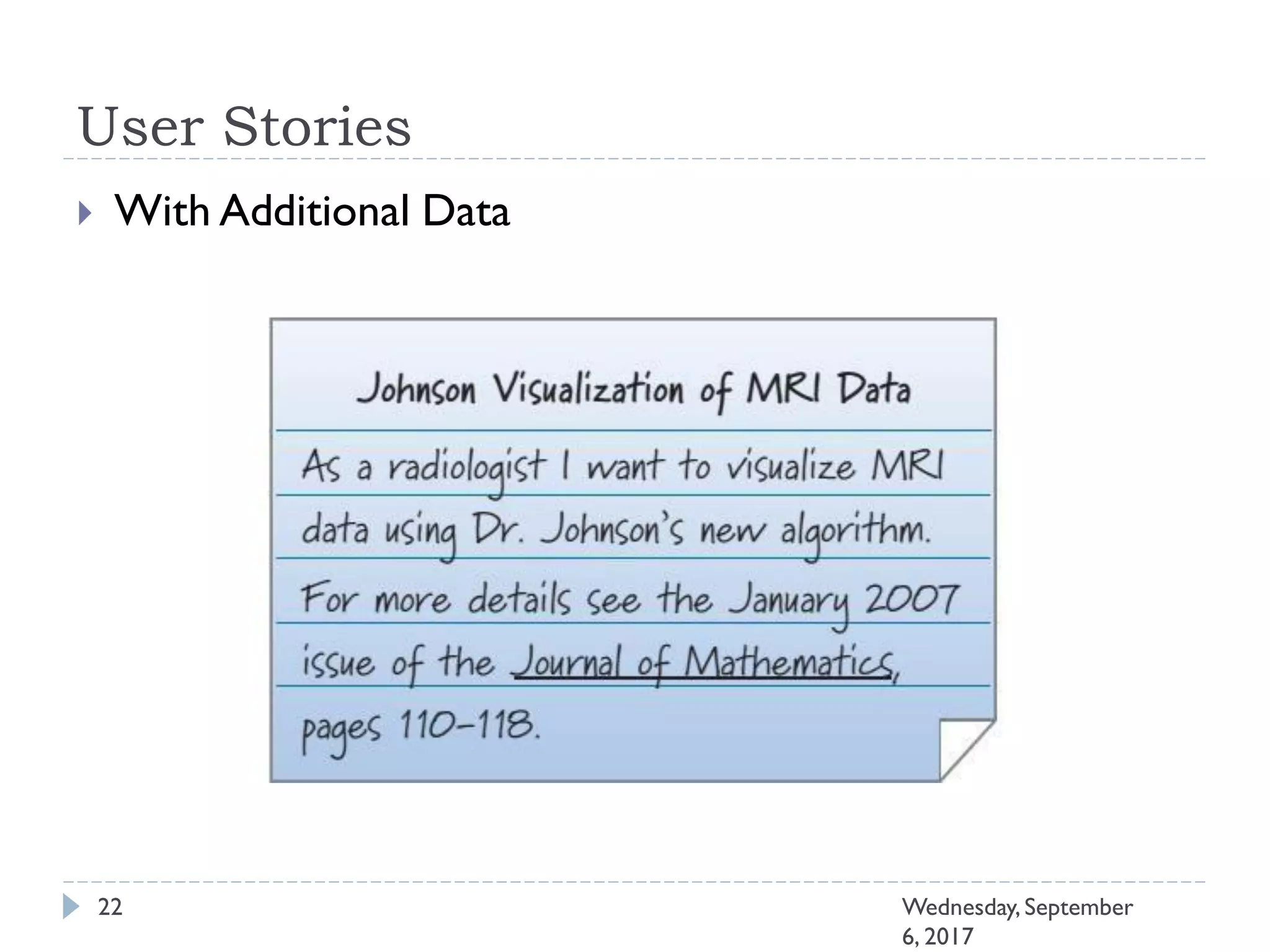
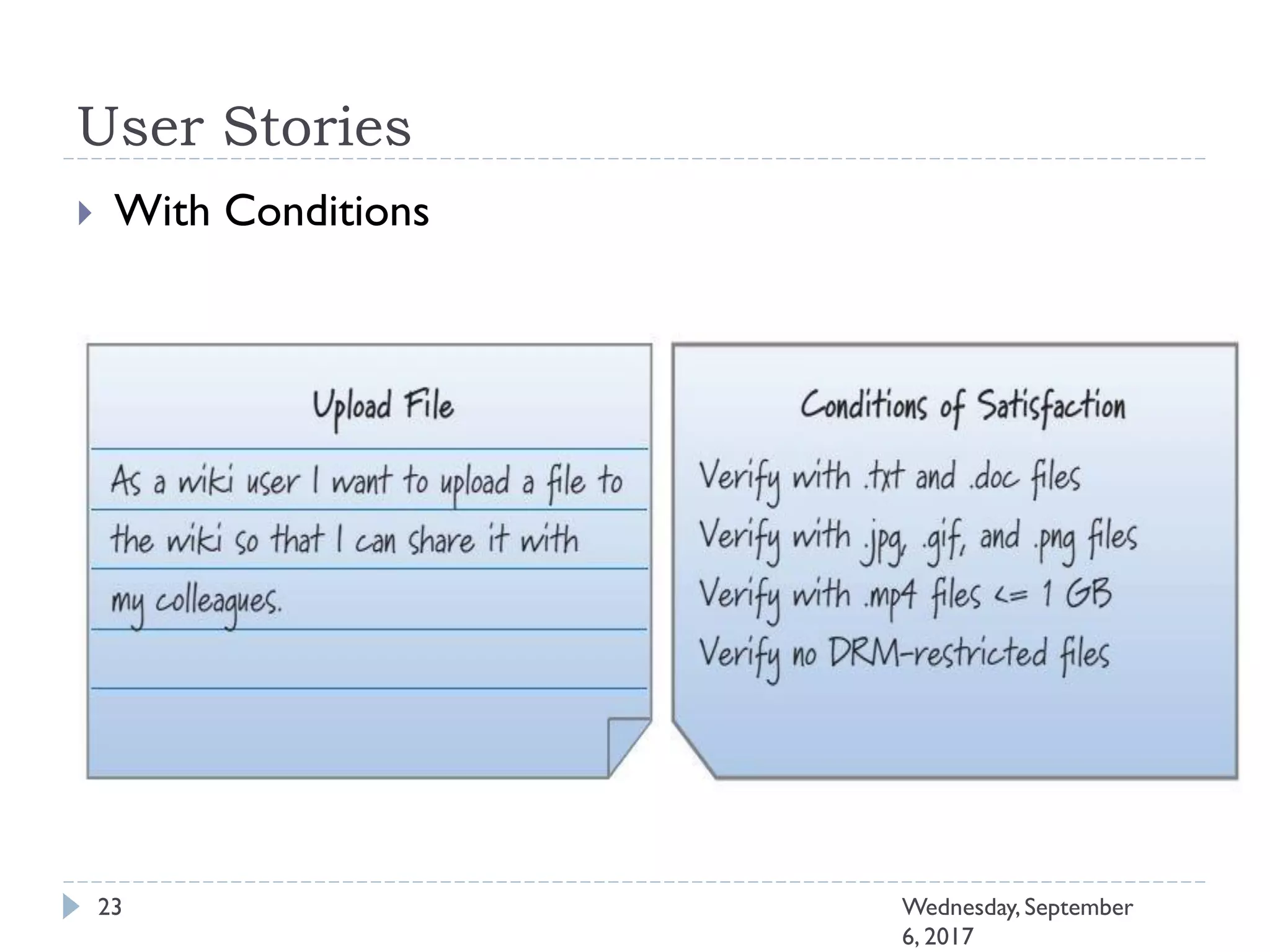
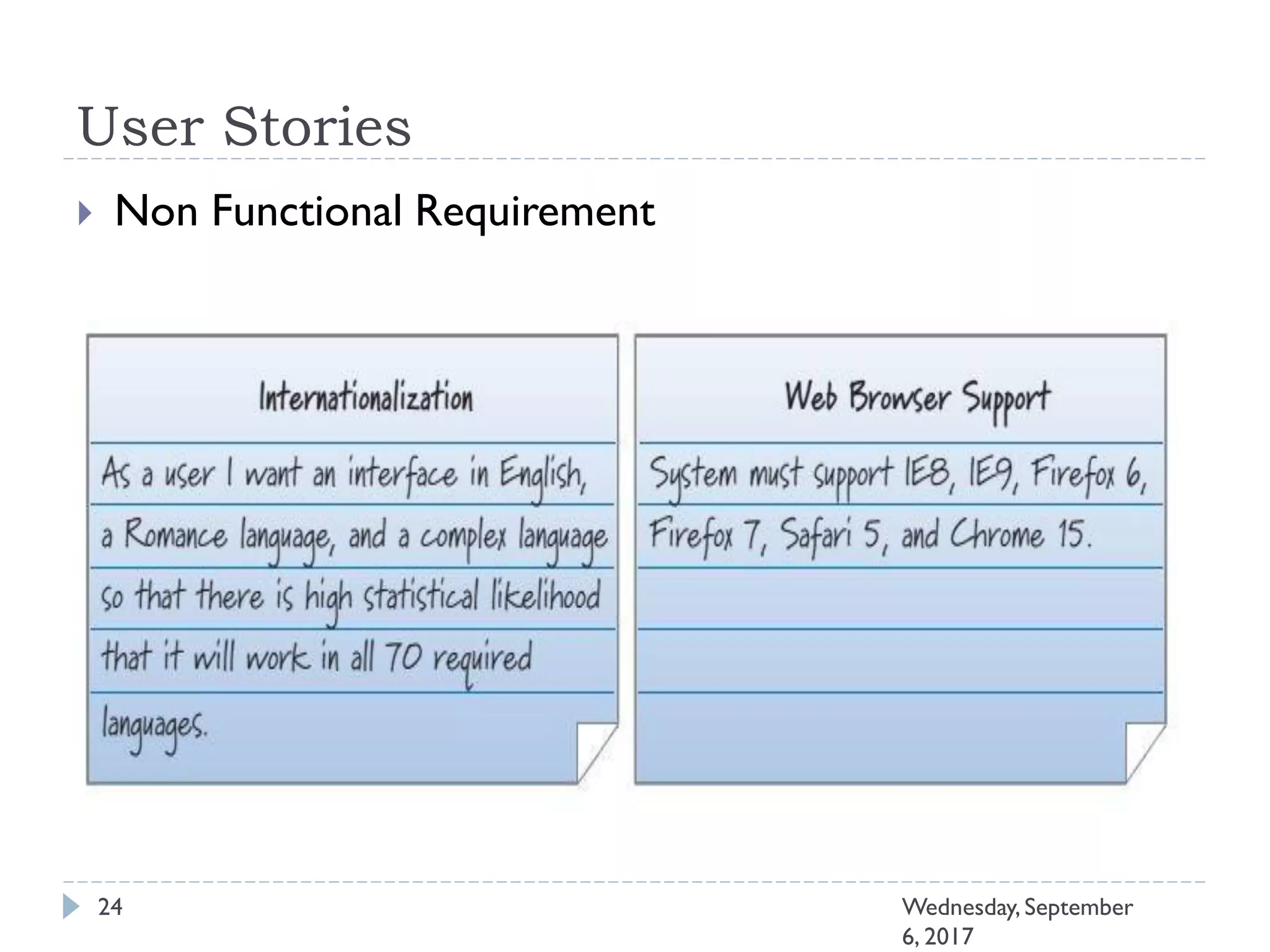
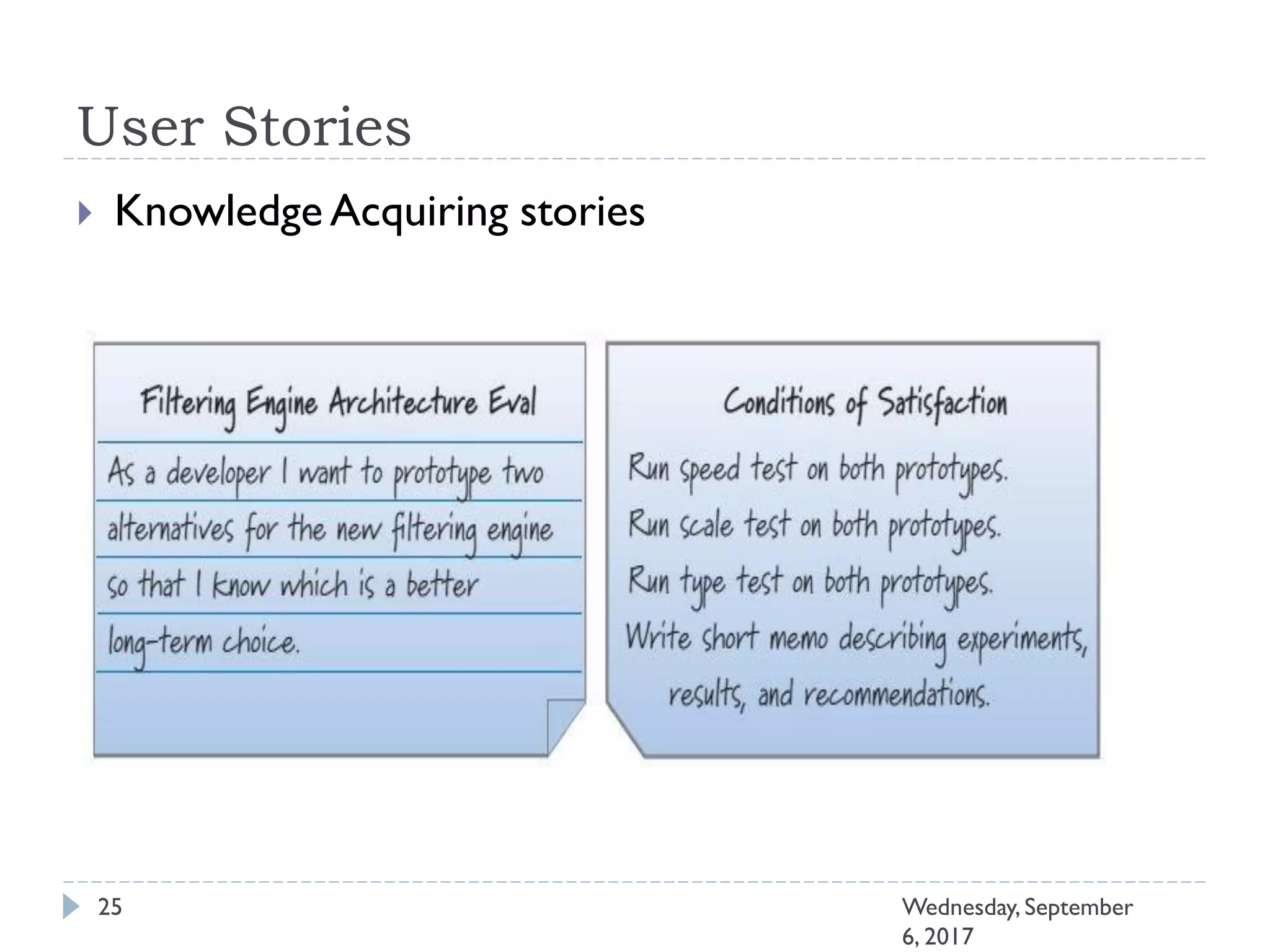
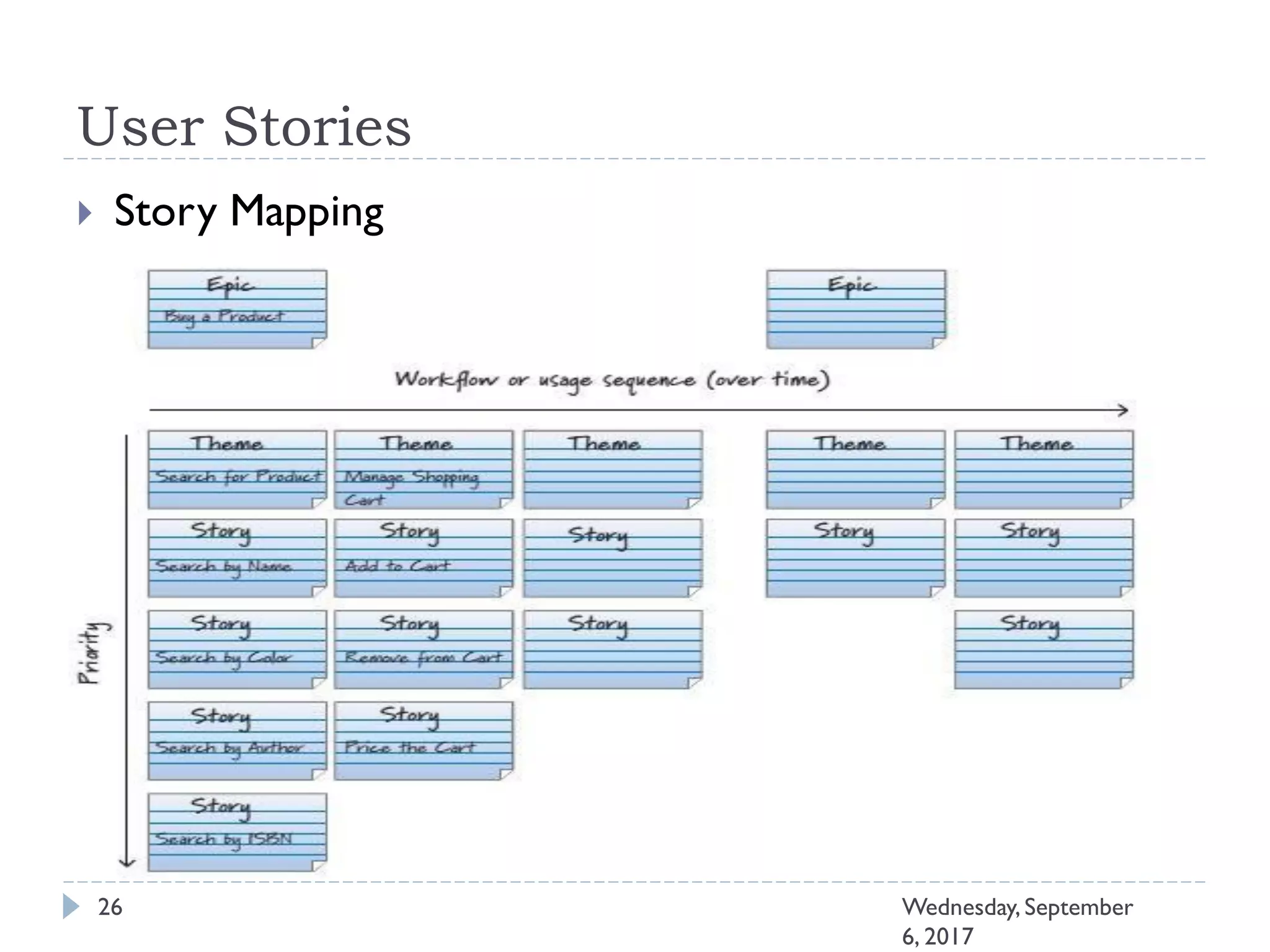
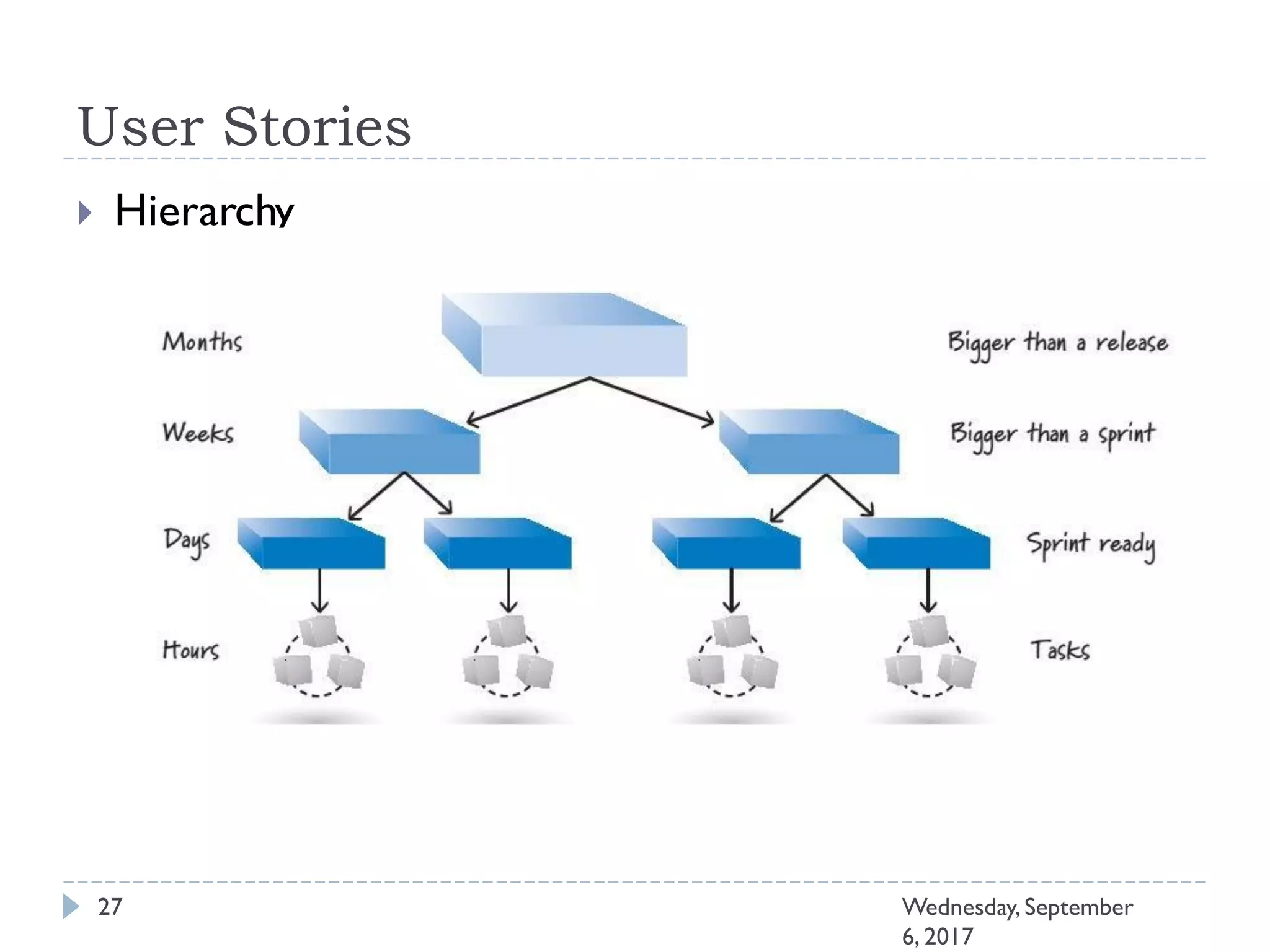
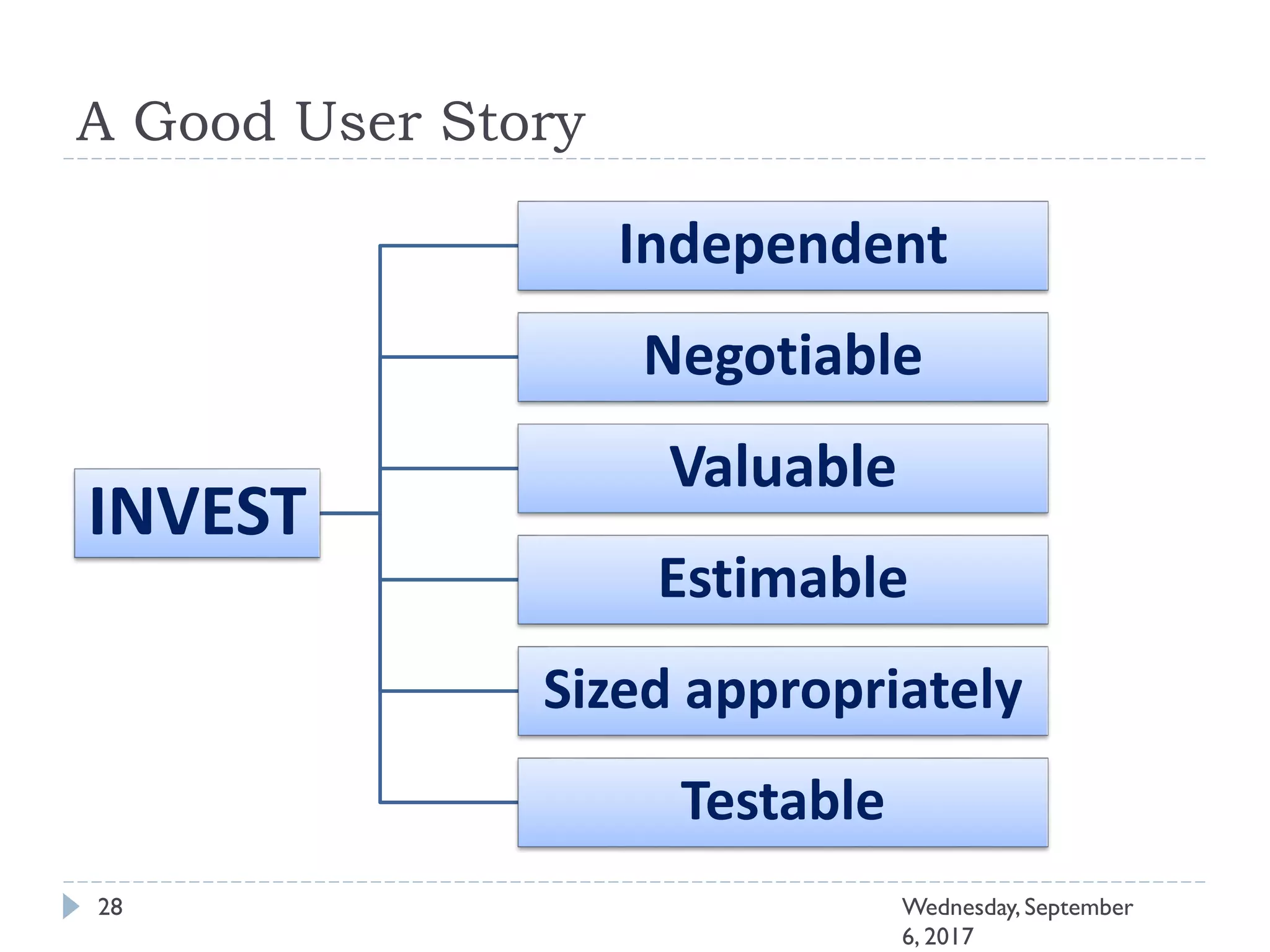
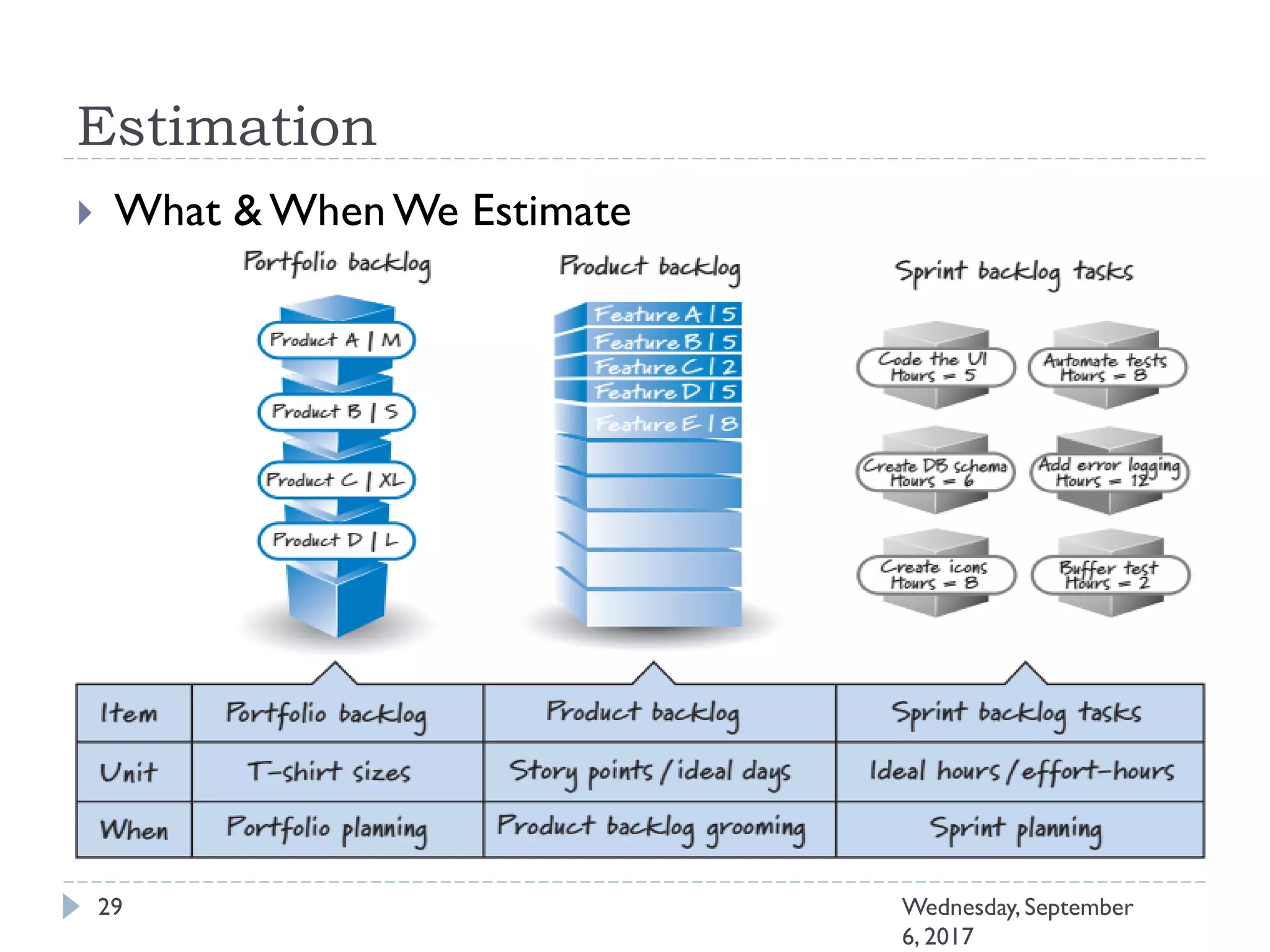
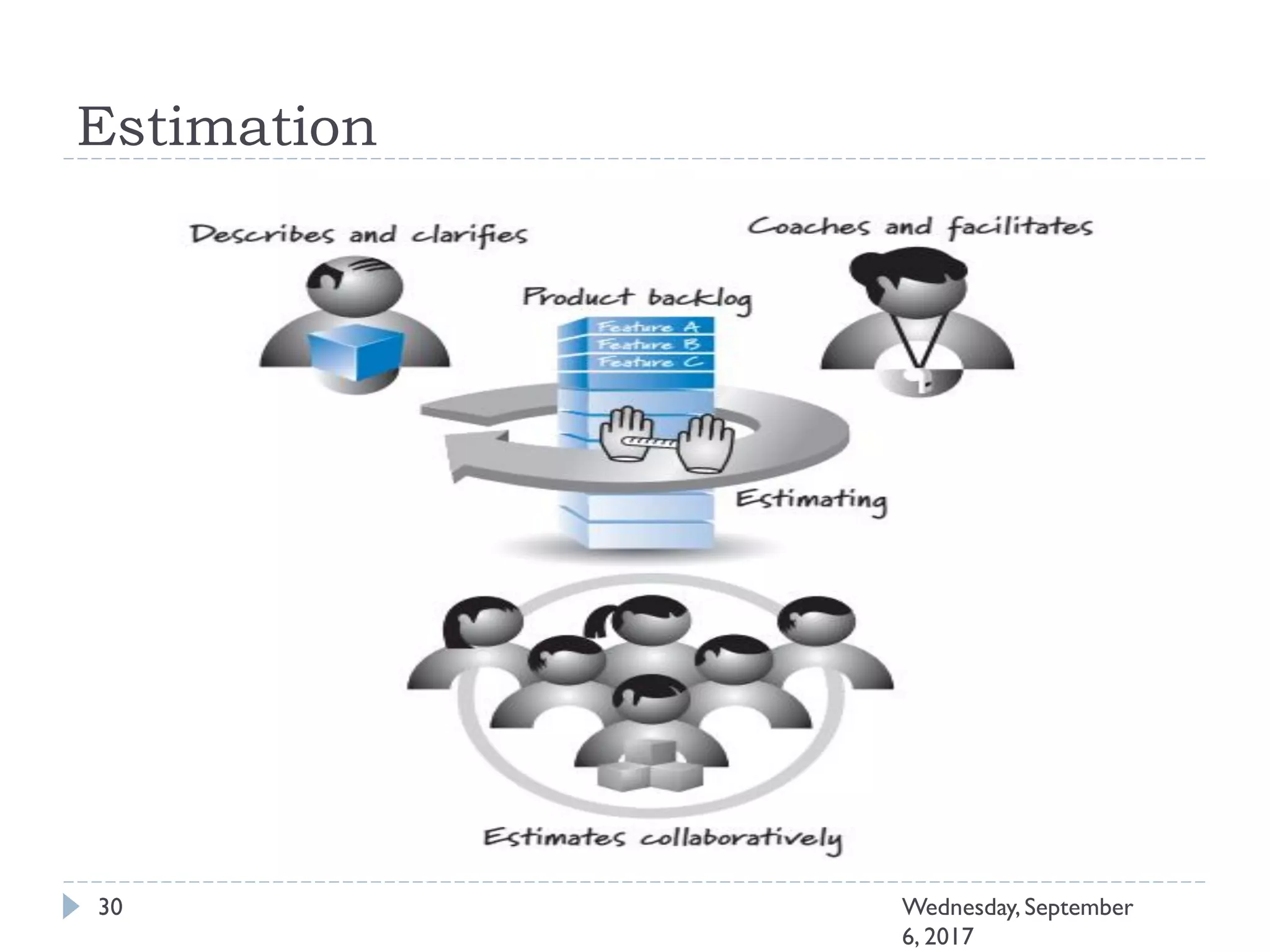
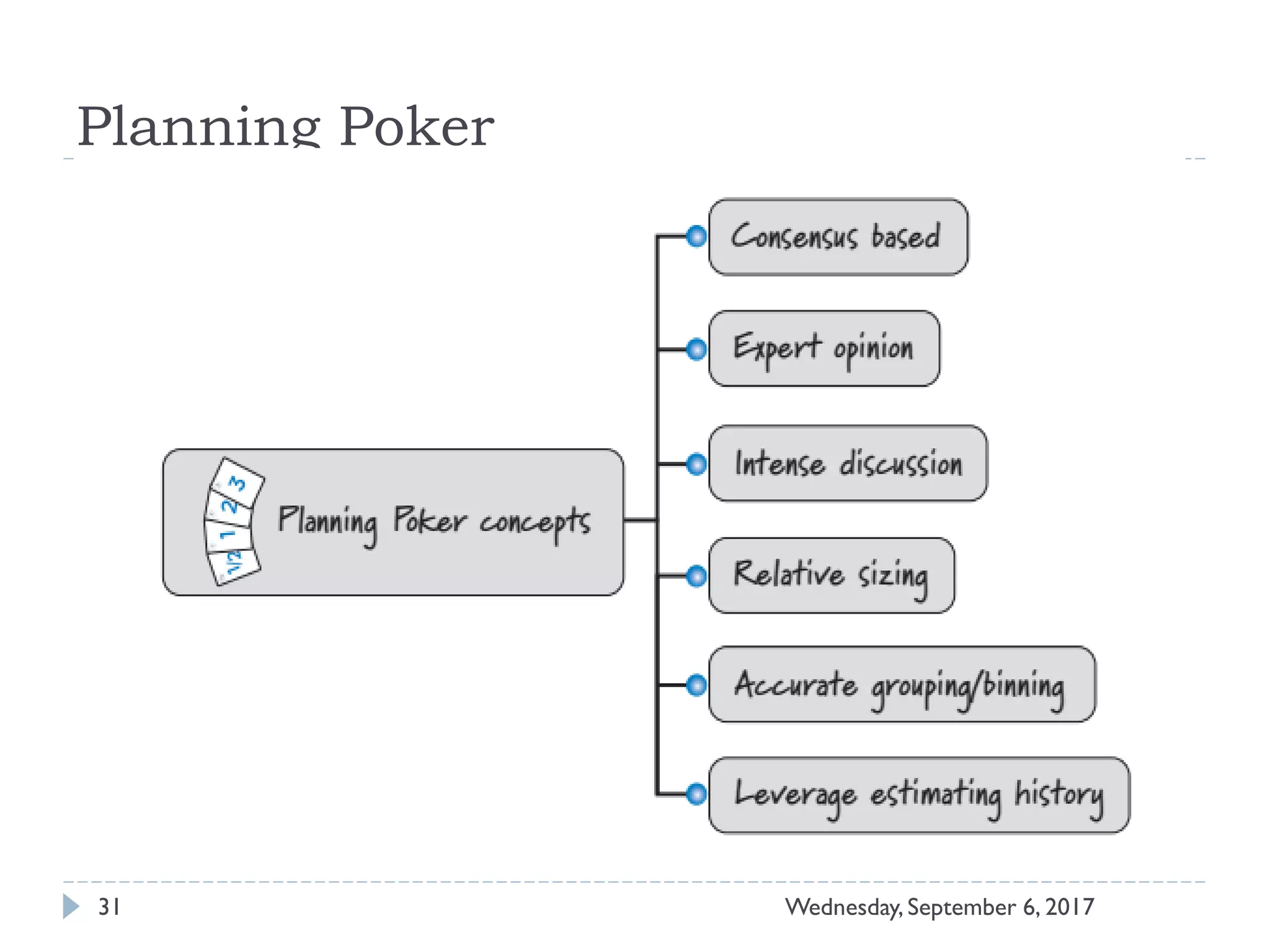
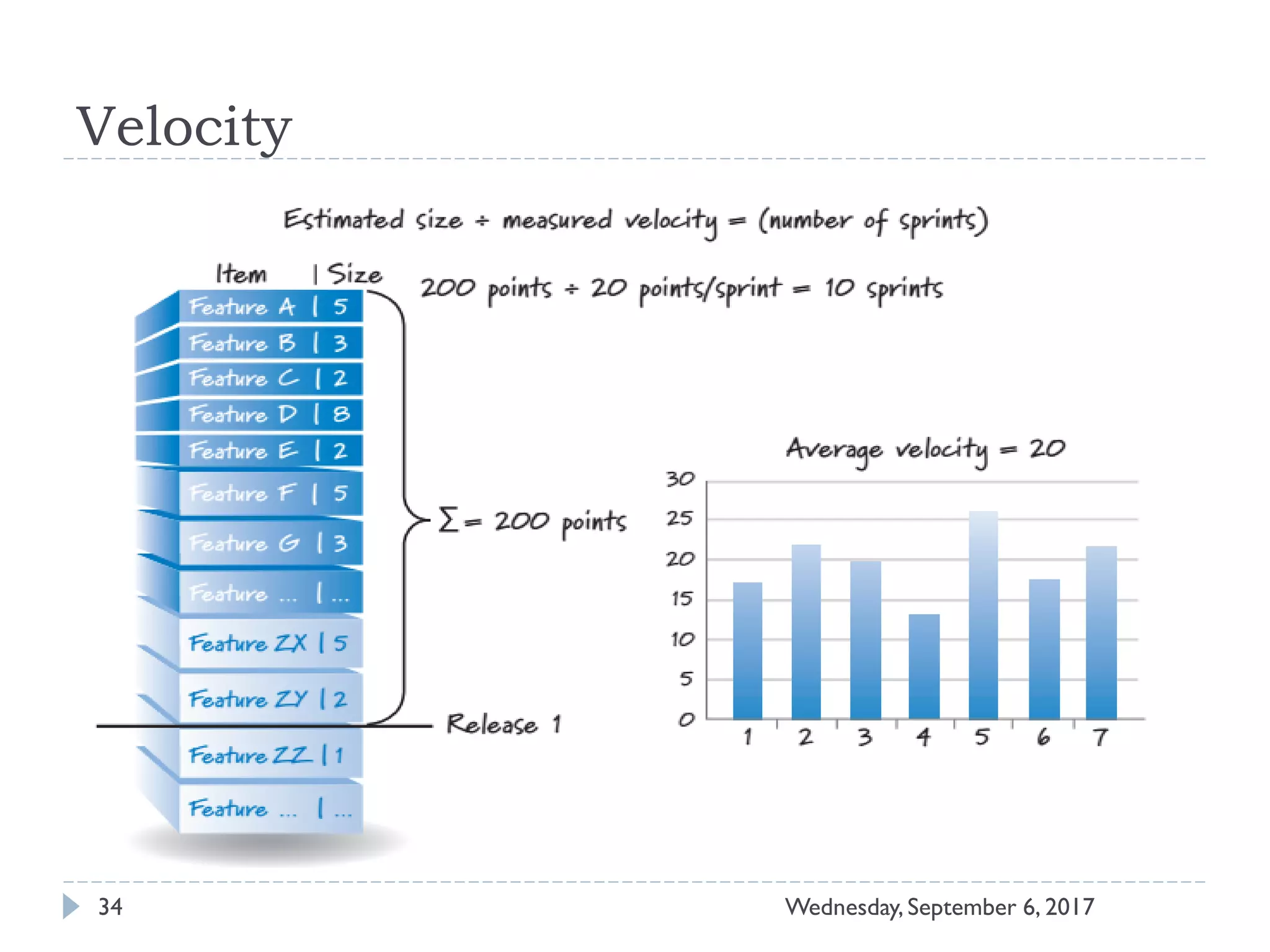
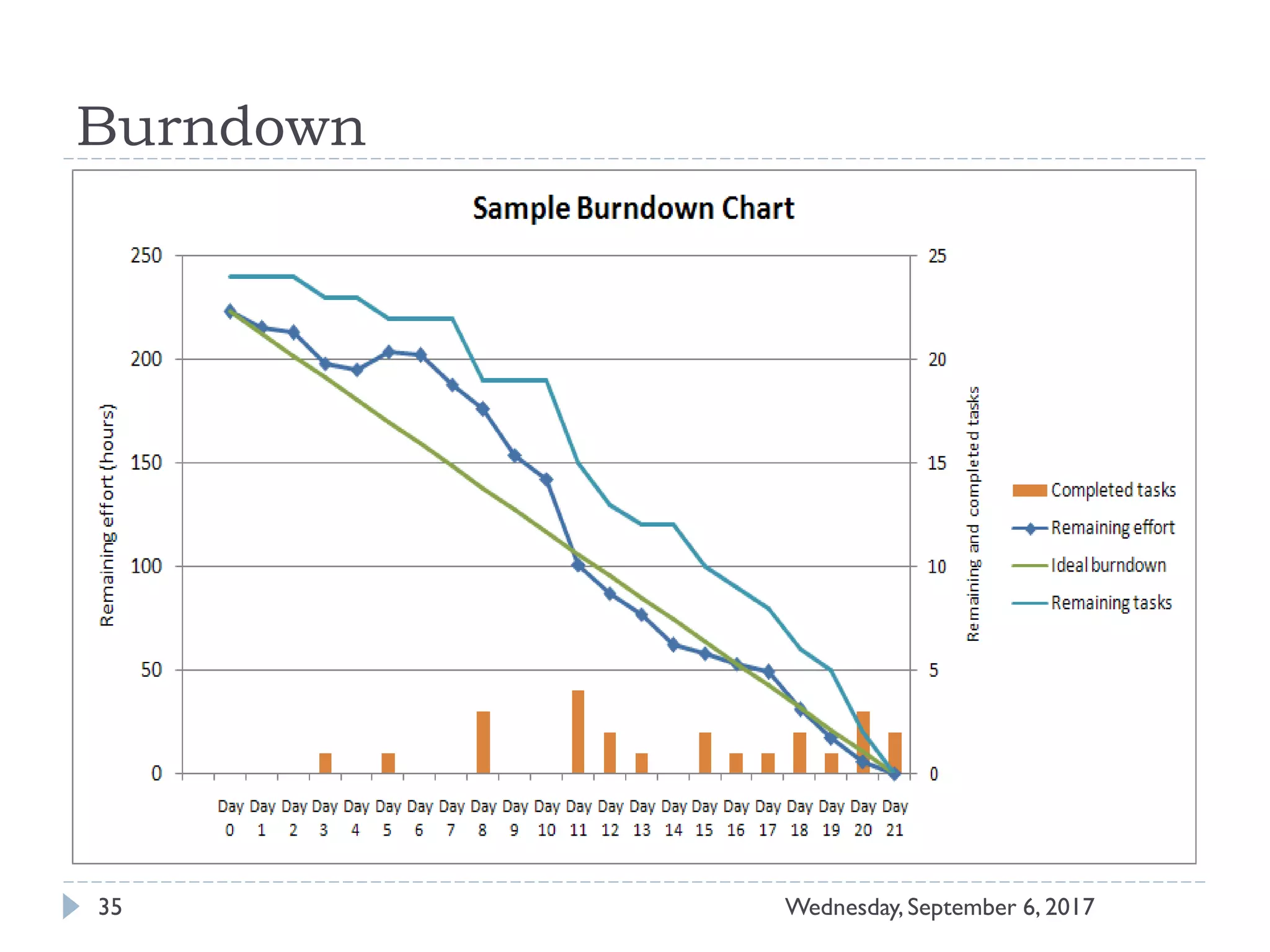
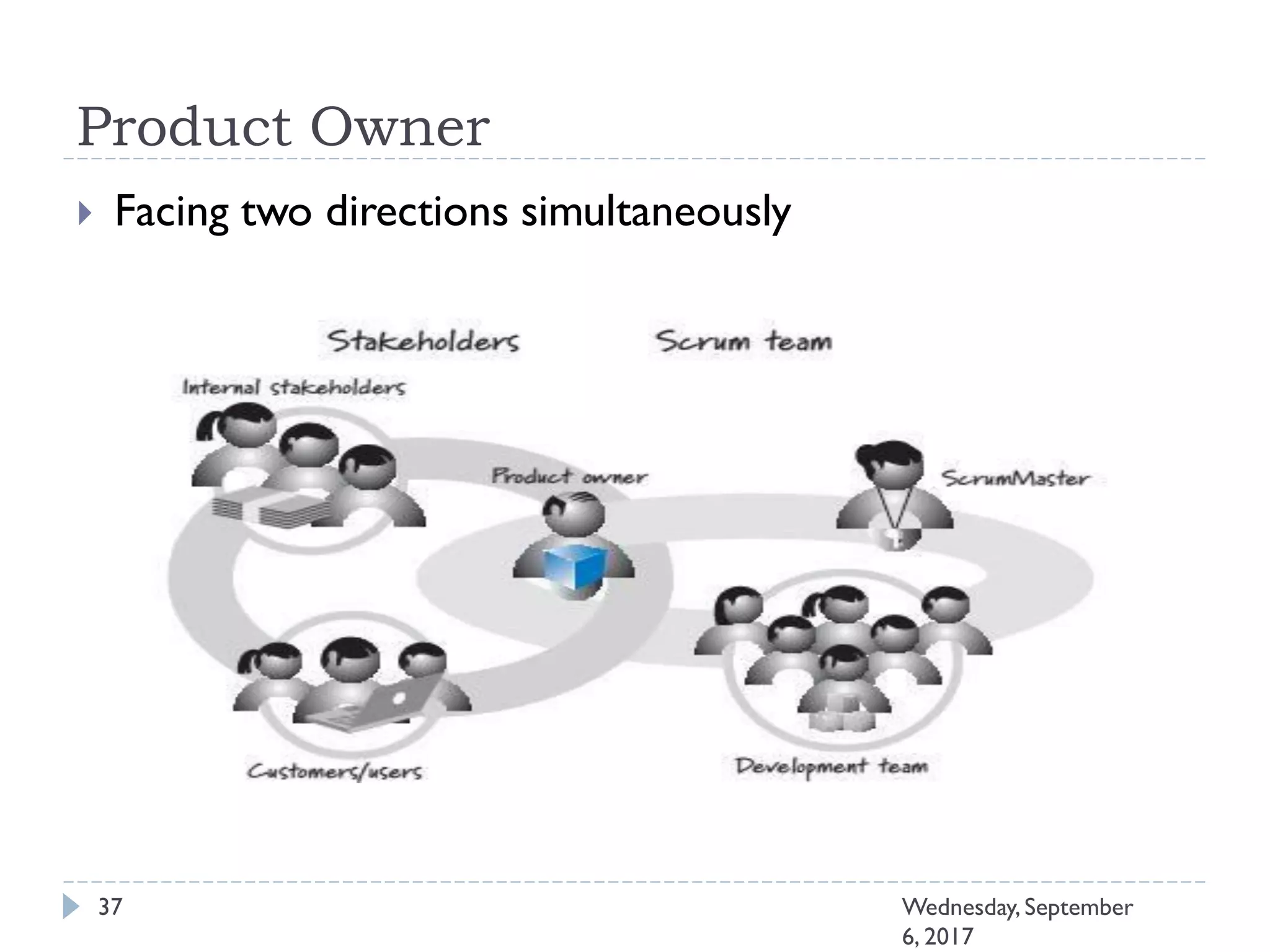
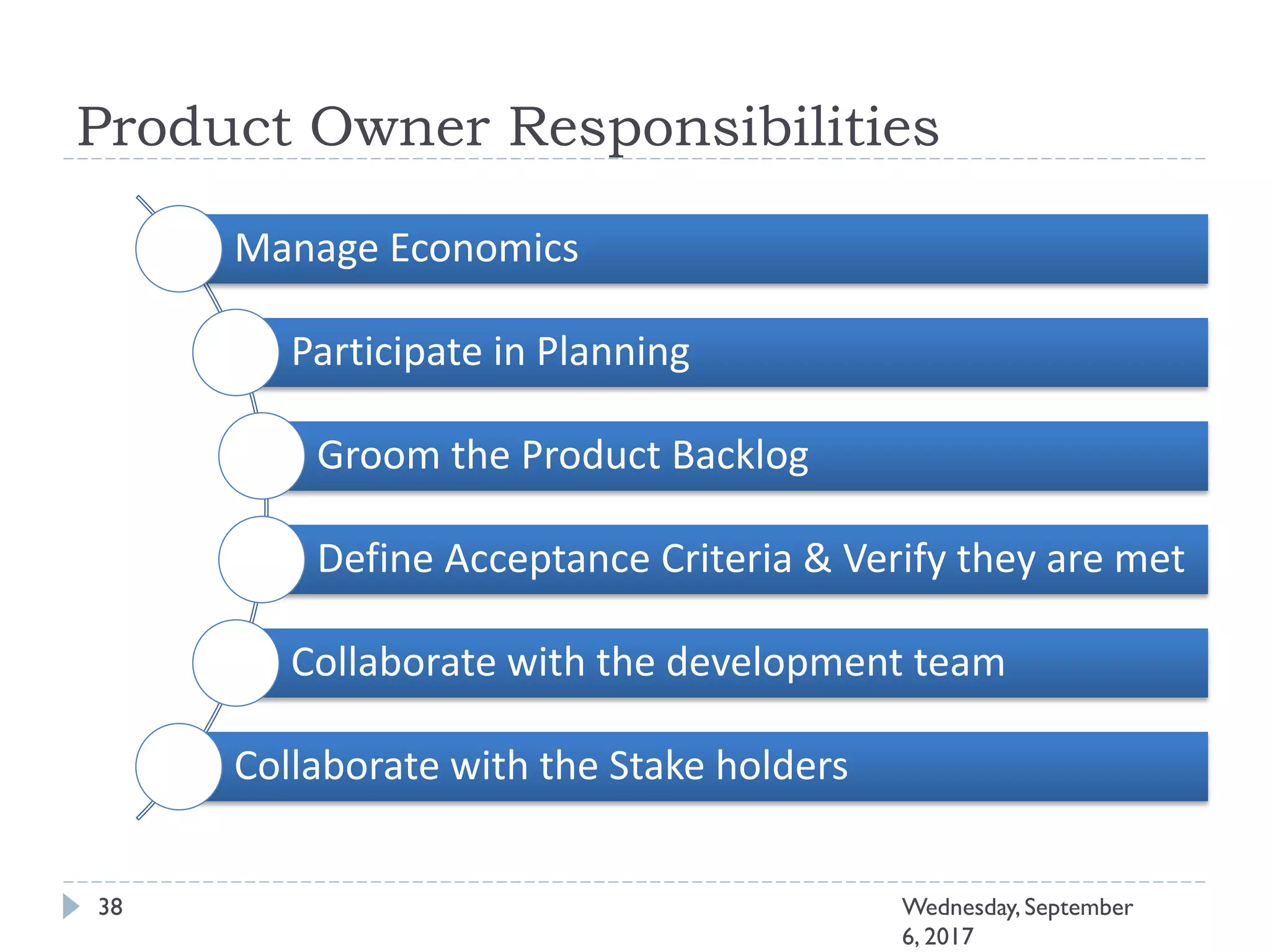
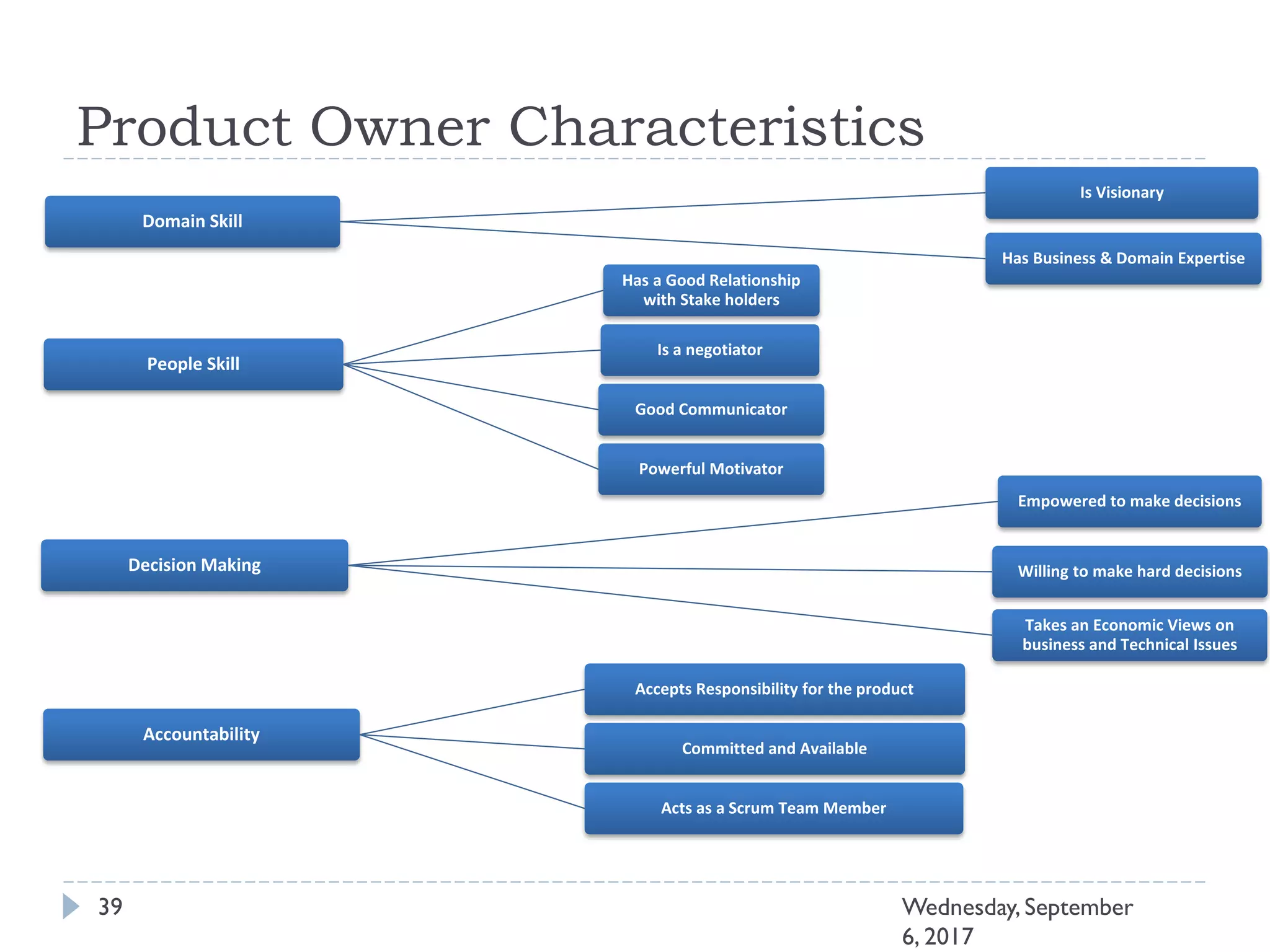
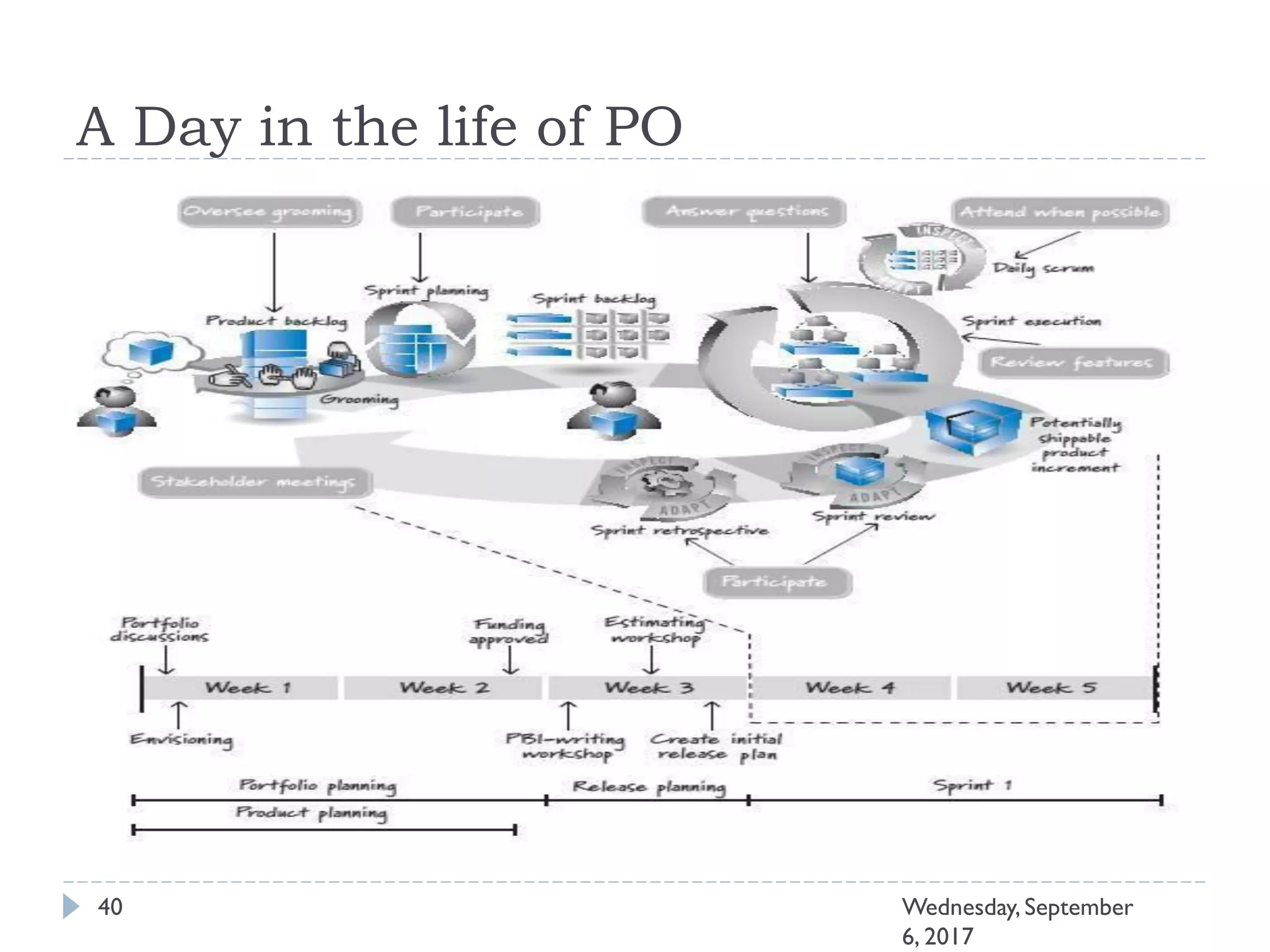
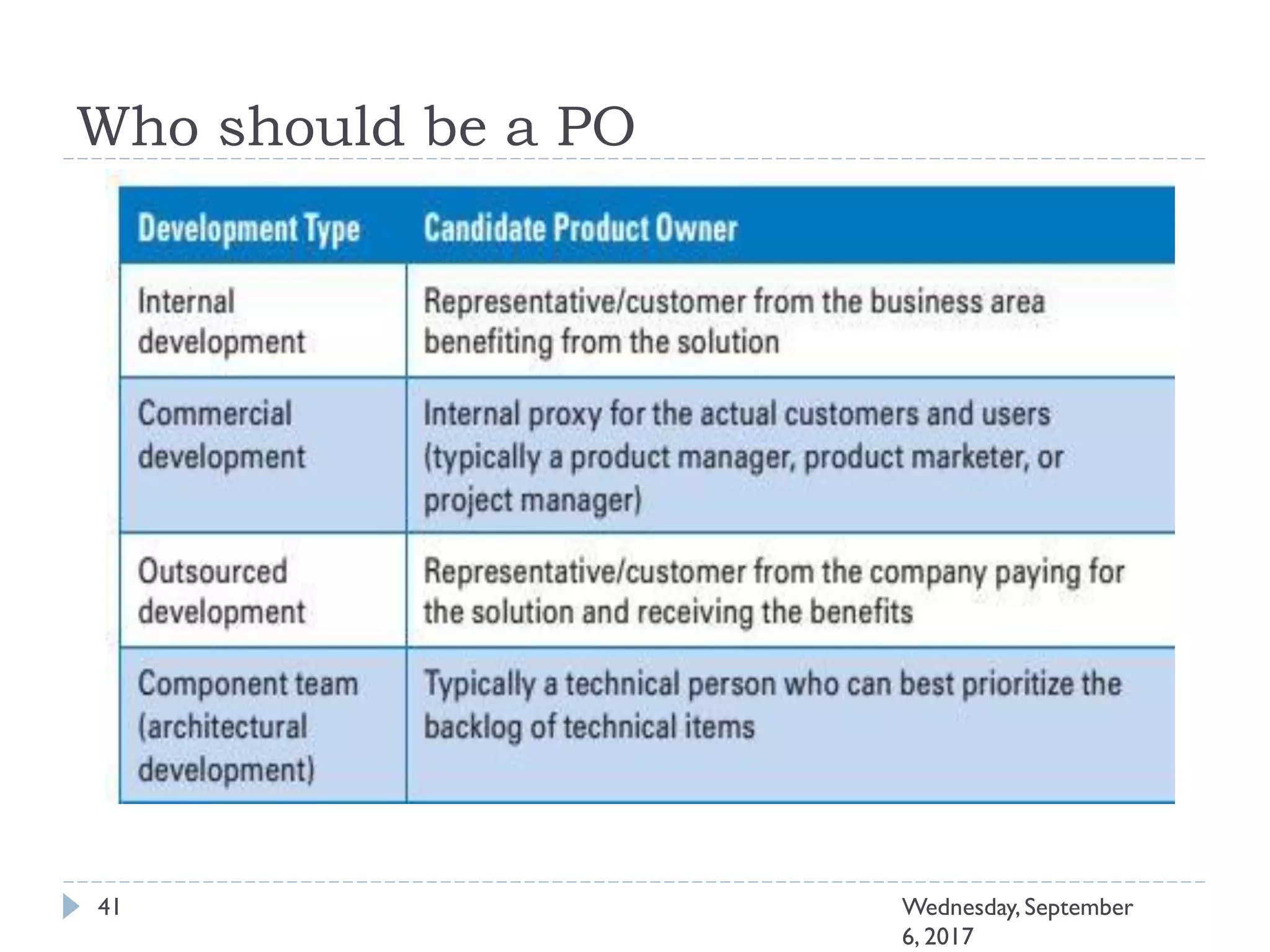
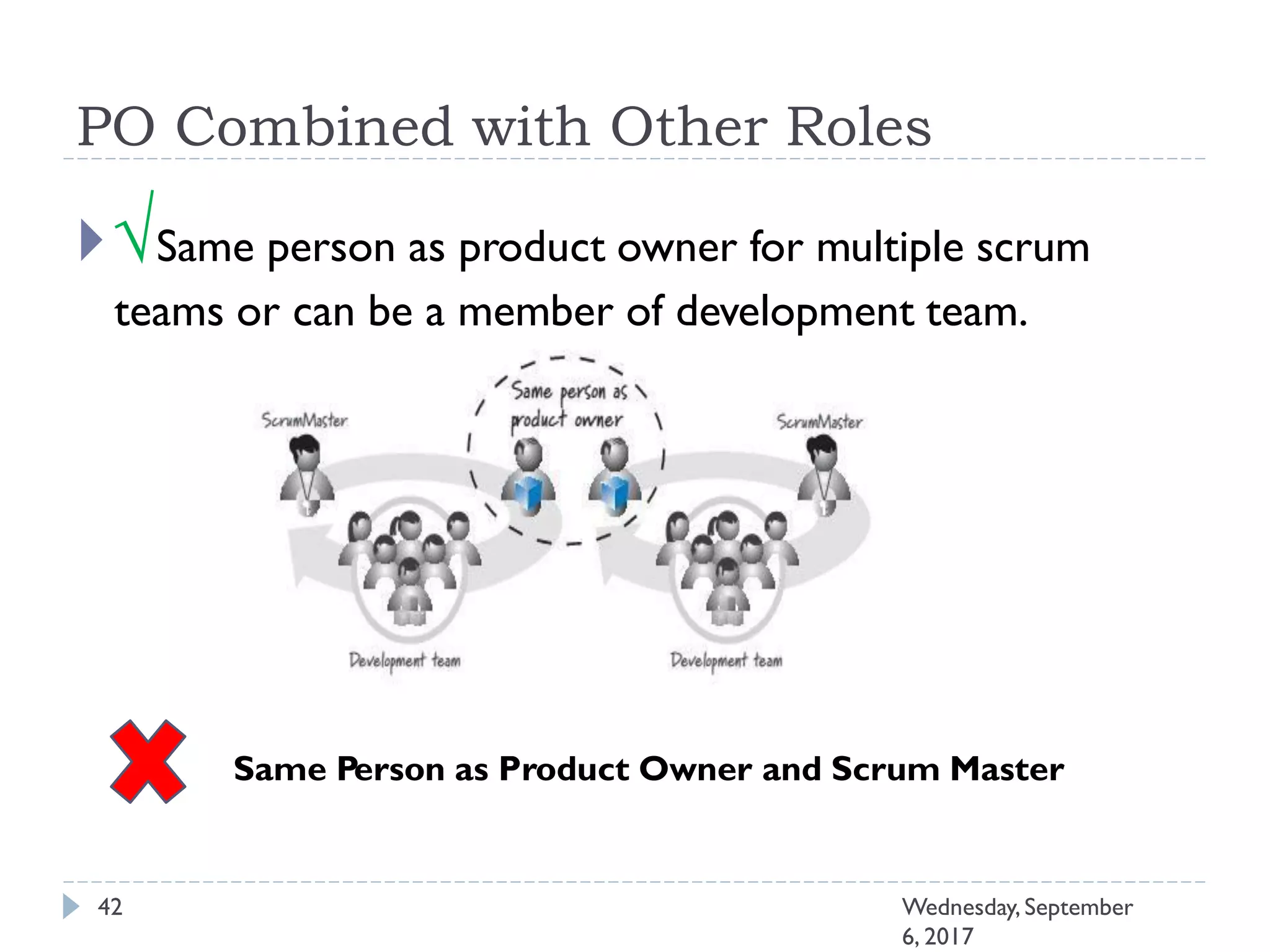
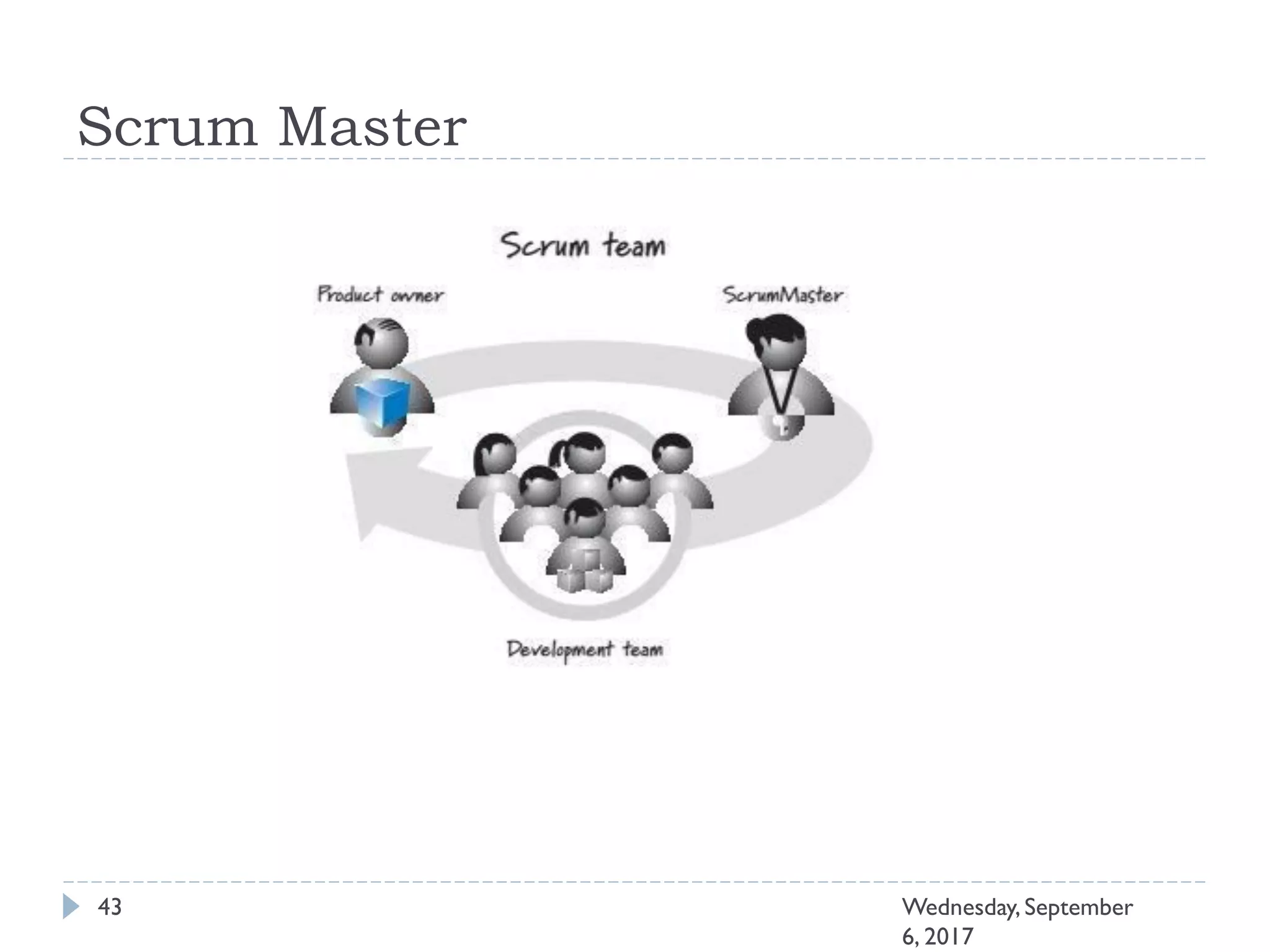
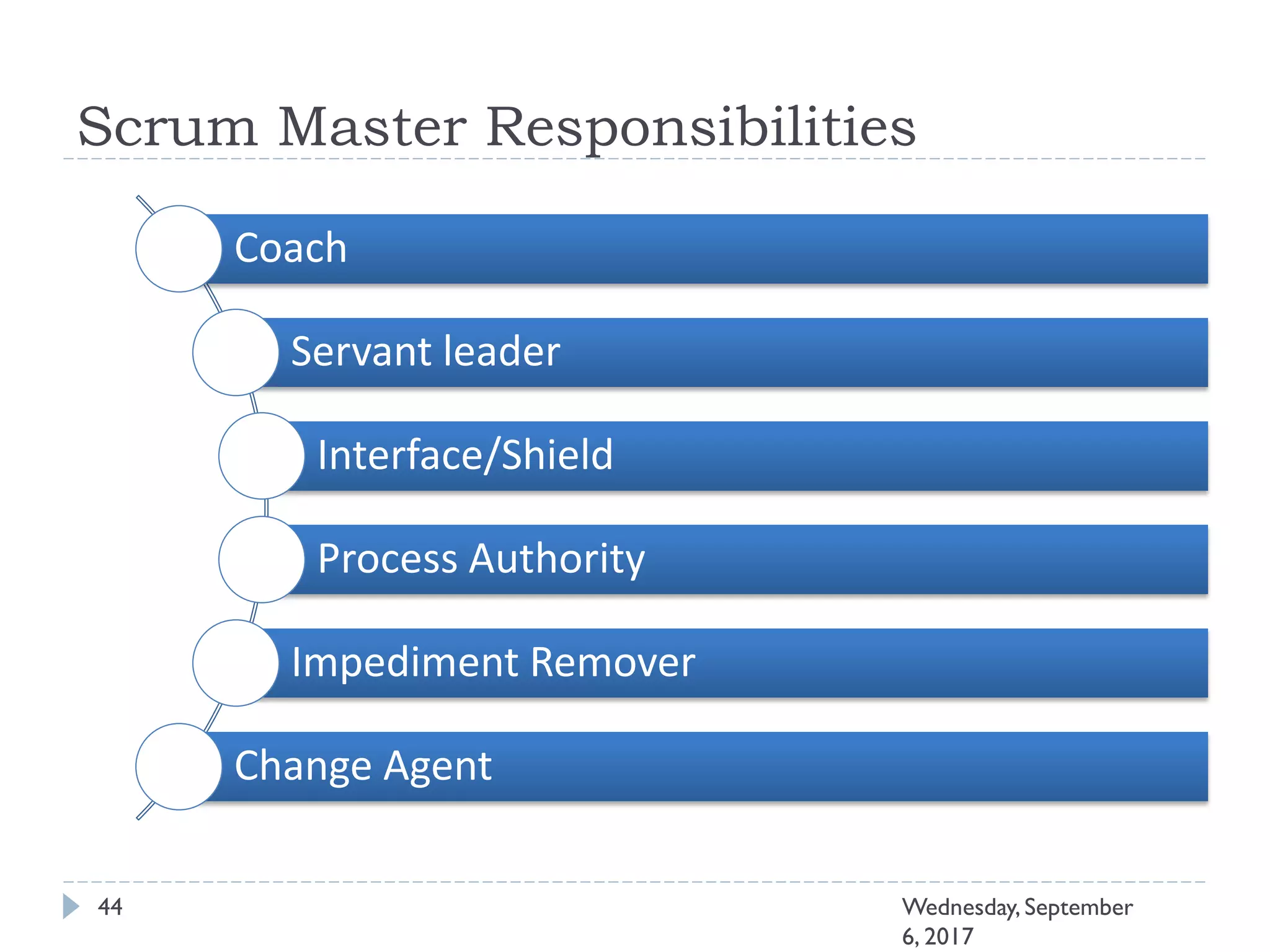
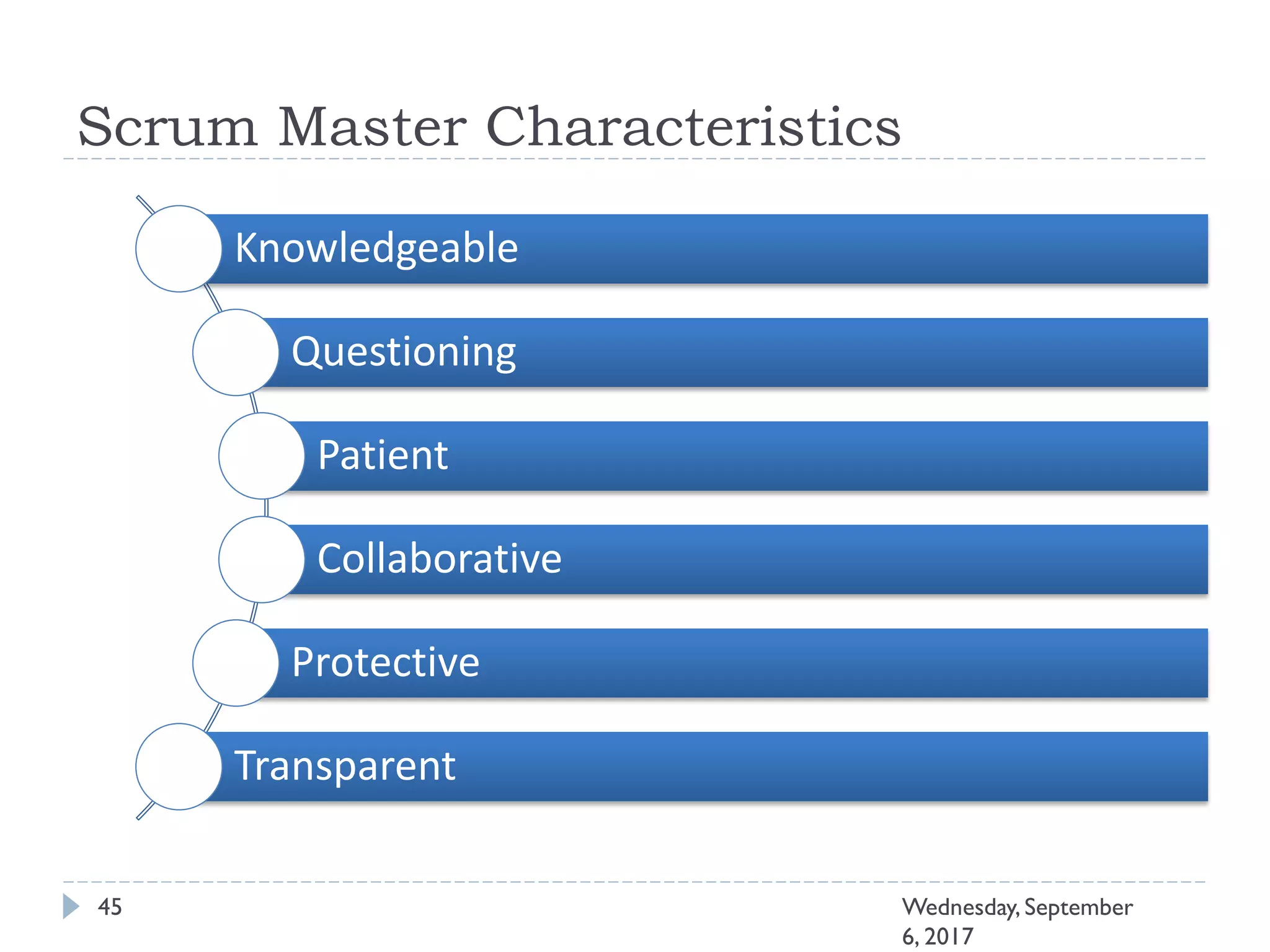
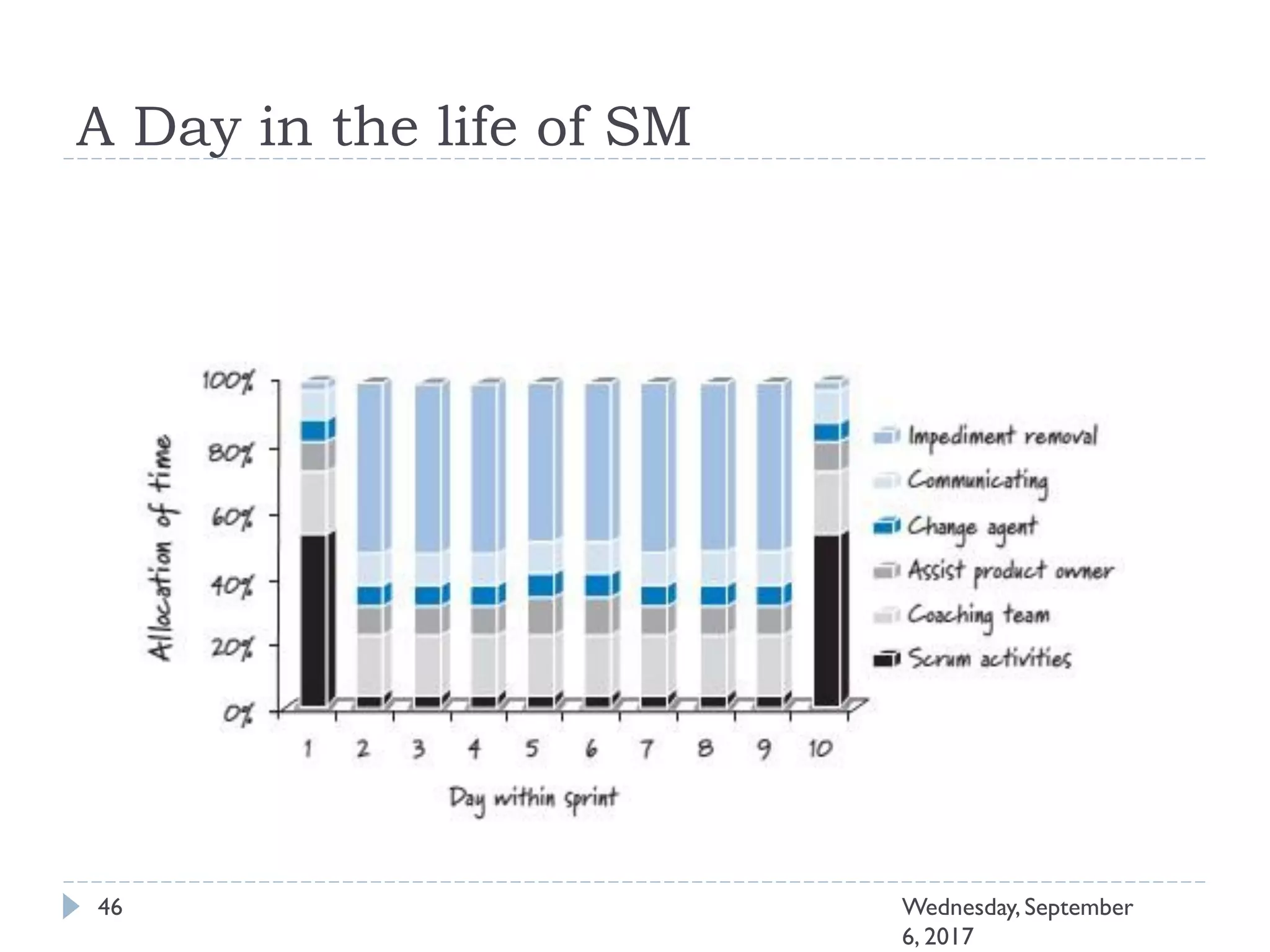
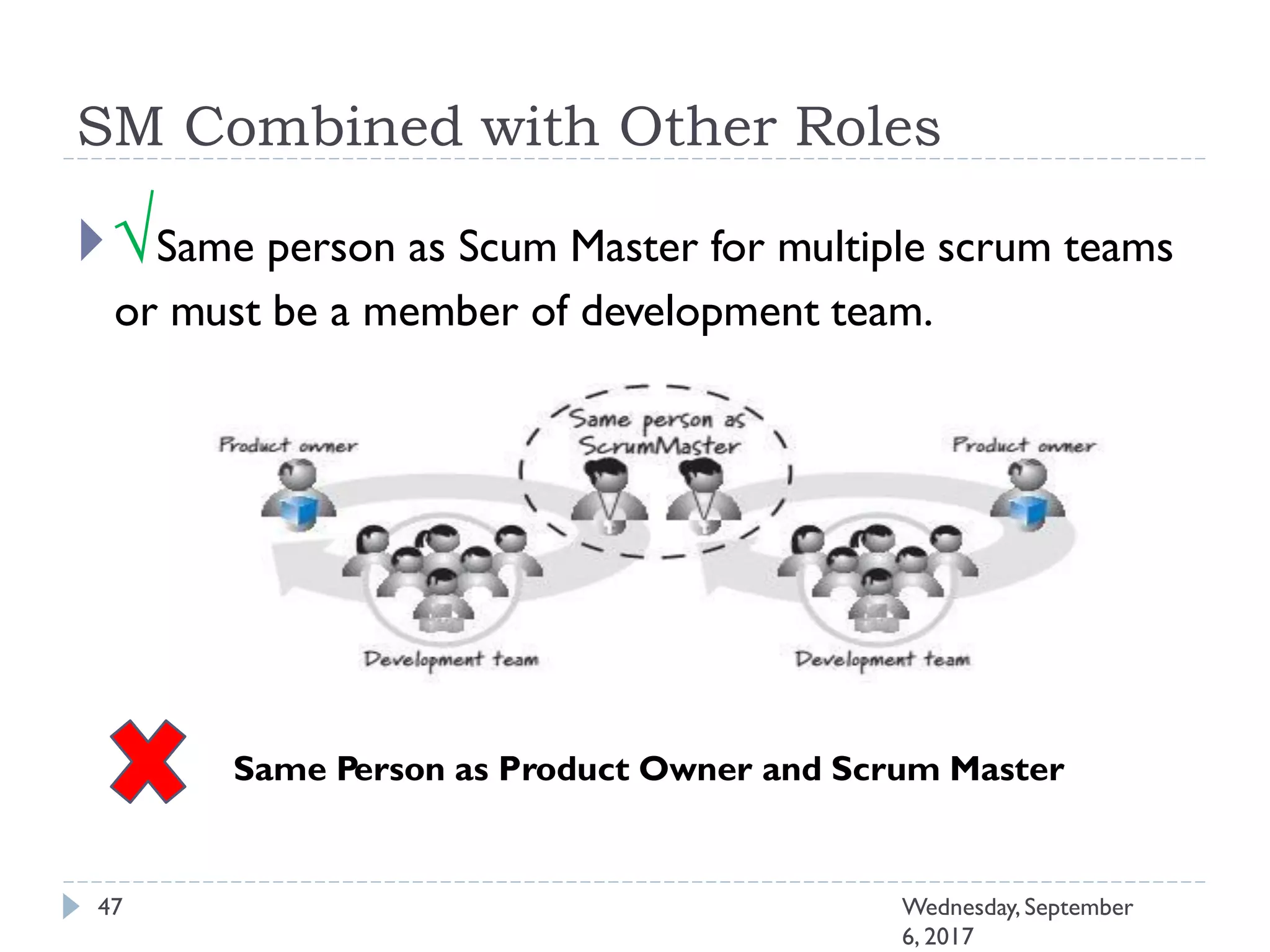
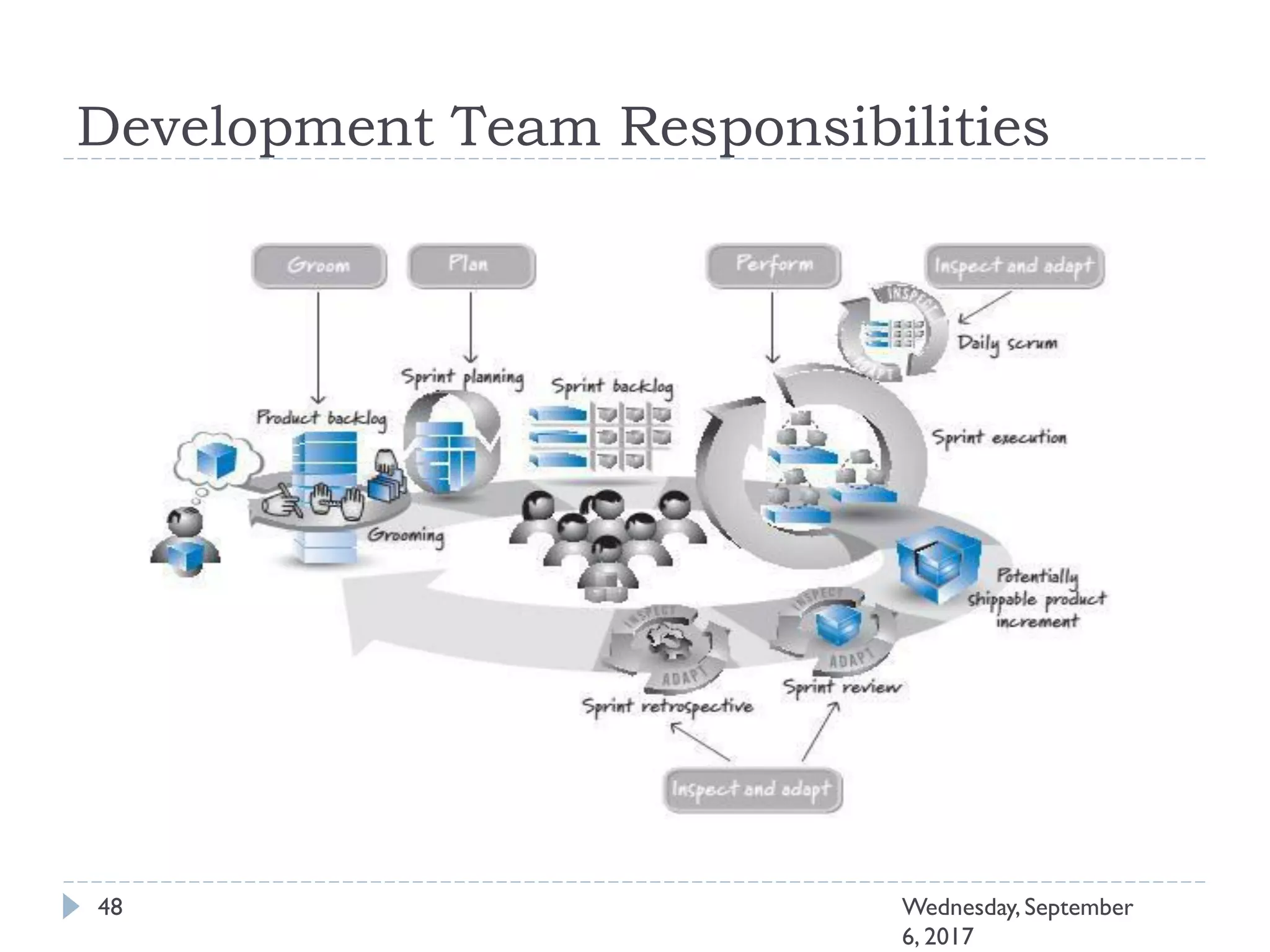
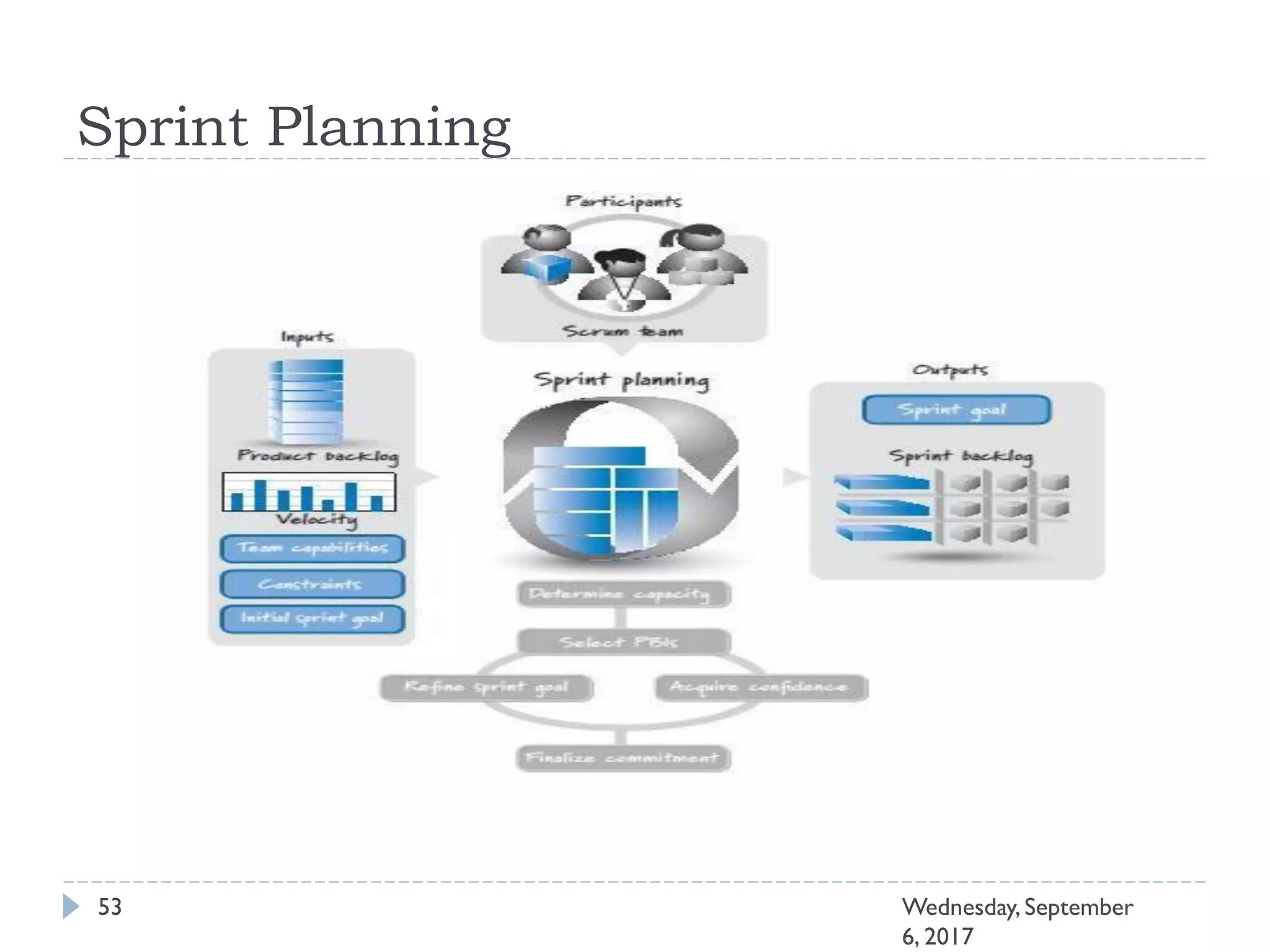
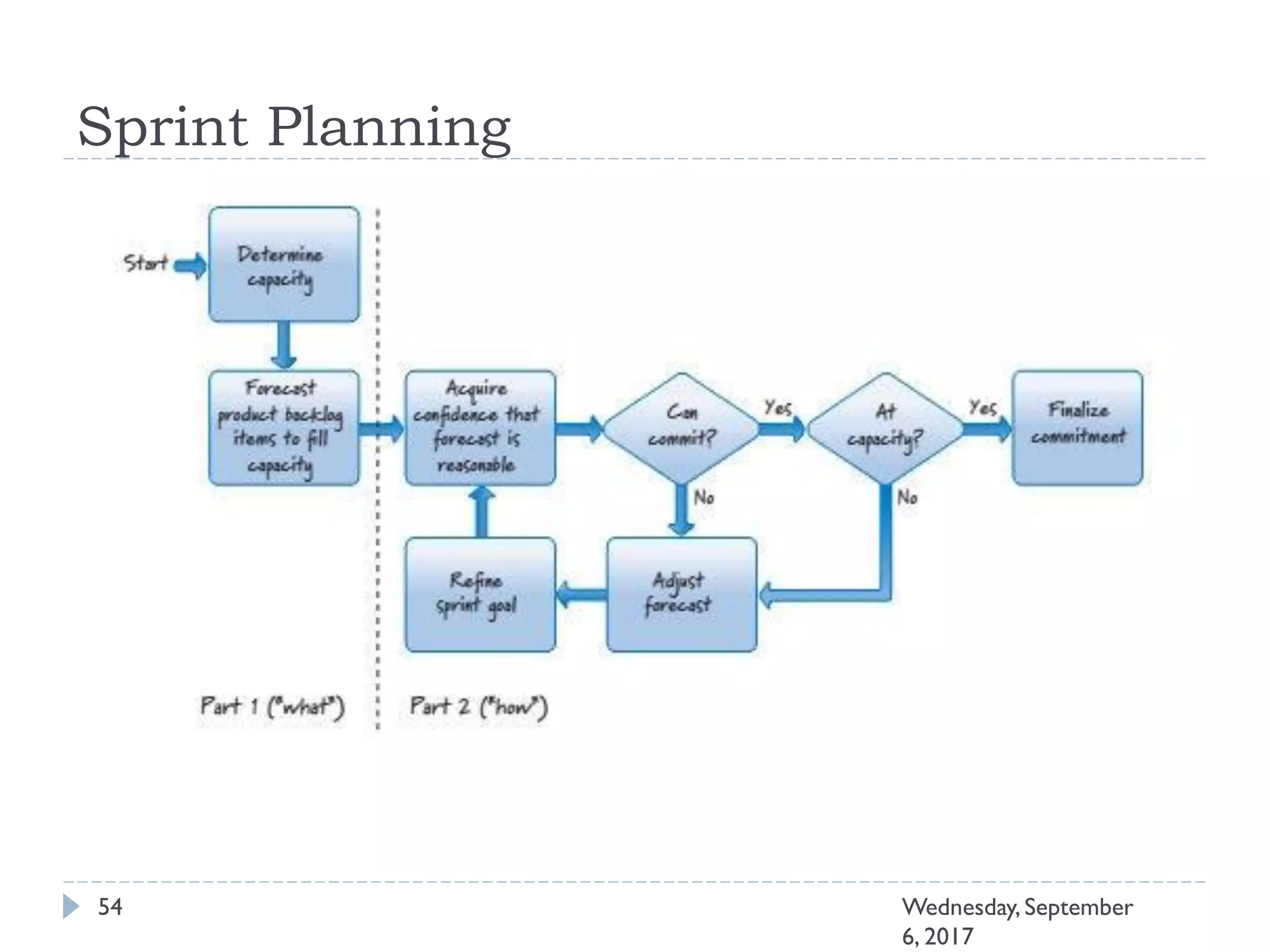
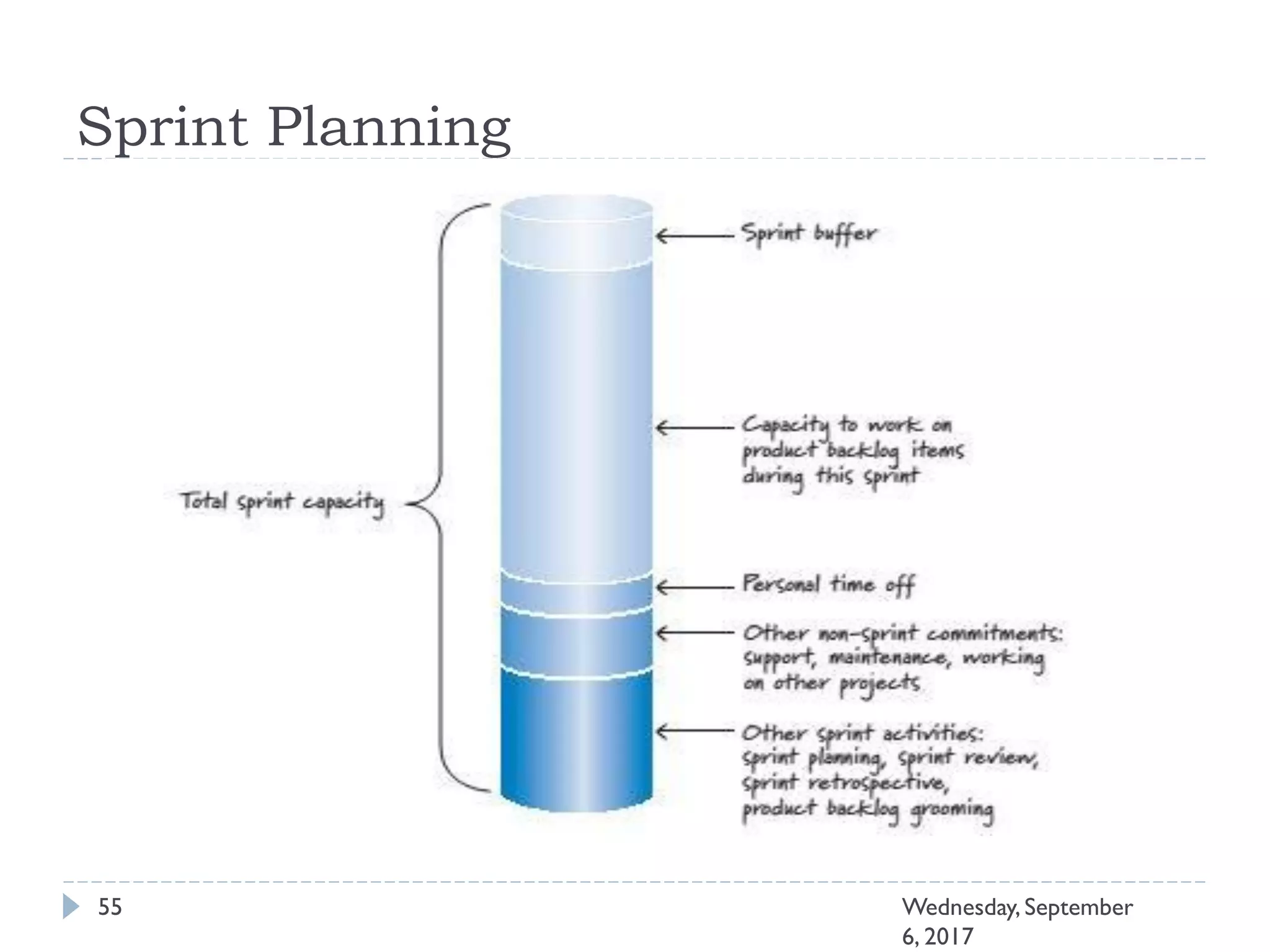
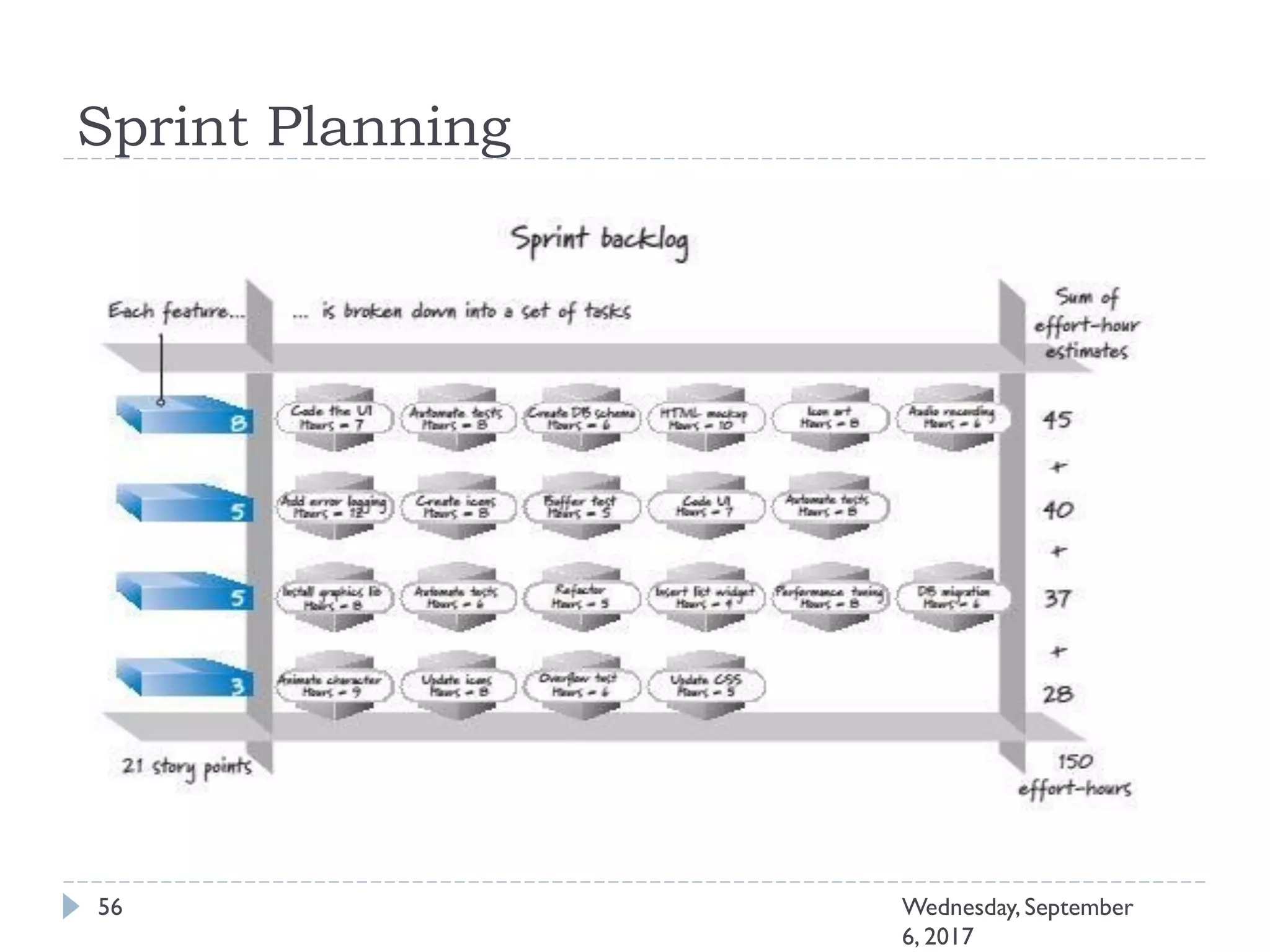
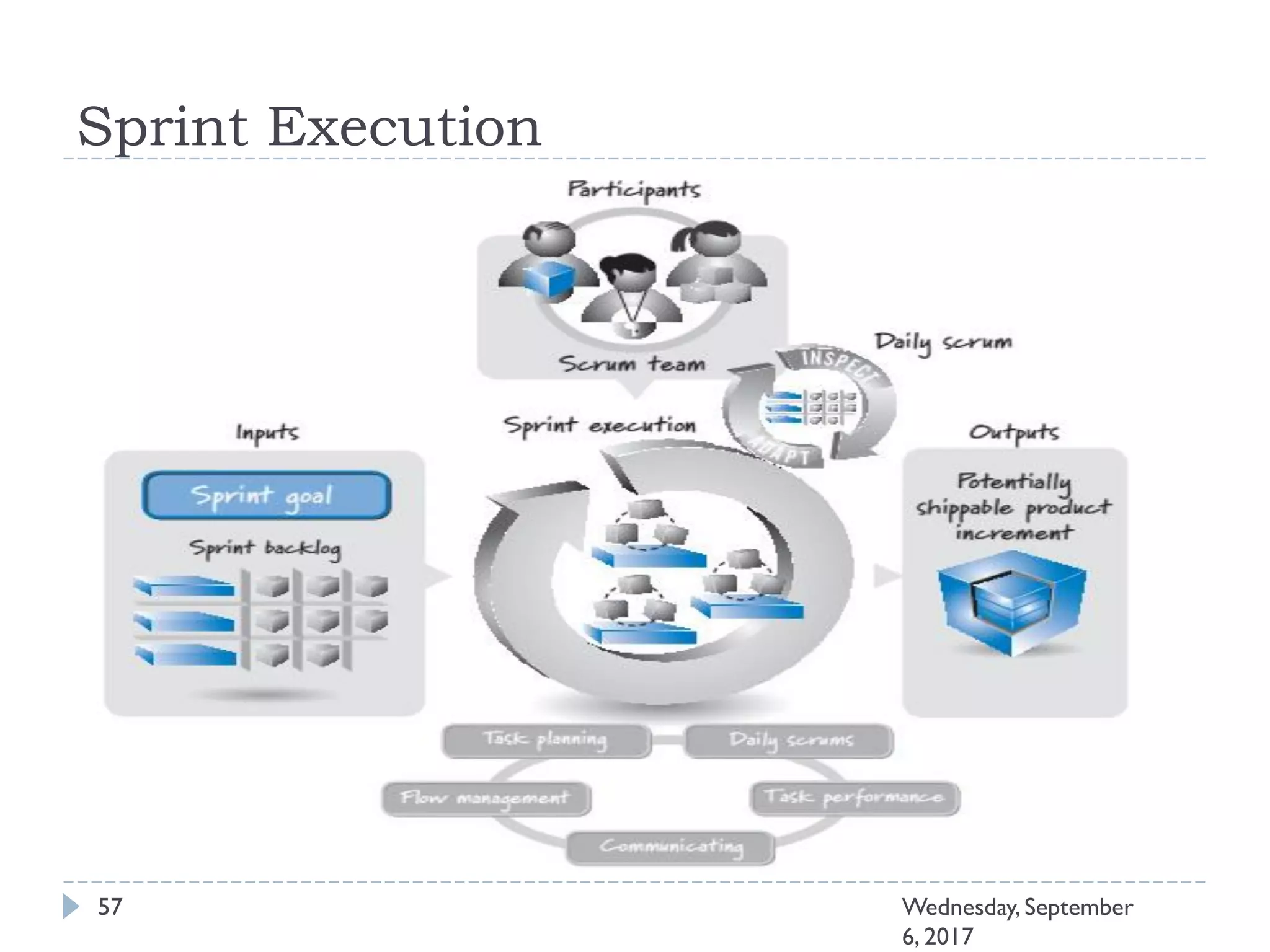
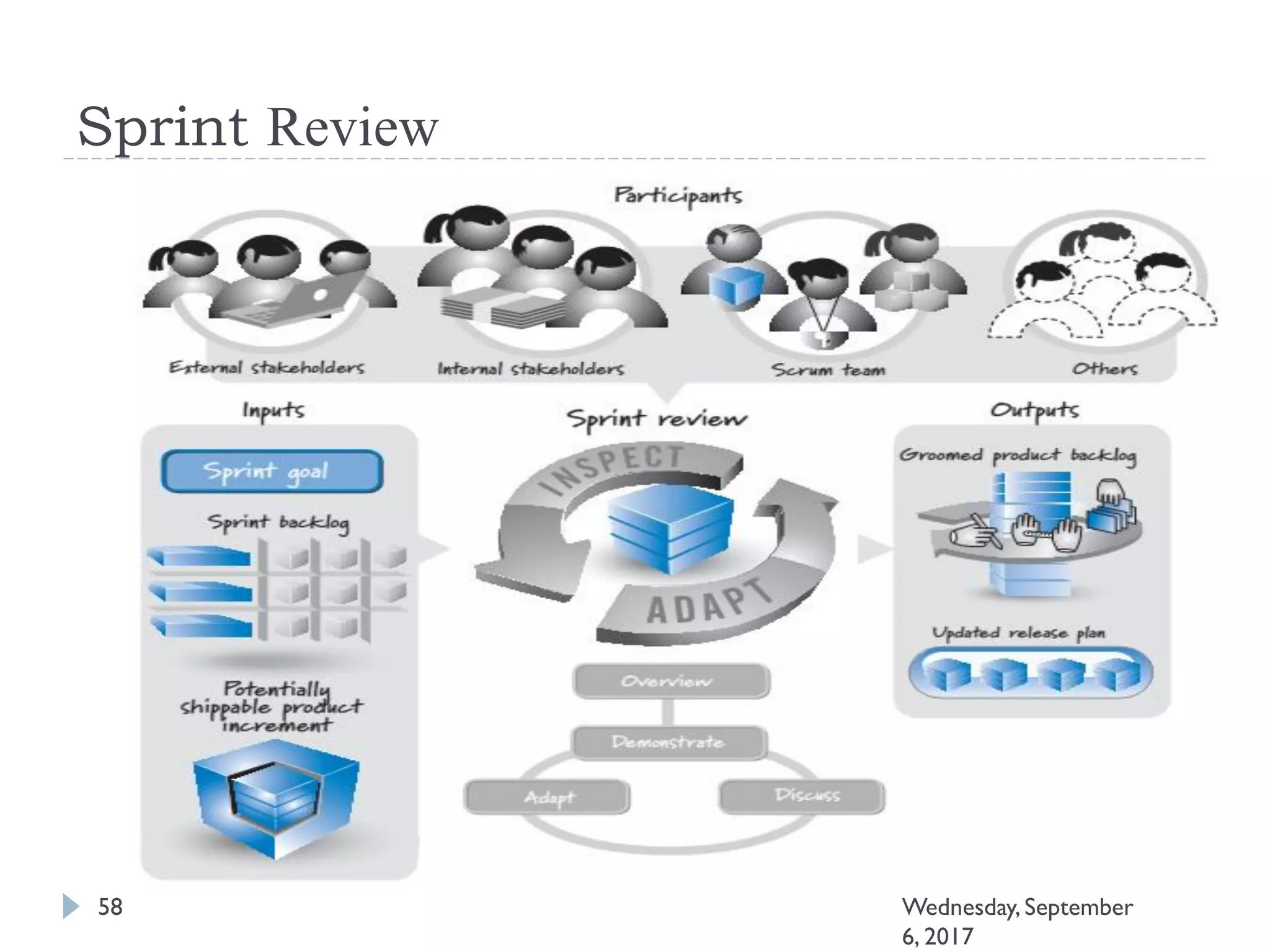
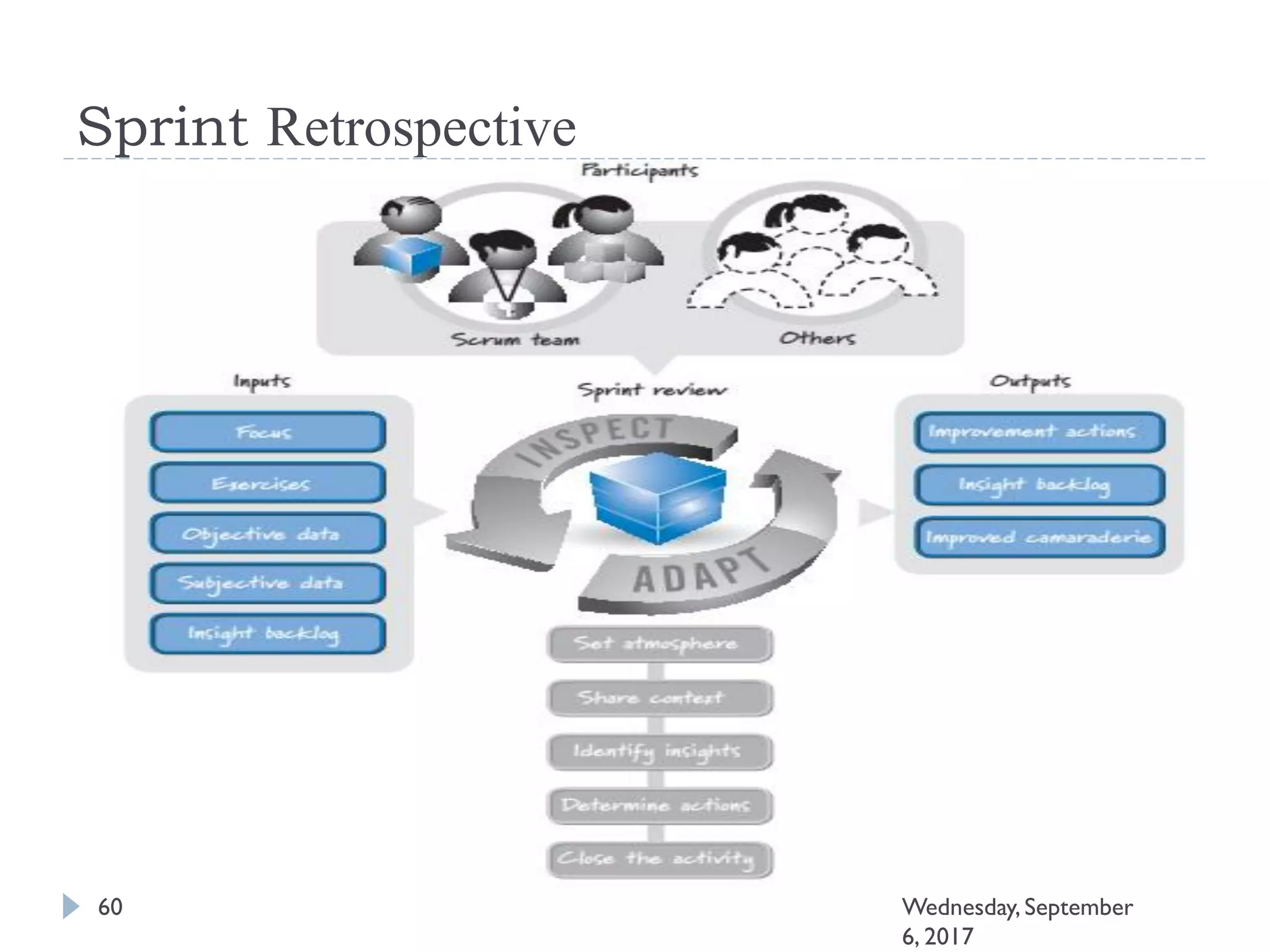
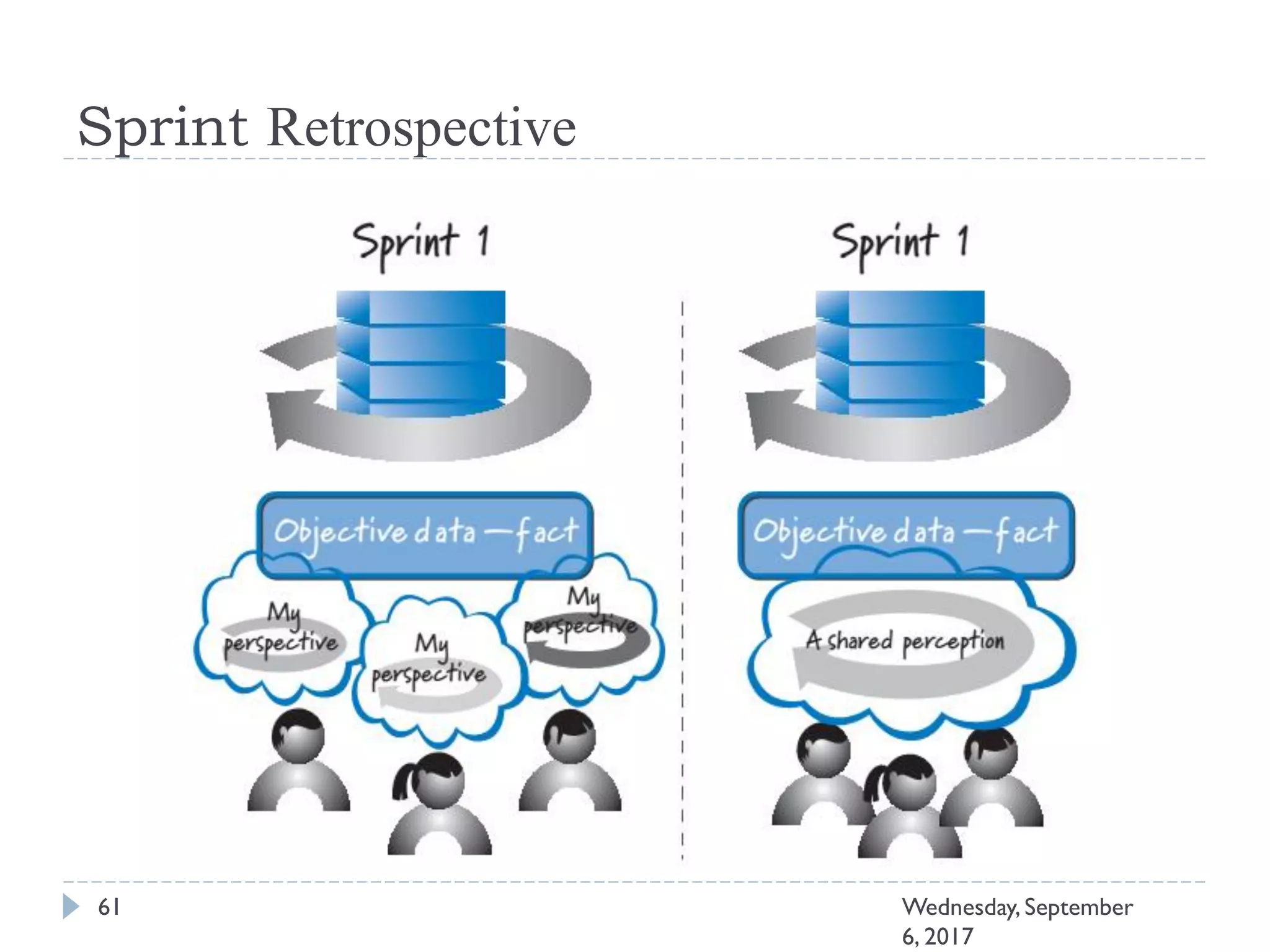
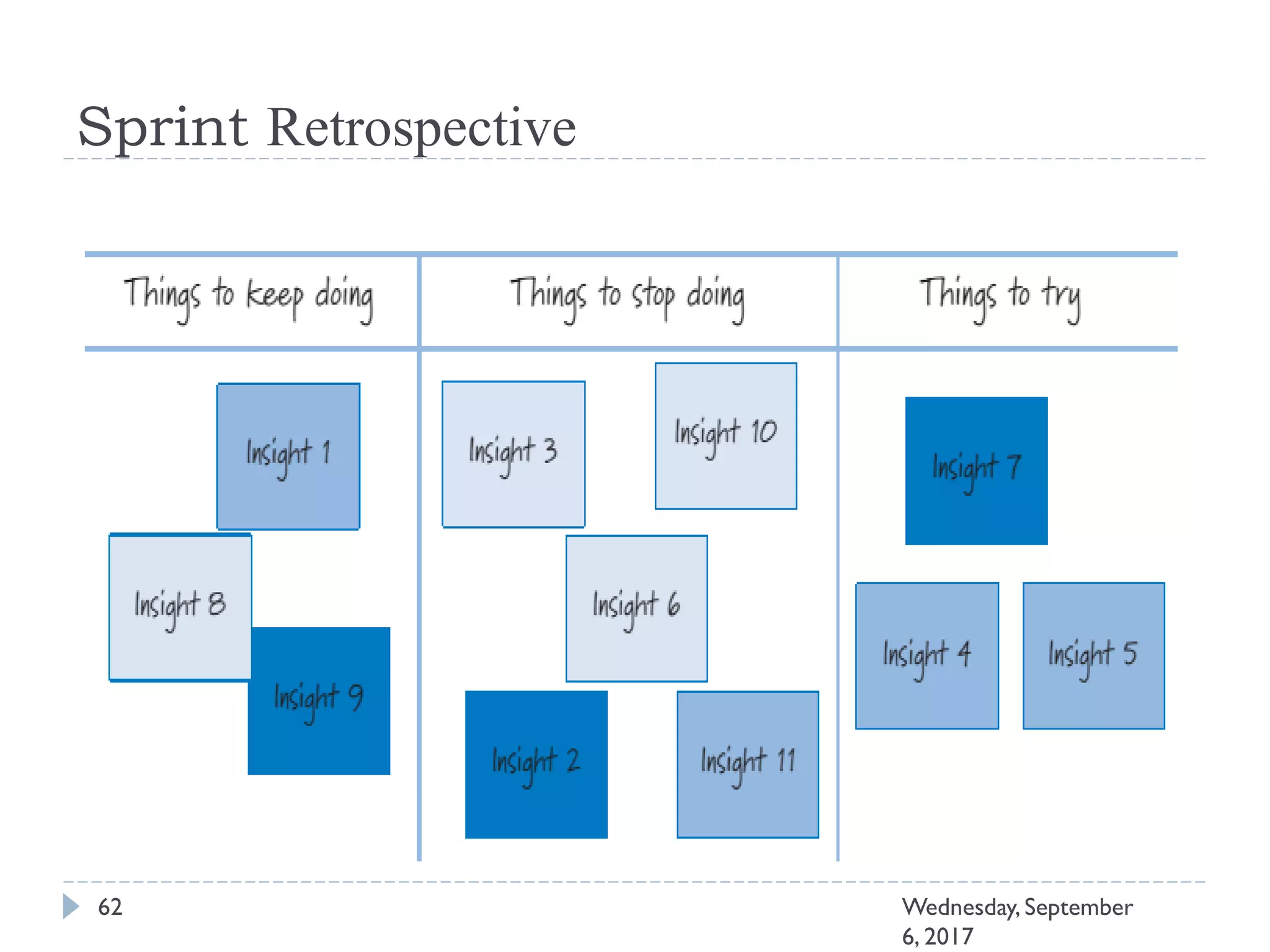
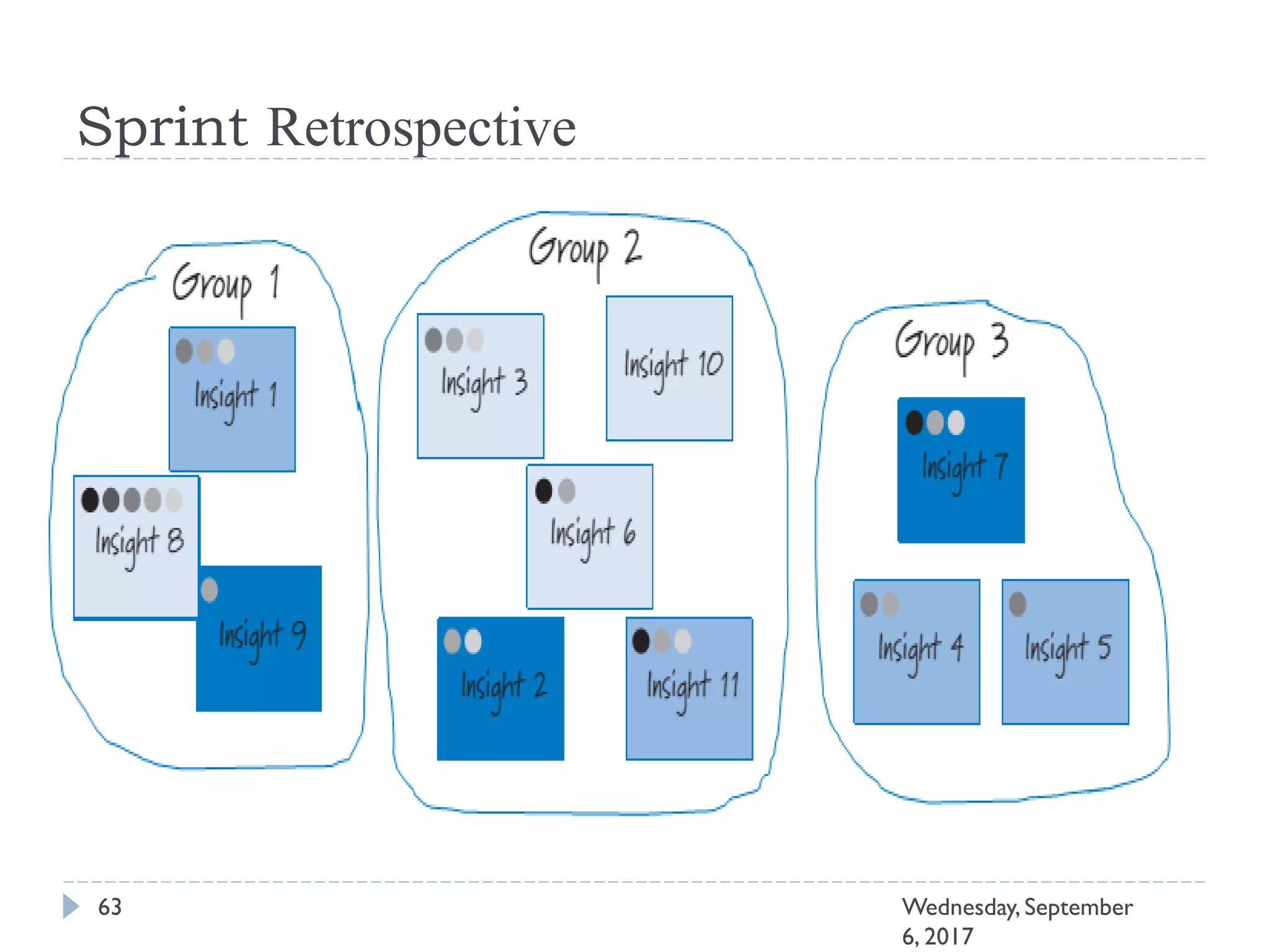
This document outlines an agenda for a course on Agile development methods. The course covers core Agile concepts like the Agile Manifesto and principles. It then details the Scrum framework, including roles like Product Owner and Scrum Master, artifacts like product and sprint backlogs, and ceremonies like sprint planning, daily standups, reviews, and retrospectives. Other topics include user stories, estimation techniques, and implementing Agile practices in Microsoft Team Foundation Server. The document provides an overview of the topics to be discussed during the course sessions.