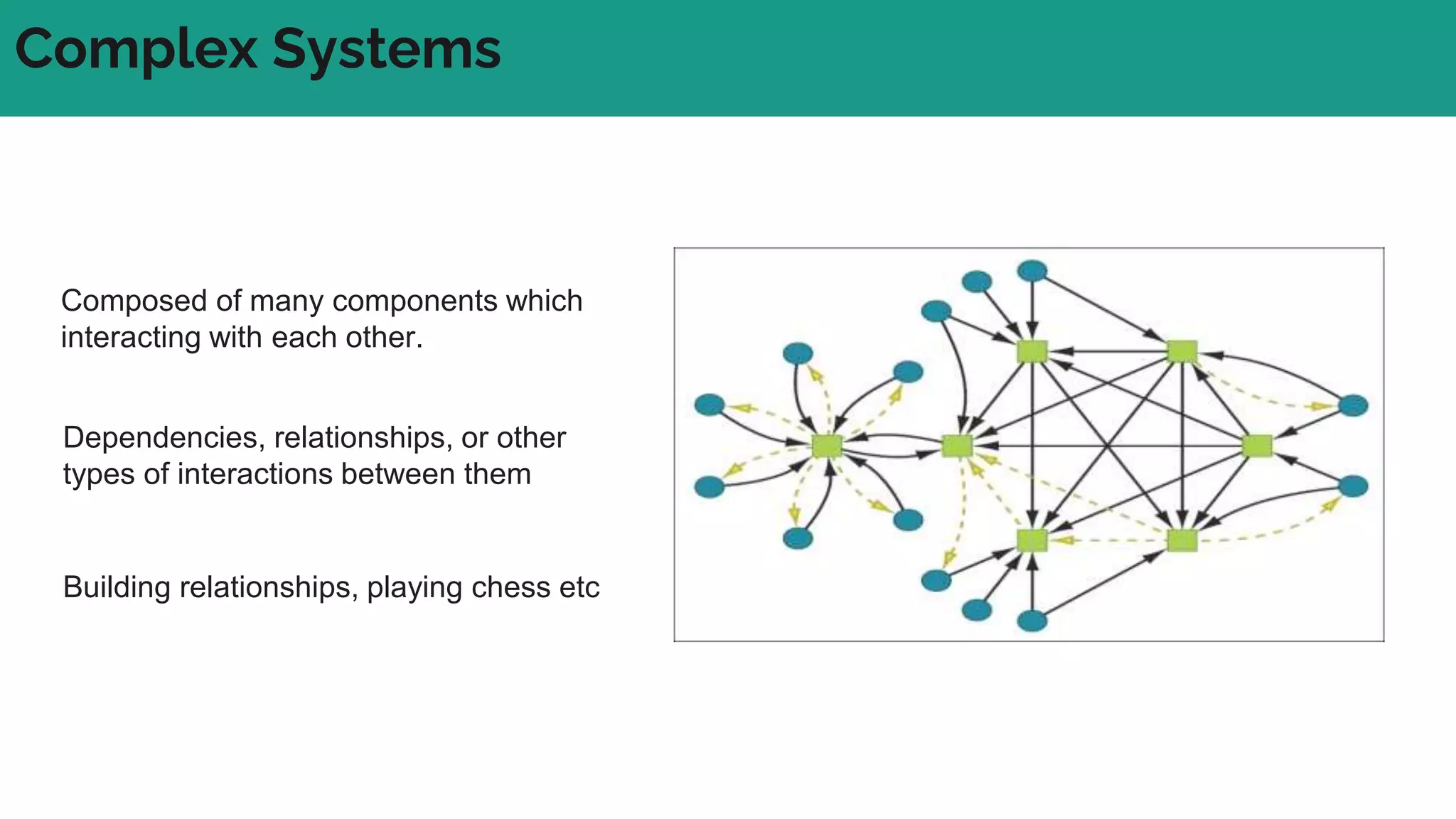
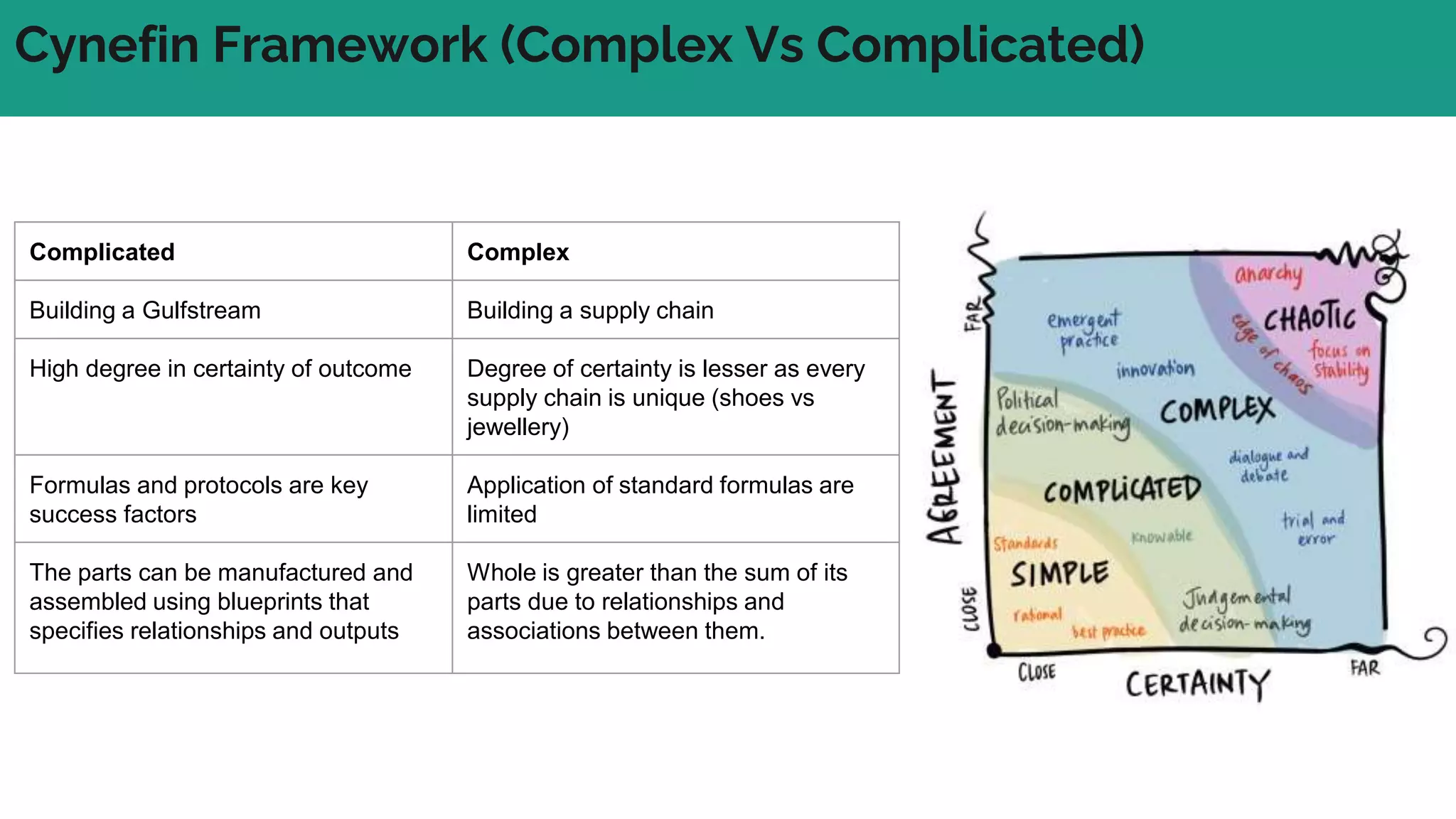
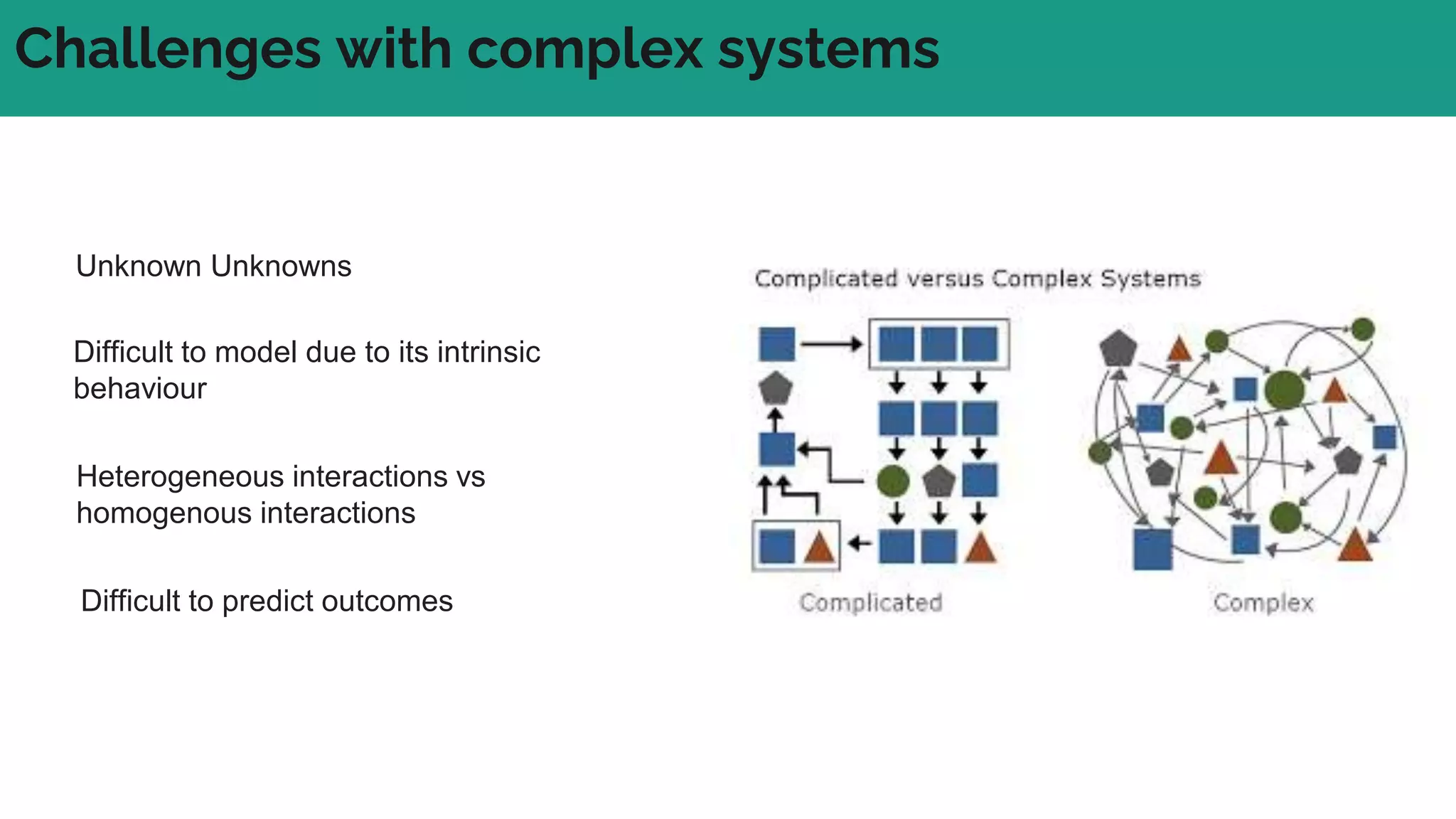
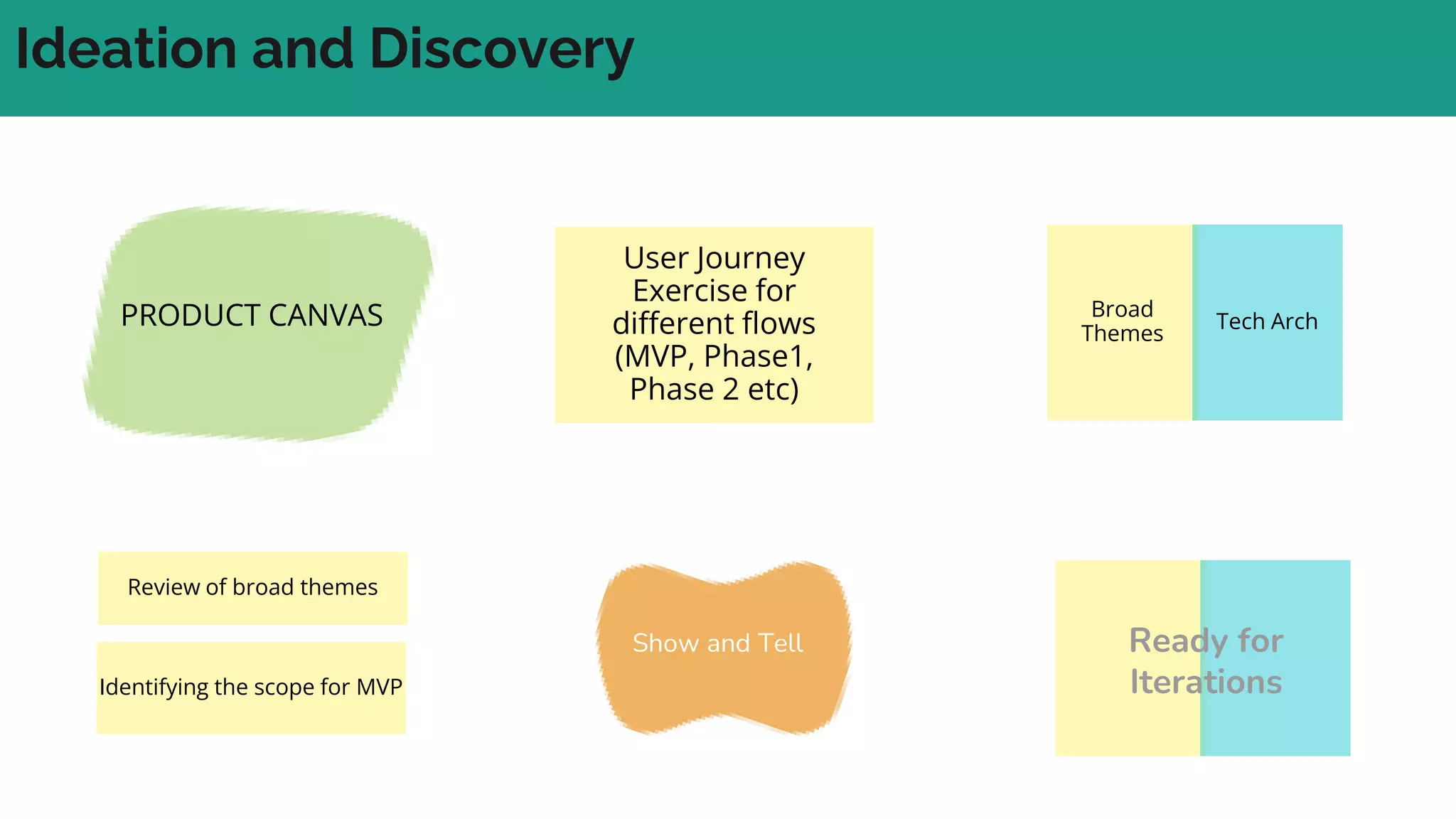
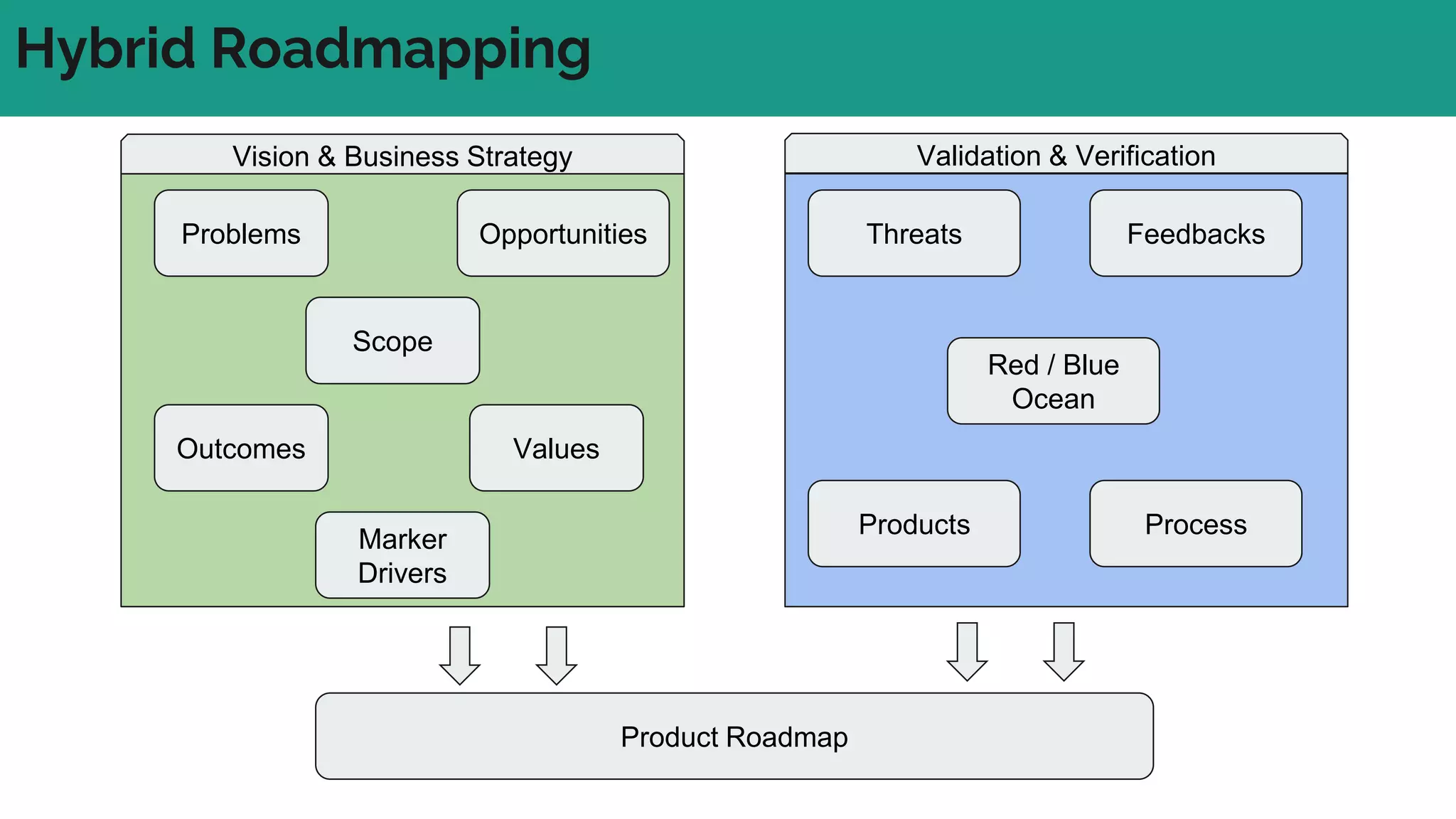
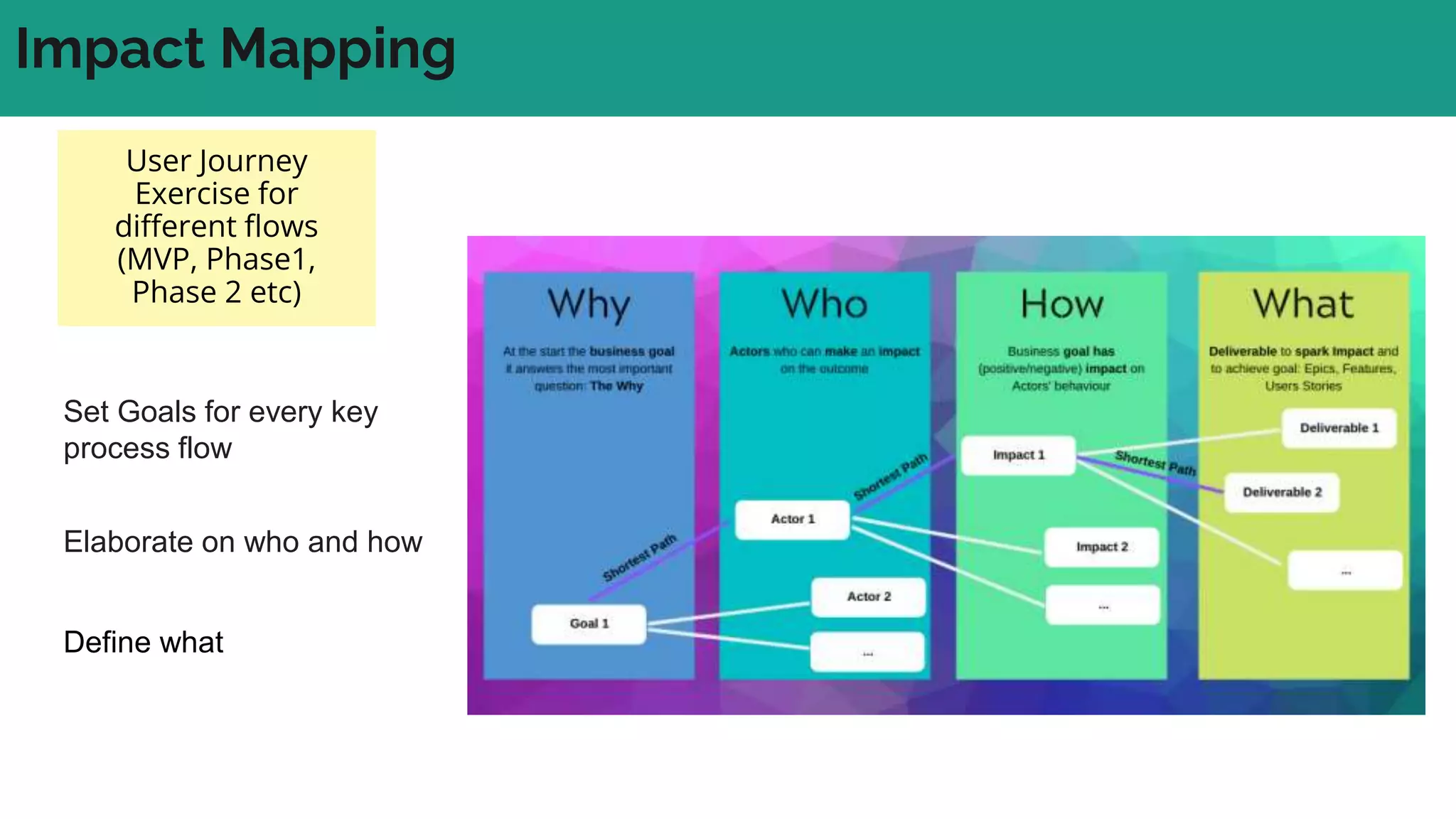
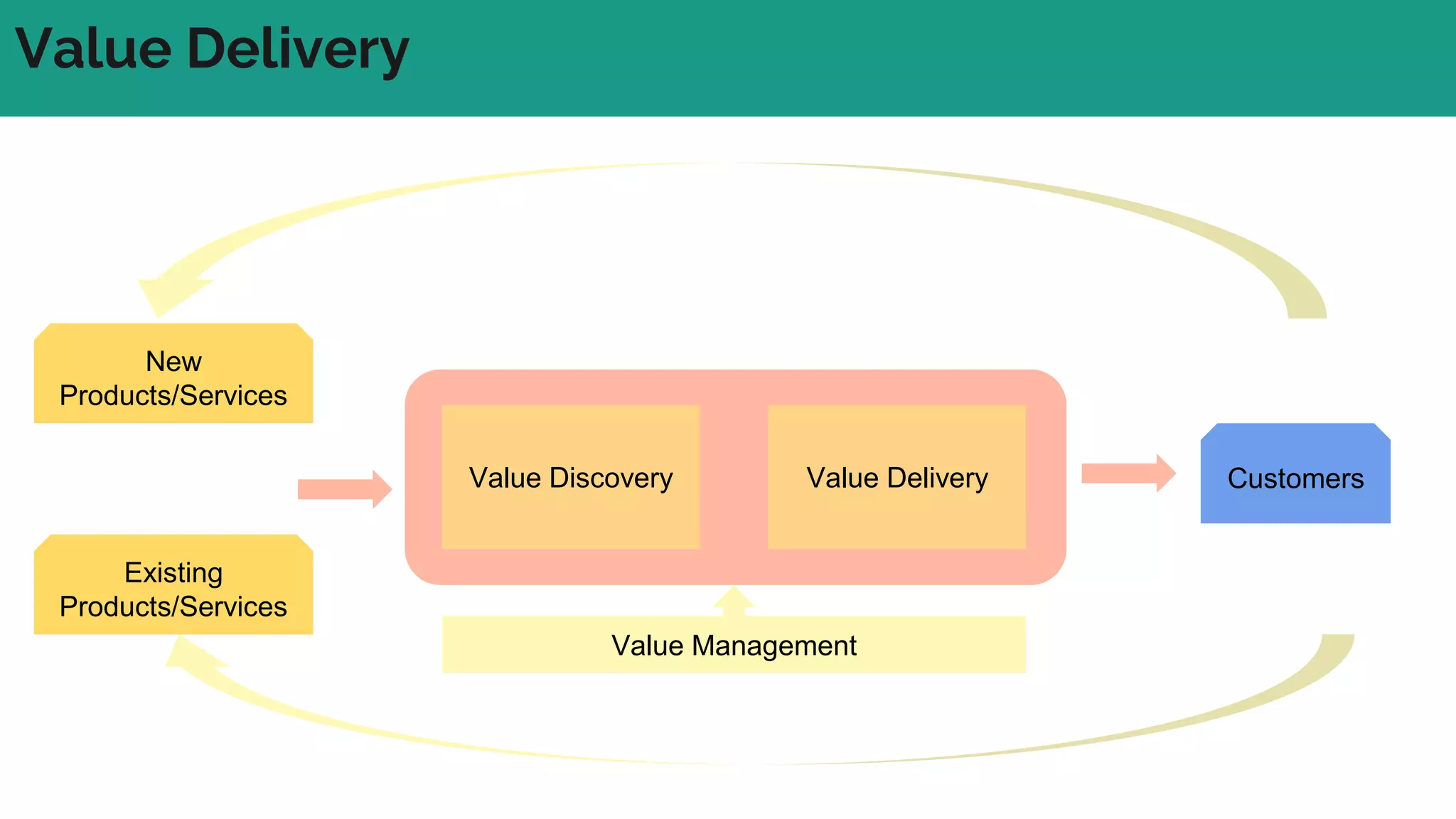
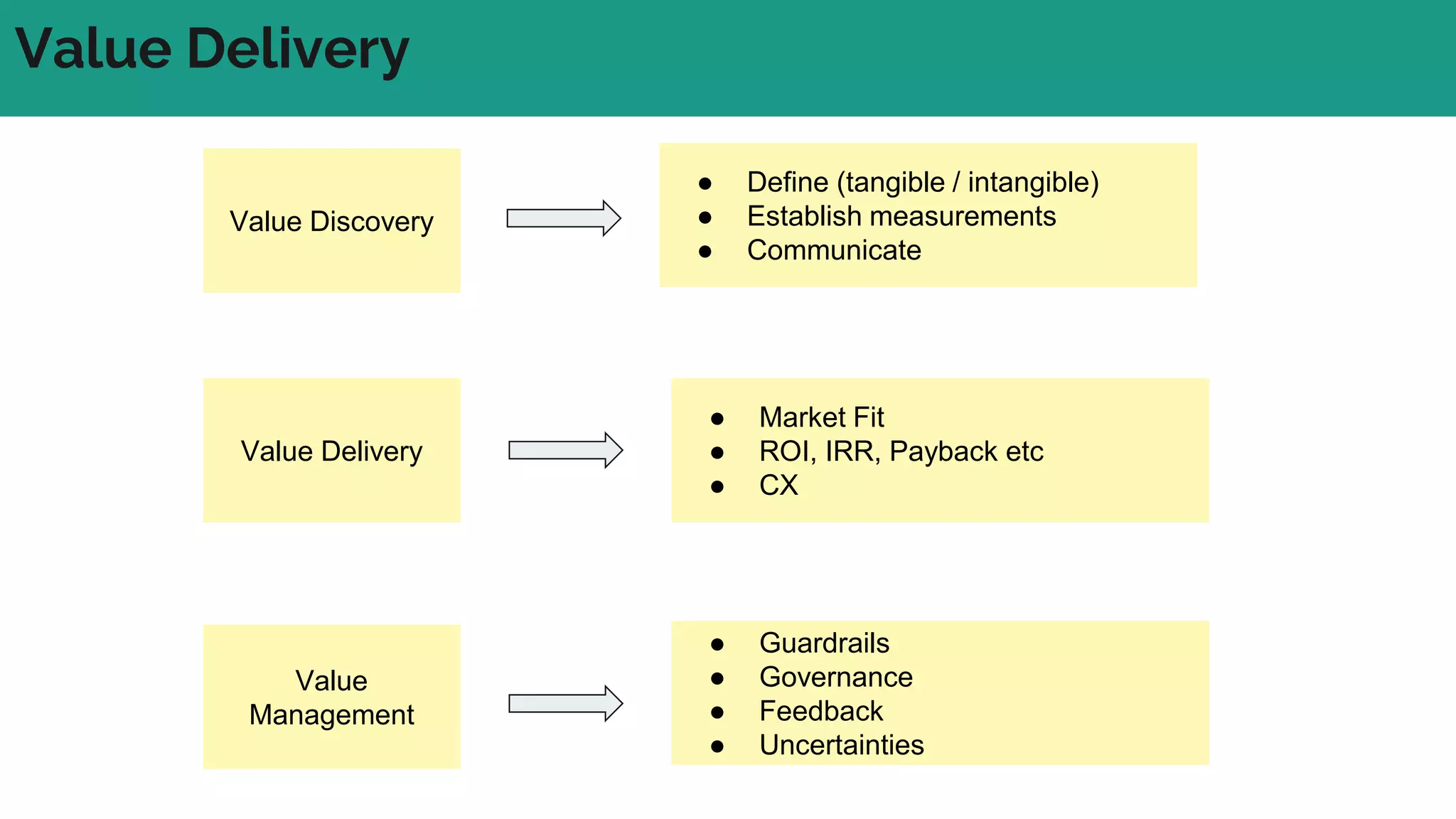
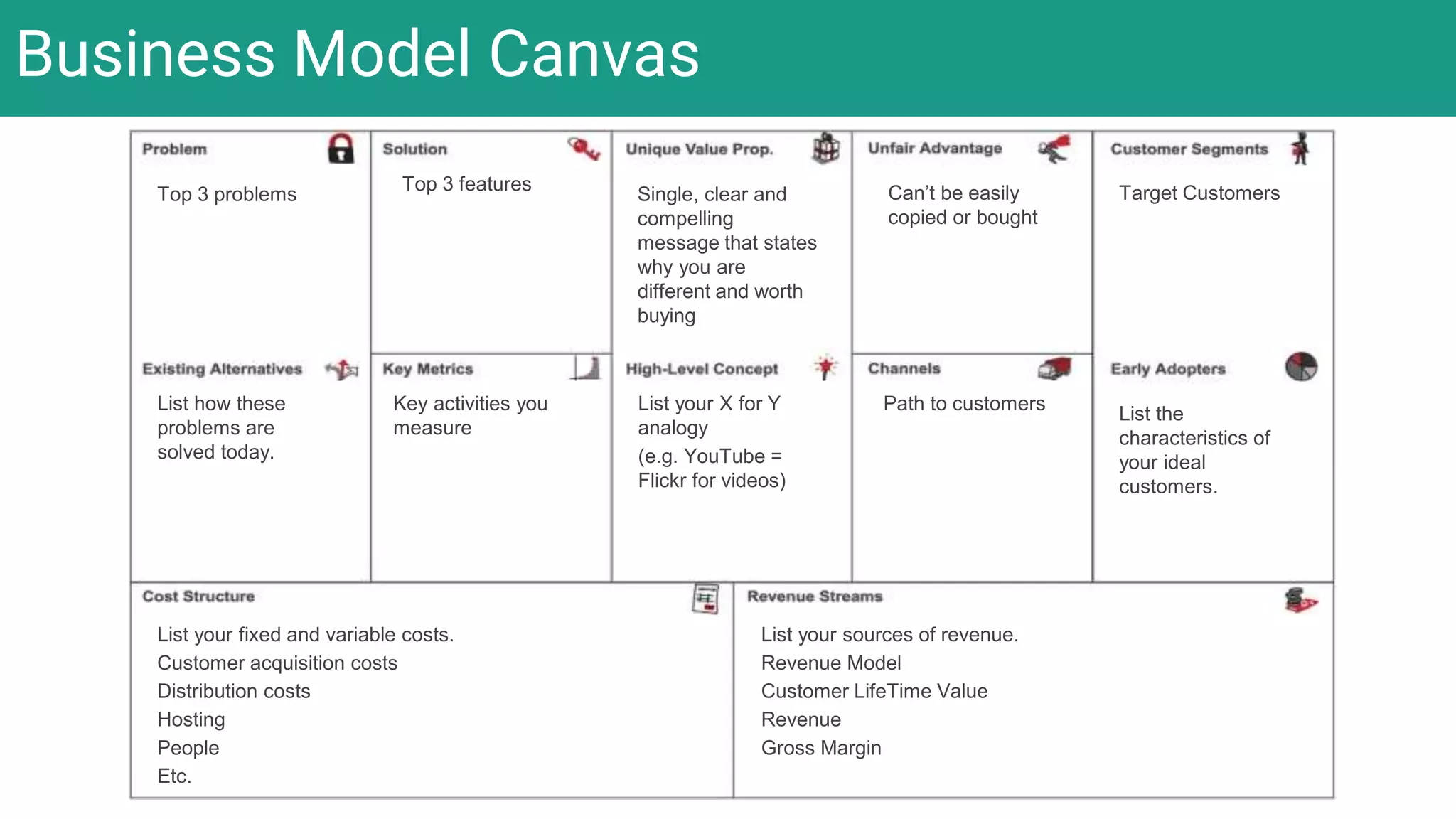
In complex systems composed of many interacting components, the relationships between components are important and outcomes are difficult to predict. In complex supply chains, standard formulas have limited application and the whole is greater than the sum of its parts. To deliver value in complex systems, one must establish contexts, generate ideas through discovery, create hybrid roadmaps, map impacts, and continuously deliver, discover, and manage value while accepting uncertainties. The key is understanding relationships, iterating ideas and solutions, defining value metrics, and getting feedback to govern value delivery over time.