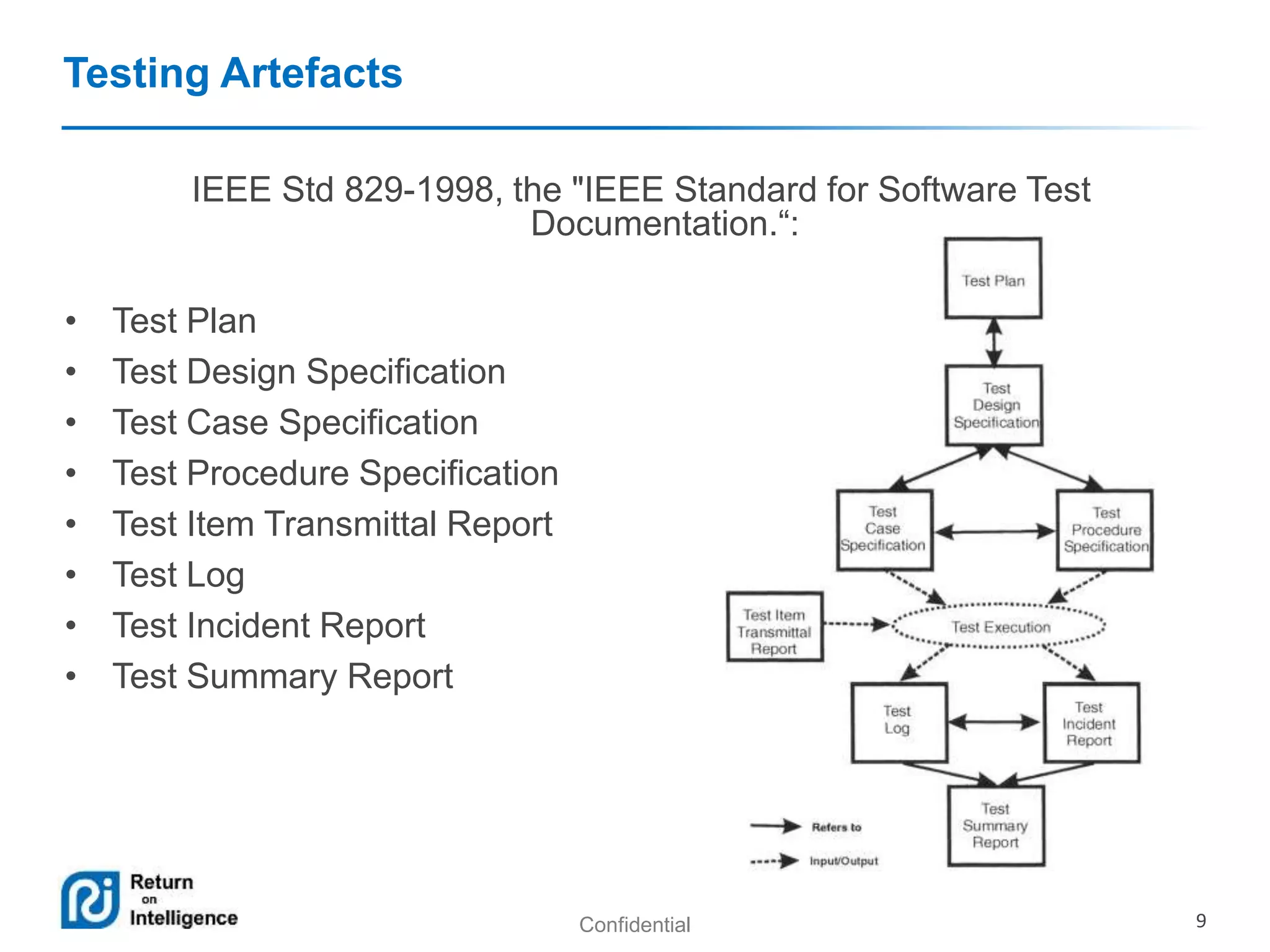
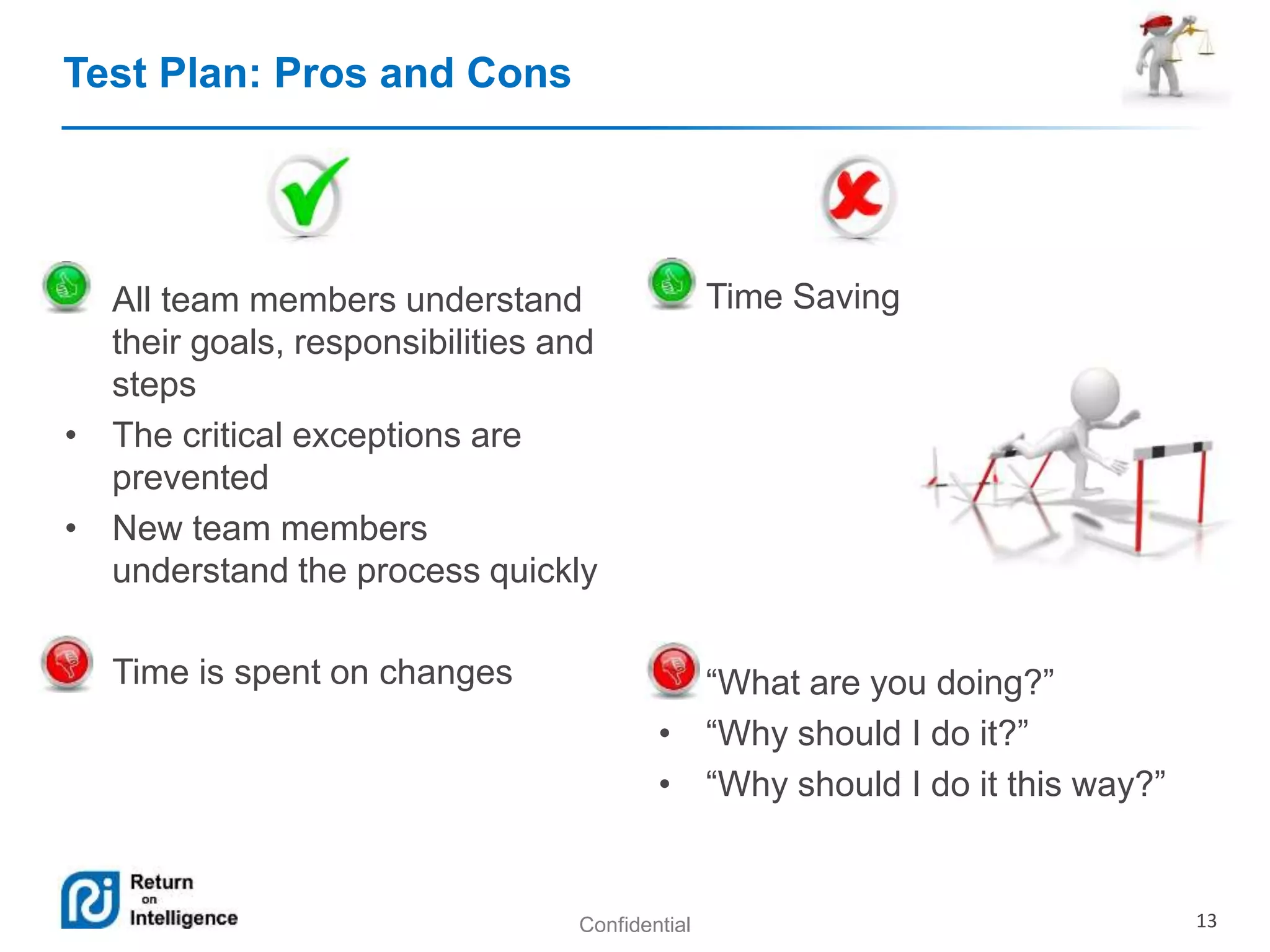
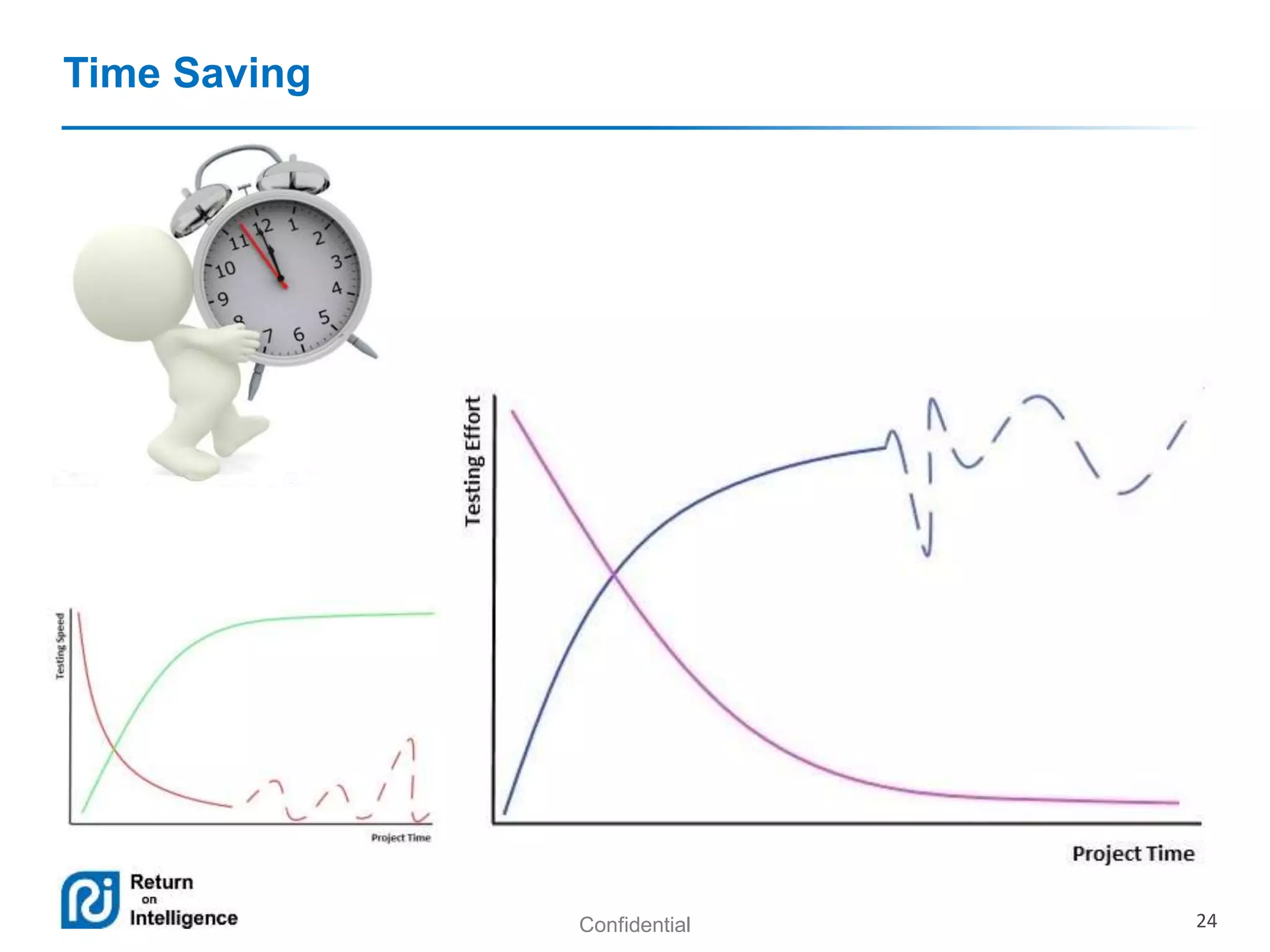
Maria Teryokhina presented on testing artifacts in agile projects. She discussed common testing artifacts like test plans, test cases, defects, and reports/metrics. She outlined the pros and cons of having these artifacts, noting they provide assurance and understanding but can also take time. She suggested not writing certain artifacts for small teams/projects or those with dynamic products where risks are not a priority. The presentation aimed to provide solutions to decrease effort on testing documentation in agile while still maintaining quality.