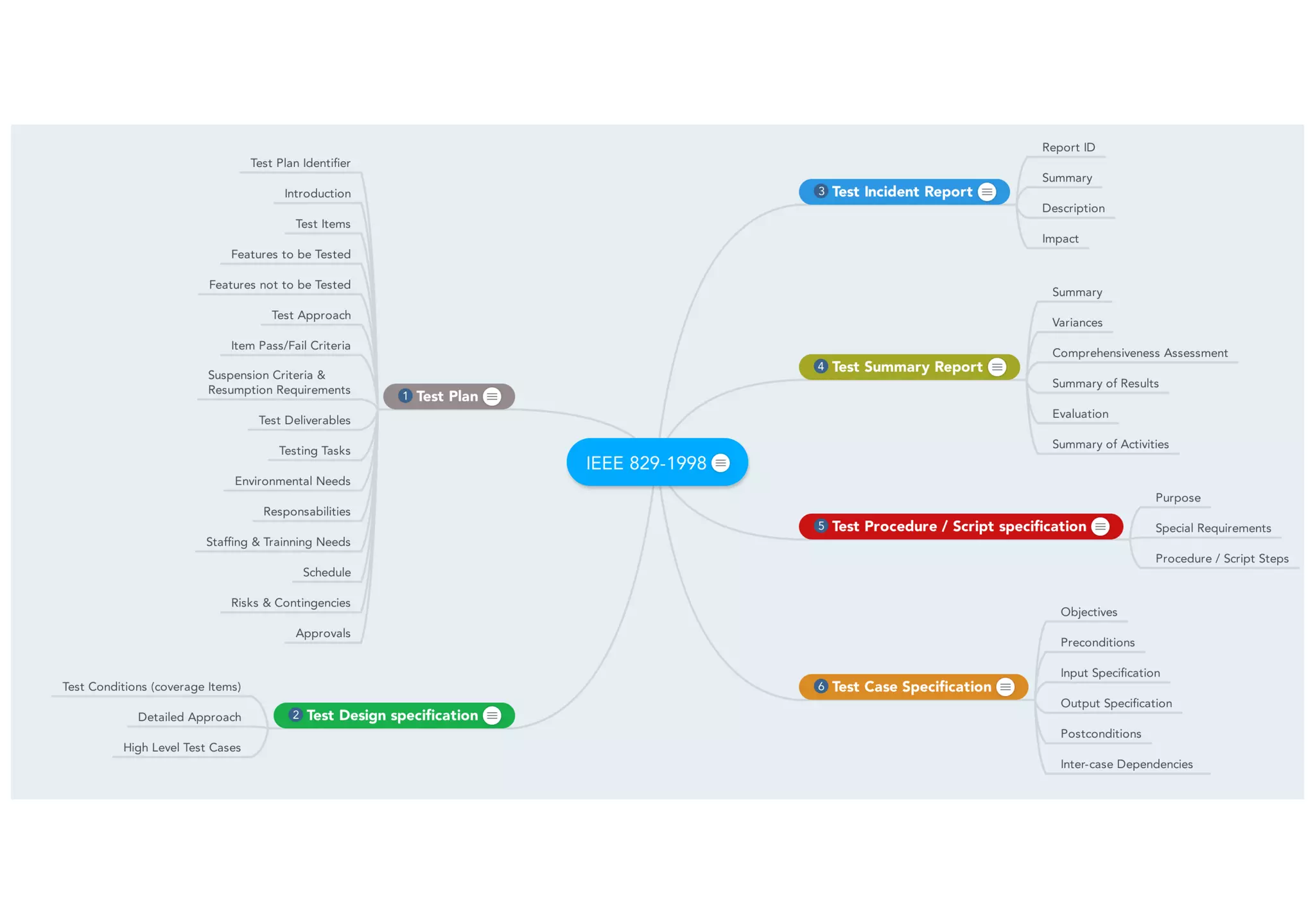
The document describes the IEEE 829 standard for software and system test documentation. The standard specifies eight types of documents for different stages of testing: Master Test Plan, Level Test Plan, Level Test Design, Test Plan, Test Summary Report, Test Case Specification, Test Procedure/Script Specification, and Test Incident Report. Each document has a specific purpose, such as the Master Test Plan providing overall test planning and the Test Incident Report describing bugs to help developers resolve issues.