ADHD – Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
Presented by: Anurag Joseph
Course: M.Sc. Final Year (Mental Health Nursing)
Institution: SMT RD GARDI Nurses Training Centre
Case Study 1 – Inattentive Type (Raju)
5th standard student
Trouble focusing in class; often daydreams
Misses deadlines; delays homework
Slow information processing; indecisive
Case Study 2 – Hyperactive-Impulsive Type (Rahul)
3rd standard student
Cannot sit still; loud and aggressive
Talks fast; interrupts; impatient
Disruptive, energetic when unsupervised
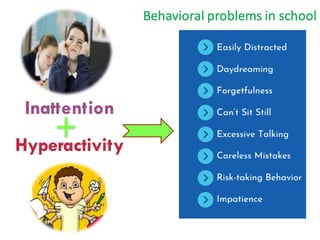
Behavioral Problems in School
Inattention + Hyperactivity
Impacts learning, peer interaction, discipline
Introduction
ADHD is a developmental disorder marked by co-existing attention problems and hyperactivity, rarely found alone.
Definition (DSM-5 Inspired)
A neurodevelopmental disorder with persistent inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity, interfering with functioning or development, starting in childhood.
Prevalence
5.1 million children diagnosed in the U.S.
6.8% (ages 4–10), 11.4% (ages 11–14), 10.2% (ages 15–17)
Symptoms may appear by age 4; diagnosable by 7
68% of affected children carry symptoms into adulthood
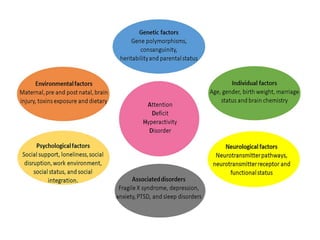
Causes of ADHD
Genetic Causes
Strong hereditary link
Runs in families
Biological Factors
Brain and neurotransmitter dysfunction
Abnormal brain region volumes
Environmental Factors
Exposure to toxins (e.g., microplastics)
Prenatal and perinatal risks
Unstable home or school environment
Psychological Contributions
Negative feedback from peers/teachers
Low self-esteem, peer rejection, isolation
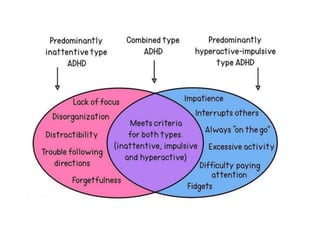
Symptoms of ADHD
1. Inattention
Easily distracted, forgetful, daydreams
Avoids long tasks, misses details
Trouble completing homework and following instructions
Difficulty processing information
2. Hyperactivity
Fidgeting, inability to sit still
Excessive talking and movement
Constantly in motion, impulsive behavior
3. Impulsiveness
Acts without thinking, interrupts frequently
Instant gratification, inappropriate outbursts
Anxiety about future events
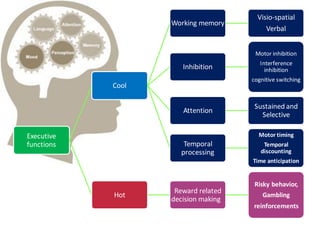
Why ADHD Children Are Different
Issues in executive functions, working memory, motor inhibition, time management, and emotional regulation
Problems with decision making, reward system, and risky behavior
Diagnosis of ADHD
Requires ≥6 symptoms (children) or ≥5 symptoms (adolescents/adults) over 6+ months in 2+ settings
Tools include:
Medical, neurological, vision, hearing exams
Psychiatric evaluation (IQ, academics)
Teacher/parent observations
Brain imaging (MRI), prenatal history
DSM-5 Key Diagnostic Points
Persistent inattention/hyperactivity
Symptoms must interfere with daily function
Inattention signs include careless mistakes, trouble focusing, forgetfulness, etc.
Management Goals & Strategies
1. Prevent Trauma
Provide structured environments
Maintain routine for predictability
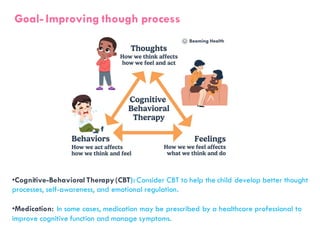
2. Improve Thought Process
Use Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Consider medication if necessary
3. Boost Self-Esteem
Encourage positive