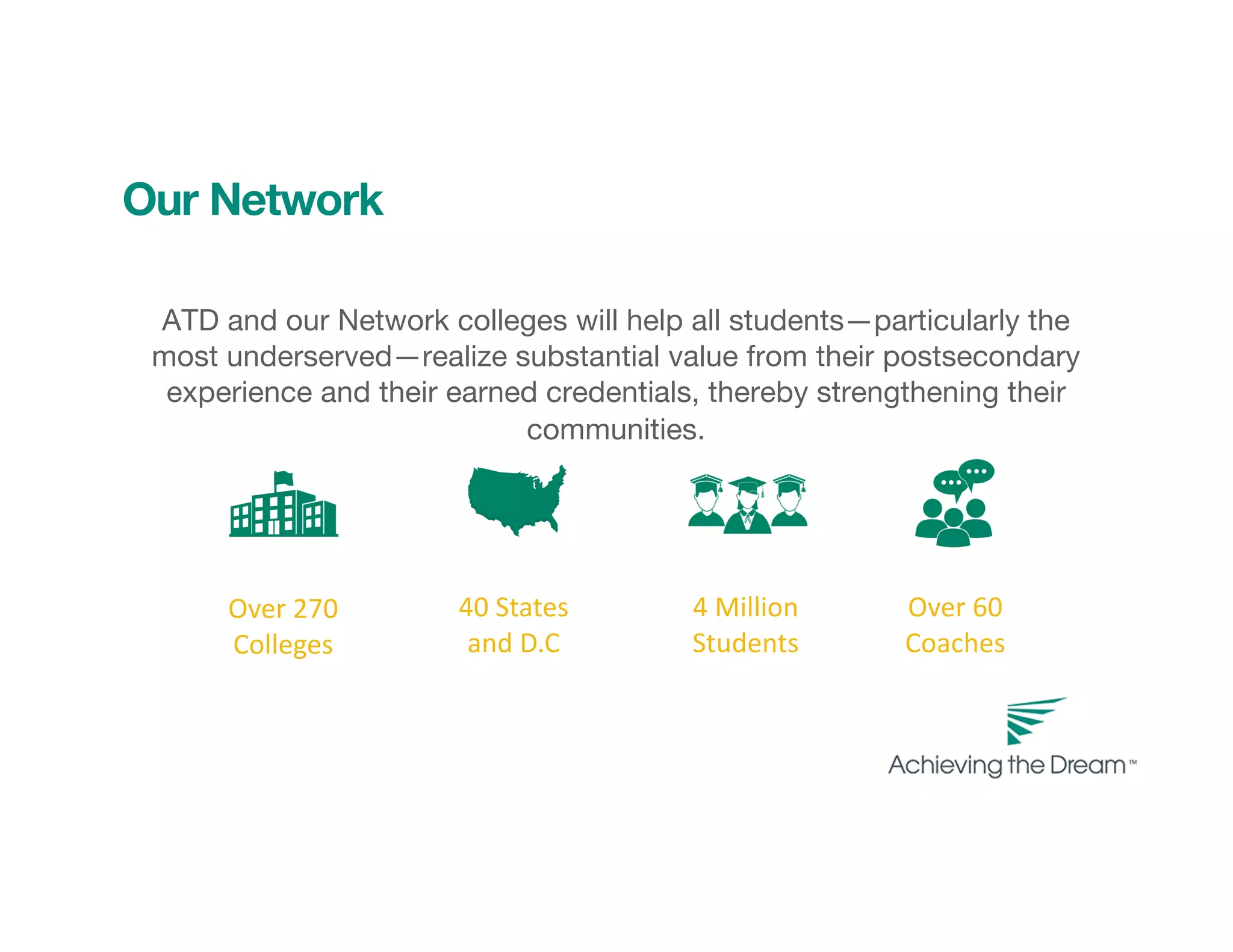
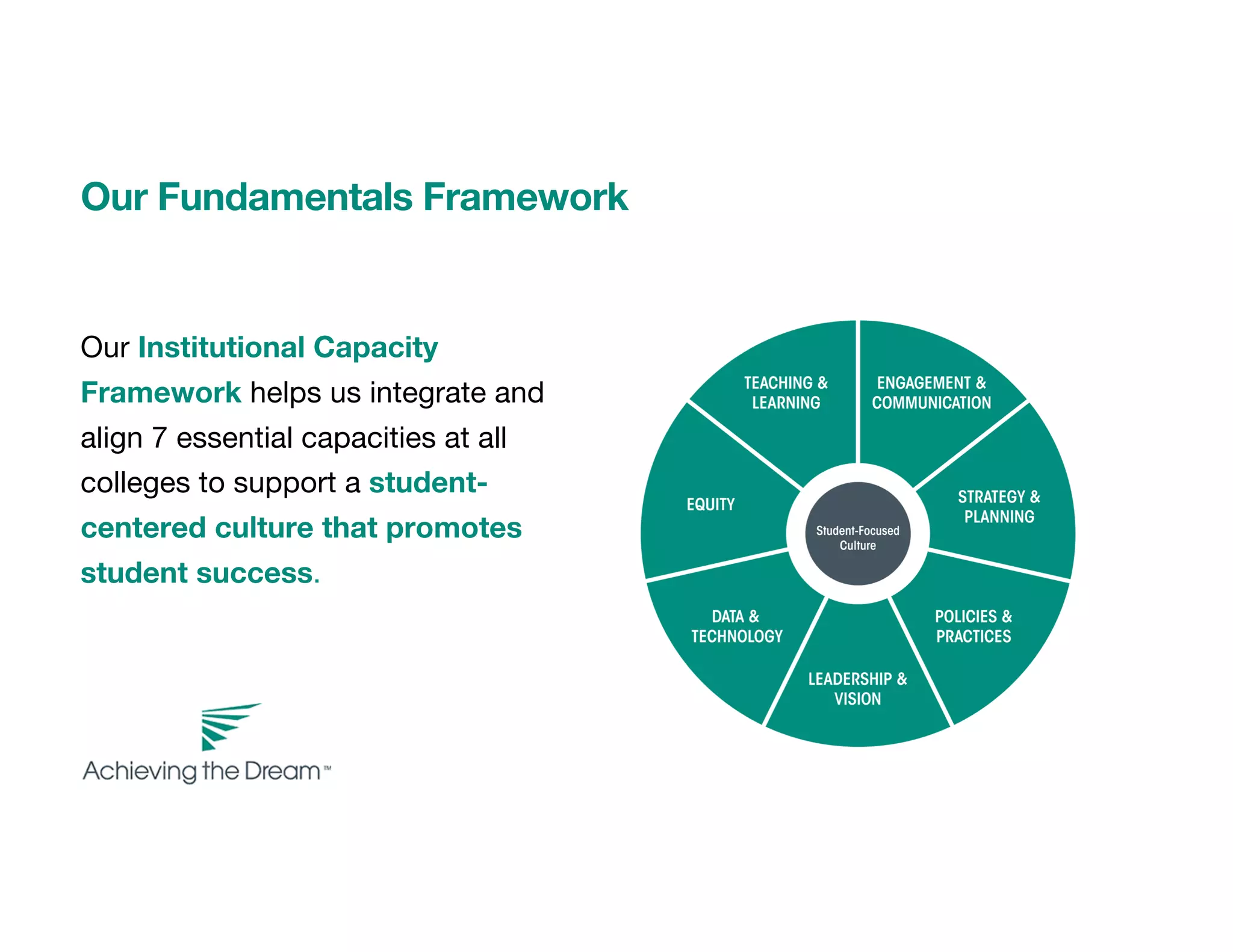
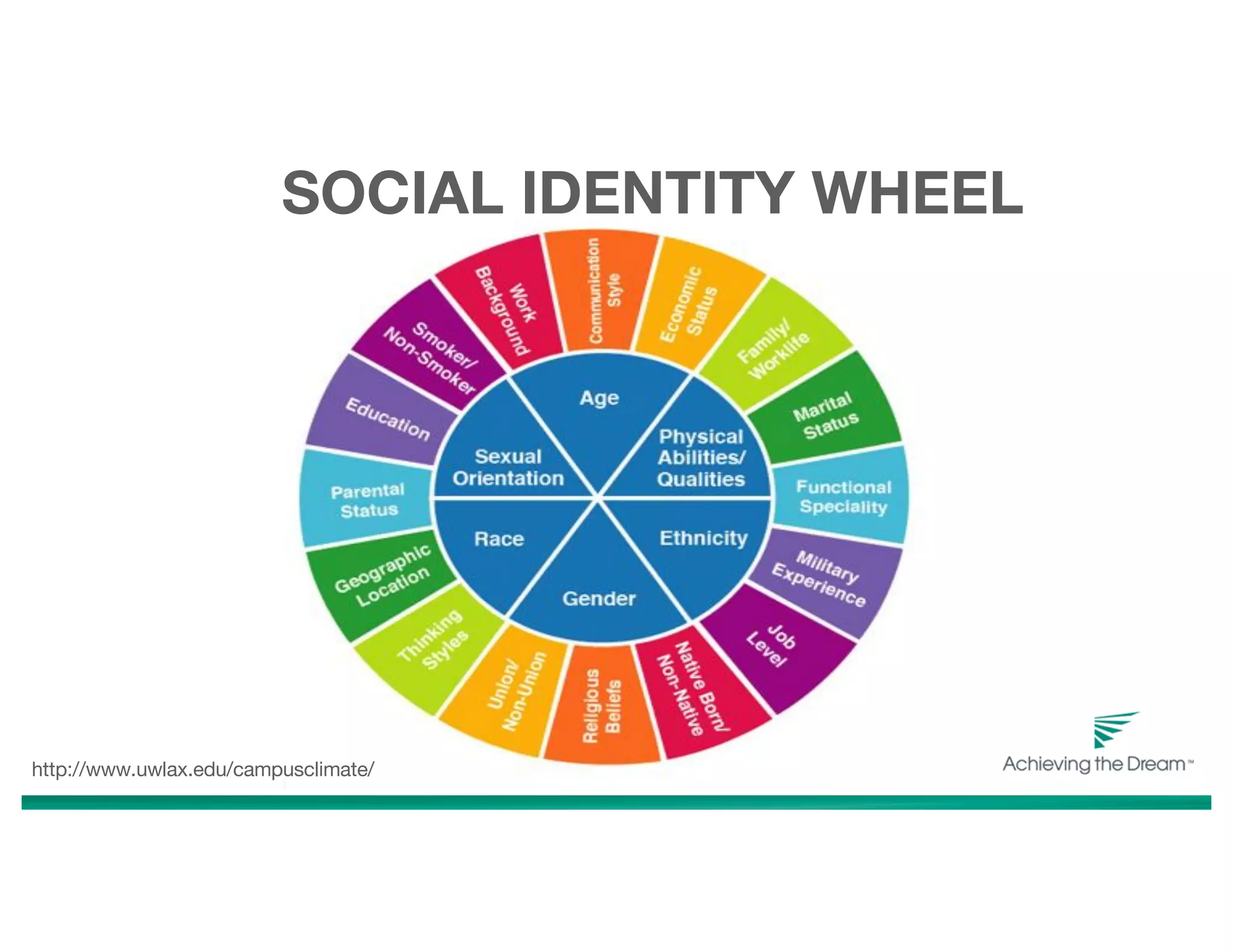
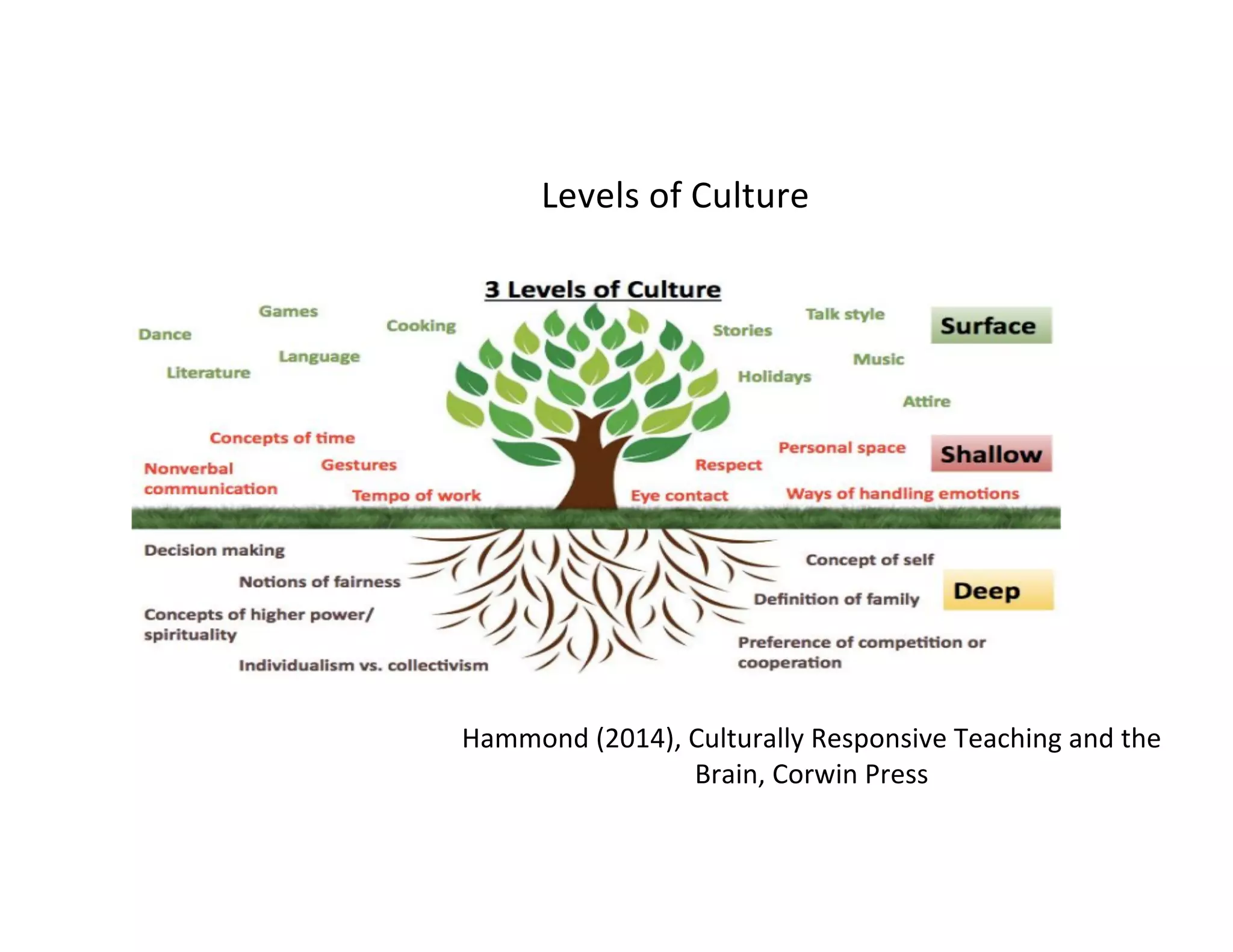
This document discusses culturally responsive teaching and learning strategies for an equitable digital learning environment. It introduces Achieving the Dream's network of over 4 million students across 40 states and outlines the goals of centering identity as a cognitive tool and visualizing strategies for equitable digital classrooms using Zaretta Hammond's framework. The framework includes four components: awareness of one's own cultural biases and student cultures; learning partnerships that empower students; information processing through connecting new concepts to student experiences; and building a community of learners through communal structures and a culture of learning.