Dmitri Popov is a radiobiologist with a PhD and MD from Russia who works for Advanced Medical Technology and Systems Inc. in Canada. His work focuses on developing countermeasures for acute radiation disease. He studies the effects of radiation exposure levels on cell death mechanisms like apoptosis and necrosis. Specifically, he examines the roles of caspase proteases and serine proteases in these cell death pathways and how inhibiting their activation after radiation exposure could help treat acute radiation syndrome.




![Acute Radiation Disease. Countermeasure Development.
Caspases, or cysteine-aspartic proteases or cysteine-
dependent aspartate-directed proteases are a family
of cysteine proteasesthat play essential roles
in apoptosis (programmed cell death), necrosis,
and inflammation.[2]
Caspases are essential in cells for apoptosis, or
programmed cell death such as Necrptosis,
in development and most other stages of adult life, and
have been termed "executioner" proteins for their roles
in the cell. Some caspases are also required in
the immune system for the maturation of lymphocytes.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acuteradiationdiseasecountermeasuredevelopment-150209130214-conversion-gate01/85/Acute-radiation-disease-countermeasure-development-5-320.jpg)


![Acute Radiation Disease. Countermeasure Development.
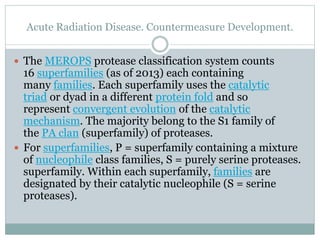
Serine proteases (or serine endopeptidases)
are enzymes that cleave peptide bonds in proteins, in
which serine serves as thenucleophilic amino acid at
the (enzyme's) active site.[1] They are found
ubiquitously in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes.
Serine proteases fall into two broad categories based
on their structure: chymotrypsin-like (trypsin-like)
or subtilisin-like.[2] In humans, they are responsible
for co-ordinating various physiological functions,
including digestion, immune response, blood
coagulation and reproduction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acuteradiationdiseasecountermeasuredevelopment-150209130214-conversion-gate01/85/Acute-radiation-disease-countermeasure-development-9-320.jpg)