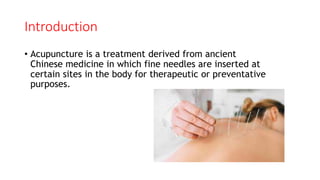
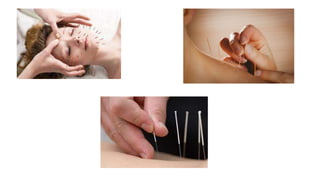
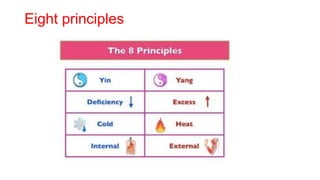
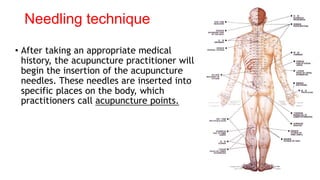
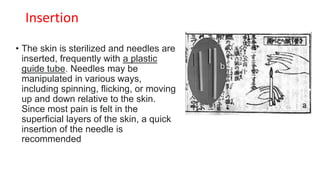
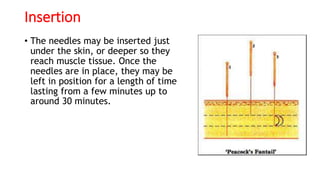
Acupuncture is an ancient Chinese practice involving inserting thin needles into specific points in the body. It is based on the belief that energy flows through meridians and balancing this energy can treat illnesses. While the mechanisms are not fully understood, acupuncture is thought to stimulate the nervous system and release chemicals that promote healing. It has been found effective for certain conditions like lower back pain and nausea. Risks are generally minor but can include pain, bleeding or fainting. Serious risks are rare with a properly trained practitioner.