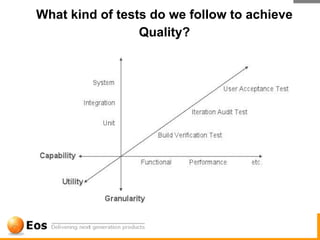
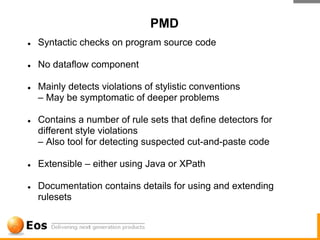
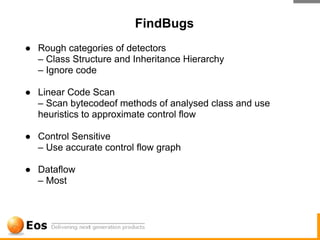
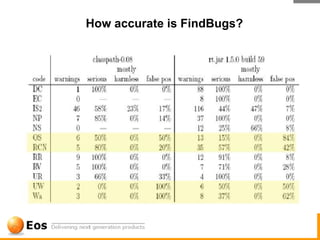
The document discusses various techniques for achieving quality in software development, including static analysis tools. It describes how bugs occur due to human errors and complex codebases, and that testing alone cannot find all bugs. It then explains static analysis tools like FindBugs and PMD that can automatically find bugs, the challenges of static analysis, distinguishing bugs from style issues, and how tools like Eclipse and EclEmma are used to fix bugs and measure test coverage. The overall goal is to reduce bugs escaping to production through efficient tooling and quality practices.