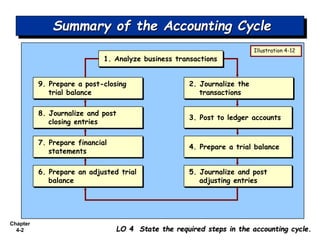
Chapter 4 outlines the accounting cycle, detailing the steps from analyzing transactions to preparing a post-closing trial balance. It emphasizes the importance of correcting entries to maintain accurate records and provides examples of correcting errors made in journalizing and posting transactions. Additionally, the chapter discusses the classification of balance sheets, focusing on organizing assets and liabilities to enhance understanding.