Recommended
PPT
PPTX
Romney_15e_accessible_fullppt_01.pptx
PPTX
Romney accounting information system ch 01
PPTX
LECTURE ONE(1) for accounting information
PPTX
ppt romney ais keren banget pokoknya keren deh
PDF
Romney_15e_accessible_fullppt_01_accessible.pdf
PPTX
romney_ais14_stppt_01.pptx_SIA week 1_upload
PPTX
PPTX
AIS Chapter 01 Overview Accounting Information System
PPTX
Accounting Information System Romney_15e_accessible_fullppt_01.pptx
PPTX
Romney Accounting Information System Ed 15
PPT
Accounting Information Systems(AIS)
PPT
AIS CH_01 Accounting Information Systems an overview.PPT
PPTX
The information system: An accountant's perspective
PPT
CH 1.ppt,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
PPT
IntroductionAccountingInformationSystems.ppt
PDF
RS_AIS_ch1.pdf - Mengenal SIA - Introduction to AIS
PPT
Accounting Information Systems; Basic Concept
PDF
(eBook PDF) AYB221 Acc Systems and Tech CB
PDF
(eBook PDF) AYB221 Acc Systems and Tech CB
PPT
Ais Romney 2006 Slides 01 Overview
PDF
(eBook PDF) AYB221 Acc Systems and Tech CB
PDF
Accounting Information Systems 13Th Chapter 1
PDF
PPT
PPT
PDF
PPT
PDF
19 January 2026 Andreas Schleicher Digital Education Outlook 2026.pdf
PPTX
Activity on Job position in Odoo 19 Recruitment
More Related Content
PPT
PPTX
Romney_15e_accessible_fullppt_01.pptx
PPTX
Romney accounting information system ch 01
PPTX
LECTURE ONE(1) for accounting information
PPTX
ppt romney ais keren banget pokoknya keren deh
PDF
Romney_15e_accessible_fullppt_01_accessible.pdf
PPTX
romney_ais14_stppt_01.pptx_SIA week 1_upload
PPTX
Similar to Accpounting for Information Systems Fraud Error
PPTX
AIS Chapter 01 Overview Accounting Information System
PPTX
Accounting Information System Romney_15e_accessible_fullppt_01.pptx
PPTX
Romney Accounting Information System Ed 15
PPT
Accounting Information Systems(AIS)
PPT
AIS CH_01 Accounting Information Systems an overview.PPT
PPTX
The information system: An accountant's perspective
PPT
CH 1.ppt,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
PPT
IntroductionAccountingInformationSystems.ppt
PDF
RS_AIS_ch1.pdf - Mengenal SIA - Introduction to AIS
PPT
Accounting Information Systems; Basic Concept
PDF
(eBook PDF) AYB221 Acc Systems and Tech CB
PDF
(eBook PDF) AYB221 Acc Systems and Tech CB
PPT
Ais Romney 2006 Slides 01 Overview
PDF
(eBook PDF) AYB221 Acc Systems and Tech CB
PDF
Accounting Information Systems 13Th Chapter 1
PDF
PPT
PPT
PDF
PPT
Recently uploaded
PDF
19 January 2026 Andreas Schleicher Digital Education Outlook 2026.pdf
PPTX
Activity on Job position in Odoo 19 Recruitment
PPTX
Accounting Theory Group Presentation - Why Study Accounting Theory
PDF
Types of Artificial Intelligence: Capabilities and Functionality Explained
PDF
BÀI GIẢNG POWERPOINT CHÍNH KHÓA PHIÊN BẢN AI TIẾNG ANH 6 CẢ NĂM, THEO TỪNG BÀ...
PDF
GIÁO ÁN KẾ HOẠCH BÀI DẠY NĂNG LỰC SỐ MÔN TIẾNG ANH LỚP 11 CẢ NĂM - GLOBAL SUC...
PPTX
special senses-eye, ear, nose, tongue.pptx
PPTX
How to create Article in Odoo 18 Knowledge App
PPTX
NMR Spectroscopy: Principles and Applications
PPTX
Contract Act 1872 - Sections 10, 11 13-by Judge Nazmul Hasan.pptx
PPTX
Insertion of Suppositories..........pptx
PPTX
ANTISEPTICS AND DISINFECTANTS CHAPTER NO.05.pptx
PDF
Geography unit 7-Population-Distribution`.pdf
PDF
ĐỀ MINH HỌA KỲ THI TỐT NGHIỆP TRUNG HỌC PHỔ THÔNG NĂM 2026 MÔN TIẾNG ANH 2026...
PPTX
The Creation Pattern Physical Health.pptx
PPTX
VITAMINS CHAPTER NO.05 PHARMACOGNOSY D. PHARMACY
PPTX
Pneumonia, Social and Preventive Pharmacy .pptx
PPTX
YSPH VMOC Special Report - Measles - The Americas 1-18-2026
PDF
RPT FORM 1 English (2026 academic session) SMKTS.pdf
PPTX
Nanomaterials and its types - Dr.M.Jothimuniyandi
Accpounting for Information Systems Fraud Error 1. 2. Learning Objectives
Distinguish between data and information.
Discuss the characteristics of useful information.
Explain how to determine the value of information.
Explain the decisions an organization makes and the information needed to make them.
Identify the information that passes between internal and external parties and an AIS.
Describe the major business processes present in most companies.
Explain what an accounting information system (AIS) is and describe its basic functions.
Discuss how an AIS can add value to an organization.
Explain how an AIS and corporate strategy affect each other.
Explain the role an AIS plays in a company’s value chain.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 1-2
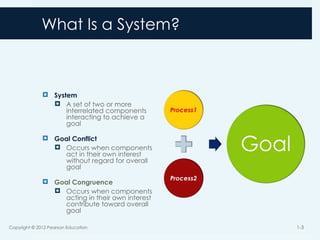
3. What Is a System?
System
A set of two or more
interrelated components
interacting to achieve a
goal
Goal Conflict
Occurs when components
act in their own interest
without regard for overall
goal
Goal Congruence
Occurs when components
acting in their own interest
contribute toward overall
goal
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 1-3
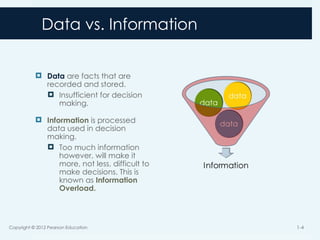
4. Data vs. Information
Data are facts that are
recorded and stored.
Insufficient for decision
making.
Information is processed
data used in decision
making.
Too much information
however, will make it
more, not less, difficult to
make decisions. This is
known as Information
Overload.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 1-4
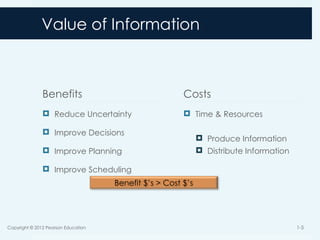
5. Value of Information
Benefits
Reduce Uncertainty
Improve Decisions
Improve Planning
Improve Scheduling
Costs
Time & Resources
Produce Information
Distribute Information
1-5
Benefit $’s > Cost $’s
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education
6. What Makes Information Useful?
Necessary characteristics:
Relevant
“The capacity of information to make a difference in a
decision by helping users to form predictions about the
outcomes of past, present, and future events or to
confirm or correct prior expectations.”
Reliable
“The quality of information that assures that information is
reasonably free from error and bias and faithfully
represents what it purports to represent.”
Complete
“The inclusion in reported information of everything
material that is necessary for faithful representation of the
relevant phenomena.”
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 1-6
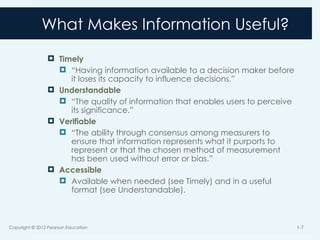
7. What Makes Information Useful?
Timely
“Having information available to a decision maker before
it loses its capacity to influence decisions.”
Understandable
“The quality of information that enables users to perceive
its significance.”
Verifiable
“The ability through consensus among measurers to
ensure that information represents what it purports to
represent or that the chosen method of measurement
has been used without error or bias.”
Accessible
Available when needed (see Timely) and in a useful
format (see Understandable).
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 1-7
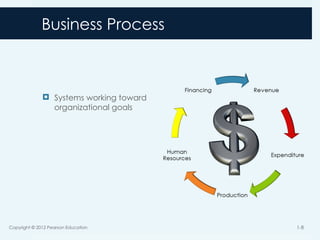
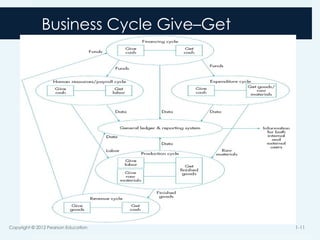
8. 9. Business Process Cycles
Revenue
Expenditure
Production
Human Resources
Financing
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 1-9
10. 11. 12. Accounting Information Systems
Collect, process, store, and report data and information
If Accounting = language of business
AIS = information providing vehicle
Accounting = AIS
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 1-12
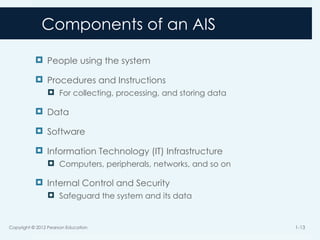
13. Components of an AIS
People using the system
Procedures and Instructions
For collecting, processing, and storing data
Data
Software
Information Technology (IT) Infrastructure
Computers, peripherals, networks, and so on
Internal Control and Security
Safeguard the system and its data
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 1-13
14. AIS and Business Functions
Collect and store data about organizational:
Activities, resources, and personnel
Transform data into information enabling
Management to:
Plan, execute, control, and evaluate
Activities, resources, and personnel
Provide adequate control to safeguard
Assets and data
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 1-14
15. AIS Value Add
Improve Quality and Reduce Costs
Improve Efficiency
Improve Sharing Knowledge
Improve Supply Chain
Improve Internal Control
Improve Decision Making
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 1-15
16. Improve Decision Making
Identify situations that require action.
Provide alternative choices.
Reduce uncertainty.
Provide feedback on previous decisions.
Provide accurate and timely information.
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 1-16
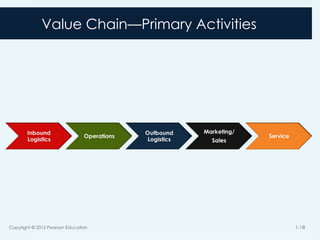
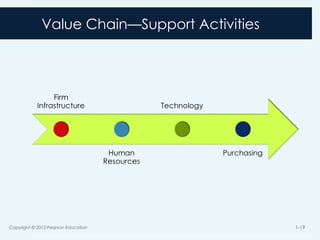
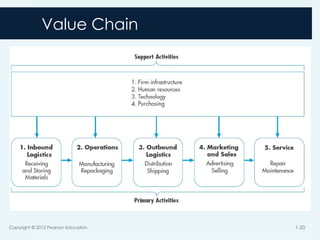
17. Value Chain
The set of activities a product or service moves along
before as output it is sold to a customer
At each activity the product or service gains value
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 1-17
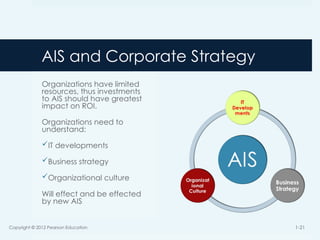
18. 19. 20. 21. AIS and Corporate Strategy
Organizations have limited
resources, thus investments
to AIS should have greatest
impact on ROI.
Organizations need to
understand:
IT developments
Business strategy
Organizational culture
Will effect and be effected
by new AIS
Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education 1-21
Editor's Notes #6 Point out to students that these characteristics are from the SFAC #2 Quality of Accounting Information (maybe have them read it). http://www.fasb.org/pdf/aop_CON2.pdf #7 Point out to students that these characteristics are from the SFAC #2 Quality of Accounting Information (maybe have them read it).