Accounting in practical life
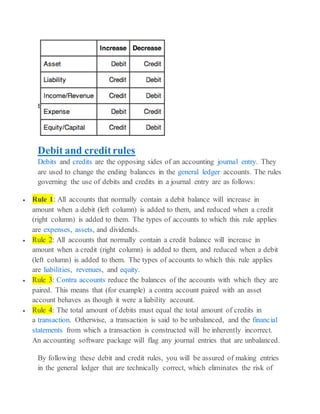
- 1. Debit and creditrules Debits and credits are the opposing sides of an accounting journal entry. They are used to change the ending balances in the general ledger accounts. The rules governing the use of debits and credits in a journal entry are as follows: Rule 1: All accounts that normally contain a debit balance will increase in amount when a debit (left column) is added to them, and reduced when a credit (right column) is added to them. The types of accounts to which this rule applies are expenses, assets, and dividends. Rule 2: All accounts that normally contain a credit balance will increase in amount when a credit (right column) is added to them, and reduced when a debit (left column) is added to them. The types of accounts to which this rule applies are liabilities, revenues, and equity. Rule 3: Contra accounts reduce the balances of the accounts with which they are paired. This means that (for example) a contra account paired with an asset account behaves as though it were a liability account. Rule 4: The total amount of debits must equal the total amount of credits in a transaction. Otherwise, a transaction is said to be unbalanced, and the financial statements from which a transaction is constructed will be inherently incorrect. An accounting software package will flag any journal entries that are unbalanced. By following these debit and credit rules, you will be assured of making entries in the general ledger that are technically correct, which eliminates the risk of
- 2. having an unbalanced trial balance. However, just following the rules does not guarantee that the resulting entries will be correct in substance, since that also requires a knowledge of how to record transactions within the applicable accounting framework (such as Generally Accepted Accounting Principles or International Financial Reporting Standards). What is a 'DrawingAccount' A drawing account is an accounting record maintained to track money withdrawn from a business by its owners. Drawing Entry : Drawing account (Dr) To cash account (Cr ) Capital Capital is the money or wealth needed to produce goods and services. In the most basic terms, it is money. All businesses must have capital in order to purchase assets and maintain their operations. Business capital comes in two main forms: debt and equity. Cost Accounting The systematic recording and analysis of the costs of material, labor, and overhead incident to production ADVANCED ACCOUNTING ADVANCED ACCOUNTING covers accounting operations, patterns, merger of public holding companies, foreign currency operations, changing financial statement prepared in foreign and local currencies. Advanced accounting also includes a variety of advanced financial accounting issues such as lease contracts, pension funds, end of service severance
- 3. investment The action or process of investing money for profit. Investment An investment is a payment made to acquire the securities of other entities, with the objective of earning a return. Examples are bonds, common stock, and preferred stock. There are two ways to earn a return on an investment, which are from ongoing payments issued by the investment or through the appreciation in value of the asset. The concept can also mean the acquisition of fixed assets for internal use, also with the objective of earning a return. This type of investment is much more likely to generate returns through positive cash flows, rather than through appreciation. Payroll A payroll is a company's list of its employees, but the term is commonly used to refer to: the total amount of money that a company pays to its employees a company's records of its employees' salaries What is a Trial Balance Trial Balance is a list of closing balances of ledger accounts on a certain date and is the first step towards the preparation of financial statements *************************** OR
- 4. What is a Trial Balance After posting all financial transactions to the accounting journals and summarizing them in the general ledger,a trial balance is prepared to verify that the debits equal the credits on the chart of accounts. The trial balance is the next step in the accounting cycle. It is actually the first step in the "end of the accounting period" process. ( B/d & B/f ) & ( C/d & C/f. ) The starting balance is b/d & b/f and for the ending balance is c/d & c/f. B/f means Brought Forward C/f means Carried Forward C/d means Carried Downward B/d means Brought Downward B/d :When youstart any account with the balance from - - previous month or - thatappearing immediately above, C/d : When youtotal-upthedebit&creditsidesofan account&put thedifferenceontheshorterside, so as to agreethetotals,you mention thedifferenceas c/d(balancecarried-down), ifit is to be carriedforward to - - nextmonth or - a line belowin thesame page
- 5. What is 'Authorized Share Capital' Authorized share capital is the number of stockunits that a company can issue as stated in its memorandum of associationor its articles of incorporation. Authorized share capital is oftennot fully used by management in order to leave room for future issuance of additional stock in case the companyneeds to raise capital quickly. Another reason to keep shares in the company treasury is to retain a controlling interest in the company. WHO WAS THE FIRST ACCOUNTANT? Ans. Pacioli was the Father of Accounting . Top Ten Famous Accountants 1. John Grisham 2. Kenny G. 3. Bob Newhart 4. Gibby Haynes 5. Tim DuBois 6. Walter Diemer 7. J. P. Morgan 8. Walter L. Morgan 9. Arthur Blank 10. Josiah Wedgewood
- 6. Memorandum & Articles Of Association The memorandum and articles of association are the governing documents of a company and it is essential that the documents correctly reflect the objectives of the company. Memorandum Of Association The memorandum of association is the main document by which the registration of a company is achieved and the provisions contained within the memorandum will prevail over any conflicting provisions contained in the articles of association. The memorandum of association has five compulsory clauses: The name clause; The object’s clause; The liability clause; The capital clause; and The subscription clause. Alteration Of TheMemorandum Of Association The memorandum of a company may not be altered, except in cases for which the method and extent is provided for in the Companies Act 1963. Given this, each clause should be reviewed distinctly in respect of the authorised method of alteration. Articles Of Association The articles of association binds a company with its members and contains a company’s internal rules and regulations. The provisions contained in Table A of the First Schedule of the Companies Act 1963 apply to companies unless they are altered or excluded by the articles of association. The model articles contained in Table A are inappropriate for many private companies and the majority of companies will adopt a modified version of Table A as their articles. Alteration Of The Articles Of Association The articles may be amended by the passing of a special resolution of the company. A company has a positive power to alter its articles but there are four notable restrictions on the members’ right to alter a company’s articles by special resolution: Where the alteration is contrary to law; Where an additional liability is imposed on the members; Where class rights are altered; and Where the articles have been amended and the members did not act bona fide and in the interests of the company as a whole.
- 7. The New Companies Bill The new Companies Bill in Ireland was distributed on 21 December 2012 by Minister for Jobs, Enterprise and Innovation, Richard Bruton TD. The Companies Bill outlines numerous proposed changes which will transform current Irish company law. With regards to the memorandum and articles of association, the new Companies Bill has proposed the following; Companies will have a one-document constitution, rather than a memorandum and articles of association; Companies will no longer be required to have an objects clause making it easier to transact business with confidence with private companies. Reflecting The Company Agenda The directors and the members of a company should be familiar with the memorandum & articles and should refer to them when required. It should be remembered that the memorandum & articles of association are important constitutional documents of a company and should be amended to reflect the current agenda of a company as it evolves and develops. Director Of a Company A director is a person from a group of managers who leads or supervises a particular area of a company, program, or project. Companies that use this term often have many directors spread throughout different business functions or roles. Manager A person responsible for controlling or administering an organization or group of staff inward clearing & outward clearing EXAMPLE Whenwe receive inward clearing we have to debitour customeraccount and when we receive outward clearing we have to send it to relevant bank for payment. For example: A cheque drawn on “HBL” depositedin “MCB” bank is an outward cheque for “MCB” & is an inward for“HBL”
- 8. Qoutes “Failureis the condiment that givessuccessits flavor.” ― Truman Capote “It is hard to fail, but it is worse never to have tried to succeed.” “Failure is the key to Success” “You can’t let your failures define you. You have to let your failures teach you.” » Barack Obama “Failing to prepare is preparing to fail.” » John Wooden Perseverance is failing 19 times and succeeding the 20th. If you're not failing every now and again, it's a sign you're not doing anything very innovative
- 9. Voucher definition A voucher is an internal document describing and authorizing the payment of a liability to a supplier. It is most commonly used in a manual payment system. A voucher typically contains the following information: The identification number of the supplier The amount to be paid The date on which payment should be made The accounts to be charged to record the liability Any applicable early payment discount terms An approval signature or stamp Types of Vouchers 1. Cash Vouchers For all cash transactions, cash voucher is prepared. There are tw o types of cash voucher. A) Debit Voucher for Cash Payment We prepared debit voucher for all type of cash payment. Follow ing are the main payments w hose w ill record in debit voucher for cash payments. a) For paying cash expenses b) For paying the bill of buying of goods. c) For payment of investment d) For payment to creditors e) For depositing money in bank
- 10. B) Credit Voucher for Cash Receipts Credit voucher is also part of cash voucher in w hich w e w rite only cash receipt of each transaction Follow ing are main receipt a) For receipt of income b) Cash received from sales c) Cash sale of investment d) Cash from sale of fixed assets e) Cash received from our debtors What is the difference between an invoice and a voucher? An invoice from a vendor is the bill that is received by the purchaser of goods or services froman outside supplier. The vendor invoice lists the quantities of items, brief descriptions, prices, total amount due, credit terms, whereto remit payment, etc. A voucher is an internal document used in a company's accounts payable department in order to collect and organizethe necessary documentation and approvals beforepaying a vendor invoice. The voucher acts as a cover page to which the following will be attached: vendor invoice, company's purchaseorder, company's receiving report, and other information needed to process the vendor invoice for payment.
- 11. Basic accounting terms, acronyms, abbreviations and concepts to remember Check out these basic accounting terms and start to commit them to memory. That way, when you start your degree journey, you’ll already feel like you’re a step ahead and speaking the language. 1.Accounts receivable (AR) Accounts receivable (AR) definition: The amount of money owed by customers or clients to a business after goods or services have been delivered and/or used. 2. Accounting (ACCG) Accounting (ACCG) definition: A systematic way of recording and reporting financial transactions for a business or organization. 3.Accounts payable (AP) Accounts payable (AP) definition: The amount of money a company owes creditors (suppliers, etc.) in return for goods and/or services they have delivered. 4. Assets (fixed and current) (FA, CA Assets (fixed and current) definition: Current assets (CA) are those that will be converted to cash within one year. Typically, this could be cash, inventory or accounts receivable. Fixed assets (FA) are long-term and will likely provide benefits to a company for more than one year, such as a real estate, land or major machinery. 5. Asset classes Asset class definition: An asset class is a group of securities that behaves similarly in the marketplace. The three main asset classes are equities or stocks, fixed income or bonds, and cash equivalents or money market instruments. 6. Balance sheet (BS) Balance sheet (BS) definition: A financial report that summarizes a company's assets (what it owns), liabilities (what it owes) and owner or shareholder equity at a given time. 7. Capital (CAP) Capital (CAP) definition: A financial asset or the value of a financial asset, such as cash or goods. Working capital is calculated by taking your current assets subtracted from current liabilities—basically the money or assets an organization can put to work. 8. Cash flow (CF)
- 12. Cash flow (CF) definition: The revenue or expense expected to be generated through business activities (sales, manufacturing, etc.) over a period of time. 9. Certified public accountant (CPA) Certified public accountant (CPA) definition: Adesignation given to an accountant who has passed a standardized CPA exam and met government-mandated work experience and educational requirements to become a CPA. 10. Cost of goods sold (COGS) Cost of goods sold (COGS) definition: The direct expenses related to producing the goods sold by a business. The formula for calculating this will depend on what is being produced, but as an example this may include the cost of the raw materials (parts) and the amount of employee labor used in production. 11. Credit (CR) Credit (CR) definition: An accounting entry that may either decrease assets or increase liabilities and equity on the company's balance sheet, depending on the transaction. When using the double-entry accounting method there will be two recorded entries for every transaction: A credit and a debit. 12. Debit (DR) Debit (DR) definition: An accounting entry where there is either an increase in assets or a decrease in liabilities on a company's balance sheet. 13. Diversification Diversification definition: The process of allocating or spreading capital investments into varied assets to avoid over-exposure to risk. 14. Enrolled agent (EA) Enrolled agent (EA) definition: A tax professional who represents taxpayers in matters where they are dealing with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). 15. Expenses (fixed, variable, accrued, operation) (FE, VE, AE, OE) Expenses (FE, VE, AE, OE) definition: The fixed, variable, accrued or day-to-day costs that a business may incur through its operations. Fixed expenses(FE):payments like rent that will happen in a regularly scheduled cadence. Variable expenses (VE): expenses,like labor costs, that may change in a given time period. Accrued expense (AE): an incurred expense that hasn’t been paid yet. Operation expenses (OE): Business expenditures not directly associated with the production of goods or services—for example, advertising costs, property taxes or insurance expenditures.
- 13. 16. Equity and owner's equity (OE) Equity and owner's equity (OE) definition: In the most general sense, equity is assets minus liabilities. An owner’s equity is typically explained in terms of the percentage of stock a person has ownership interest in the company. The owners of the stock are known as shareholders. 17. Insolvency Insolvency definition: A state where an individual or organization can no longer meet financial obligations with lender(s) when their debts come due. 18. Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP)definition: Aset of rules and guidelines developed by the accounting industry for companies to follow when reporting financial data. Following these rules is especially critical for all publicly traded companies. 19. General ledger (GL) General ledger (GL) definition: A complete record of the financial transactions over the life of a company. 20. Trial balance Trial balance definition: A business document in which all ledgers are compiled into debit and credit columns in order to ensure a company’s bookkeeping system is mathematically correct. 21. Liabilities (current and long-term) (CL, LTL) Liabilities (current and long-term) definition: Acompany's debts or financial obligations incurred during business operations. Current liabilities (CL) are those debts that are payable within a year, such as a debt to suppliers. Long-term liabilities (LTL) are typically payable over a period of time greater than one year. An example of a long-term liability would be a multi-year mortgage for office space. 22. Limited liability company (LLC) Limited liability company (LLC) definition: An LLC is a corporate structure where members cannot be held accountable for the company’s debts or liabilities. This can shield business owners from losing their entire life savings if, for example, someone were to sue the company. 23. Net income (NI) Net income (NI) definition: A company's total earnings, also called net profit. Net income is calculated by subtracting total expenses from total revenues.
- 14. 24. Present value (PV) Present value (PV) definition: The current value of a future sum of money based on a specific rate of return. Present value helps us understand how receiving $100 now is worth more than receiving $100 a year from now, as money in hand now has the ability to be invested at a higher rate of return. See an example of the time value of money here. 25. Profit and loss statement (P&L) Profit and loss statement (P&L) definition: Afinancial statement that is used to summarize a company’s performance and financial position by reviewing revenues, costs and expenses during a specific period of time, such as quarterly or annually. 26. Return on investment (ROI) Return on investment (ROI) definition: A measure used to evaluate the financial performance relative to the amount of money that was invested. The ROI is calculated by dividing the net profit by the cost of the investment. The result is often expressed as a percentage. See an example here.