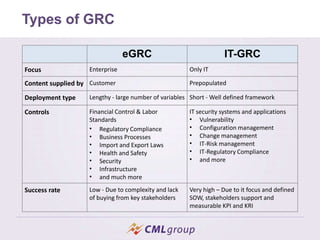
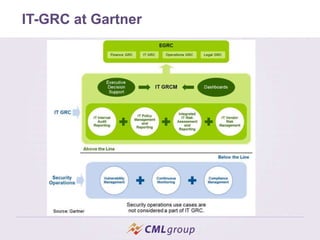
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) is an integrated approach for organizations to adhere to established guidelines across these categories, heavily influenced by events like the Enron scandal. It encompasses various components like IT-GRC, which focuses on IT-specific needs, and emphasizes the importance of effective risk management to enhance market value and protect reputations. Deploying an IT-GRC management system improves workflow management, compliance handling, and reporting efficiency.