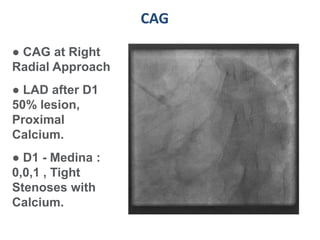
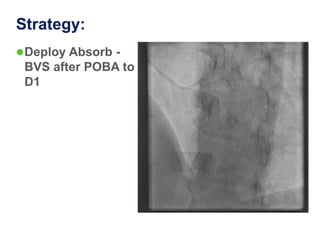
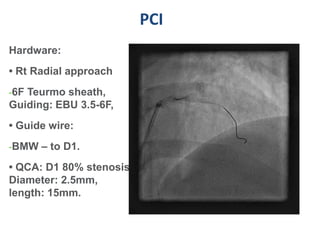
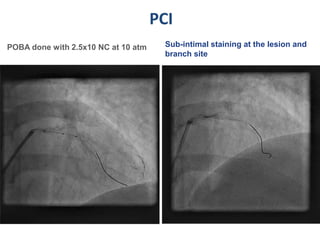
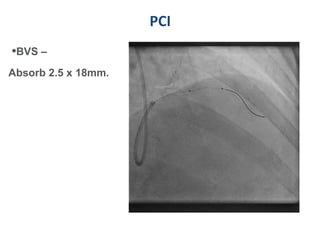
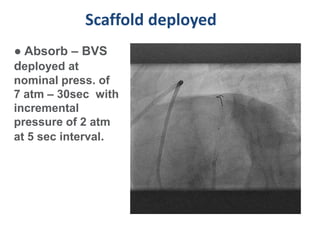
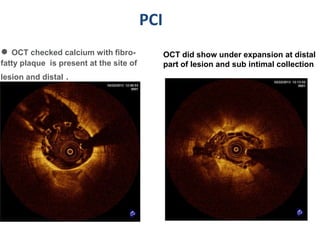
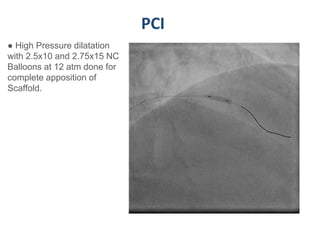
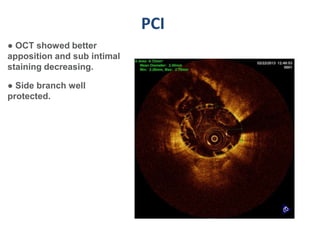
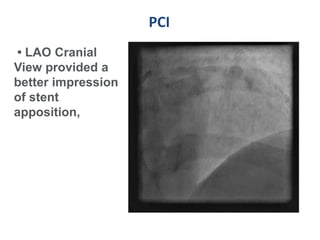
A 55-year-old male with diabetes and previous coronary artery disease underwent coronary angiography (CAG) which showed 50% lesion in the left anterior descending artery and a tight stenosis with calcium in the D1 branch. Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) was performed on the D1 branch with balloon angioplasty followed by deployment of an Absorb bioresorbable vascular scaffold (BVS). Optical coherence tomography (OCT) showed under expansion of the distal part of the scaffold. High pressure balloon dilatation was then performed to achieve complete apposition, which OCT confirmed along with decreased subintimal staining. The message conveyed is that BVS require proper preparation for calcific lesions, high pressure ballooning