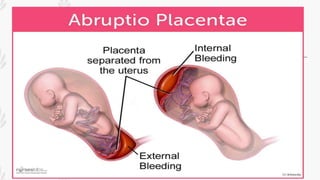
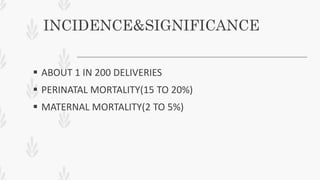
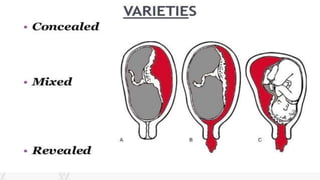
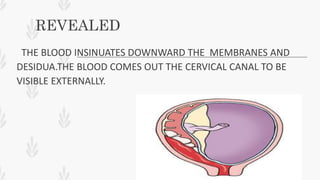
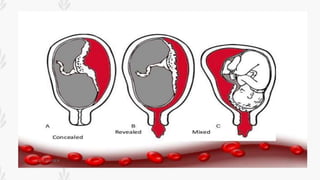
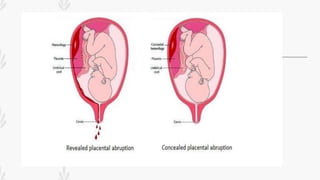
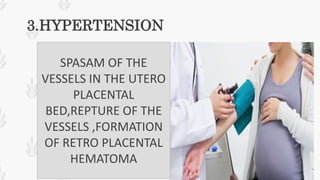
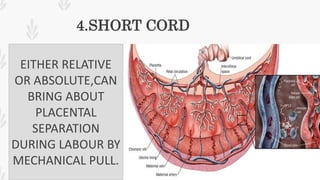
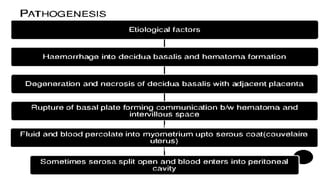
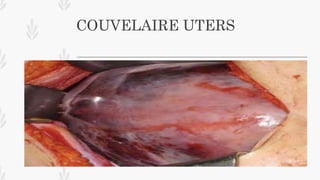
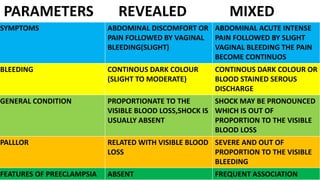
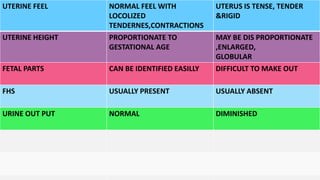
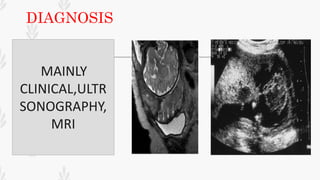
This document discusses abruption placentae, which is premature separation of a normally situated placenta, causing bleeding. It has an incidence of about 1 in 200 deliveries. It can be revealed, concealed, or mixed. Risk factors include high birth order, advancing age, hypertension, and trauma. Clinical features depend on whether it is revealed, concealed, or mixed. Diagnosis is mainly clinical with ultrasound and labs. Management includes prevention, emergency measures like IV fluids and blood, and either immediate delivery, managing complications, or expectant management depending on the situation. Nursing interventions address pain management, fluid volume deficit, ineffective tissue perfusion, risk of anemia and infection, and fetal hypoxia.