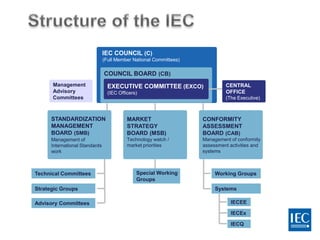
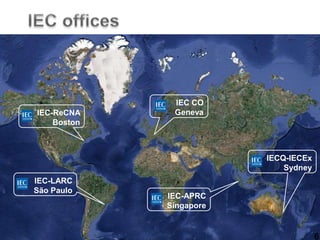
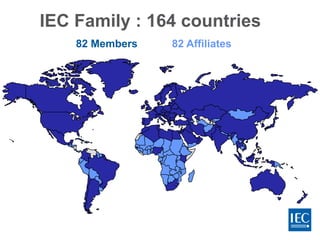
The IEC is a non-governmental organization founded in 1906 to promote international cooperation in electrotechnical standardization. It has over 12,500 experts from industries, governments, and other stakeholders in over 174 technical committees and 1,200 working groups developing over 6,900 international standards. The IEC works with 82 member countries and 82 affiliate countries through national committees to develop standards that facilitate international trade, improve safety and performance, and provide benefits such as reduced costs, access to new markets, and a competitive advantage.

















![ Putting our products into context: “Recognizing the
important contribution that international standards
and conformity assessment systems can make in
this regard by improving efficiency of production
and facilitating the conduct of international trade. . .”
“Members shall use [international standards] as a
basis for their technical regulations....”
“Members shall play a full part...in the
preparation...of international standards....”
WTO TBT Agreement](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/abouttheiec-online-130628061747-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-IEC-21-320.jpg)

