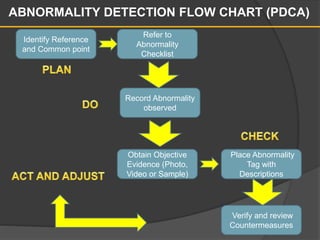
This document discusses abnormality tagging to identify issues that can lead to inefficiencies in the workplace. It defines abnormalities as undesirable anomalies that can cause performance variations, damage, quality and production problems. Abnormalities can be detected using the senses and by closely observing equipment. Techniques for tagging abnormalities include using checklists, mapping, and photographing issues. Examples of common low-hanging fruit abnormalities include missing or loose parts, unusual sounds or vibrations, safety hazards, and dirt/grime buildup. The goal of tagging abnormalities is to improve equipment performance, maintenance, and quality.