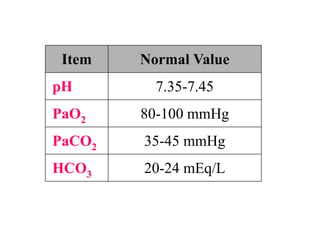
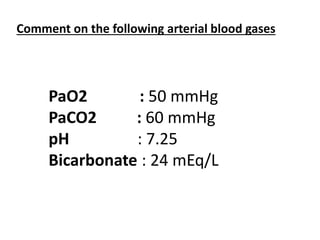
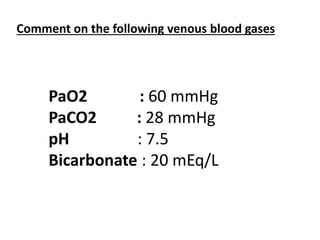
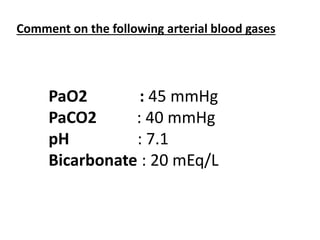
This document discusses acid-base balance and blood gas values. It notes that carbon dioxide (CO2) is the main acid and bicarbonate (HCO3) is the main alkali in the body. The lungs control PaCO2 and the kidneys control HCO3 to regulate acid-base balance. Normal blood gas values and interpretations for oxygenation, ventilation, and acid-base status are provided based on PaO2, PaCO2, pH, and HCO3 levels. Several blood gas results are presented and solicits the reader to comment on acid-base and oxygenation status for each.