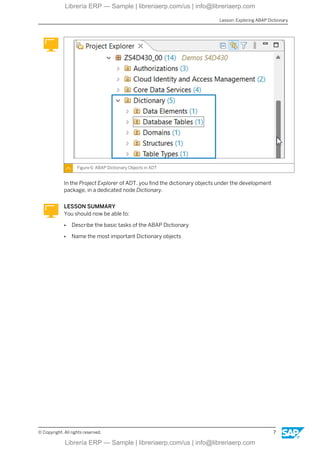
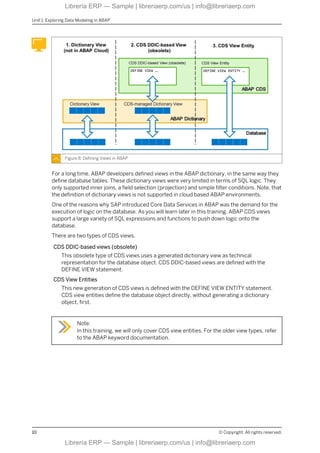
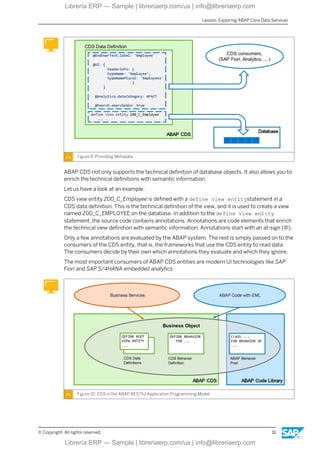
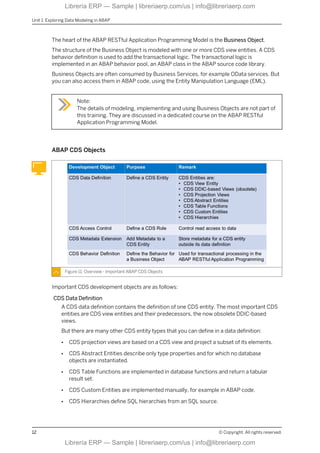
This eBook offers a focused exploration into data modeling within the ABAP environment, using the ABAP Dictionary and Core Data Services (CDS). It guides readers through defining database tables, global types, and CDS views, including relationships and associations. With insights into performance-enhancing practices like code pushdown, this content is ideal for developers and technical consultants seeking to master data structure creation and optimization in SAP BTP.