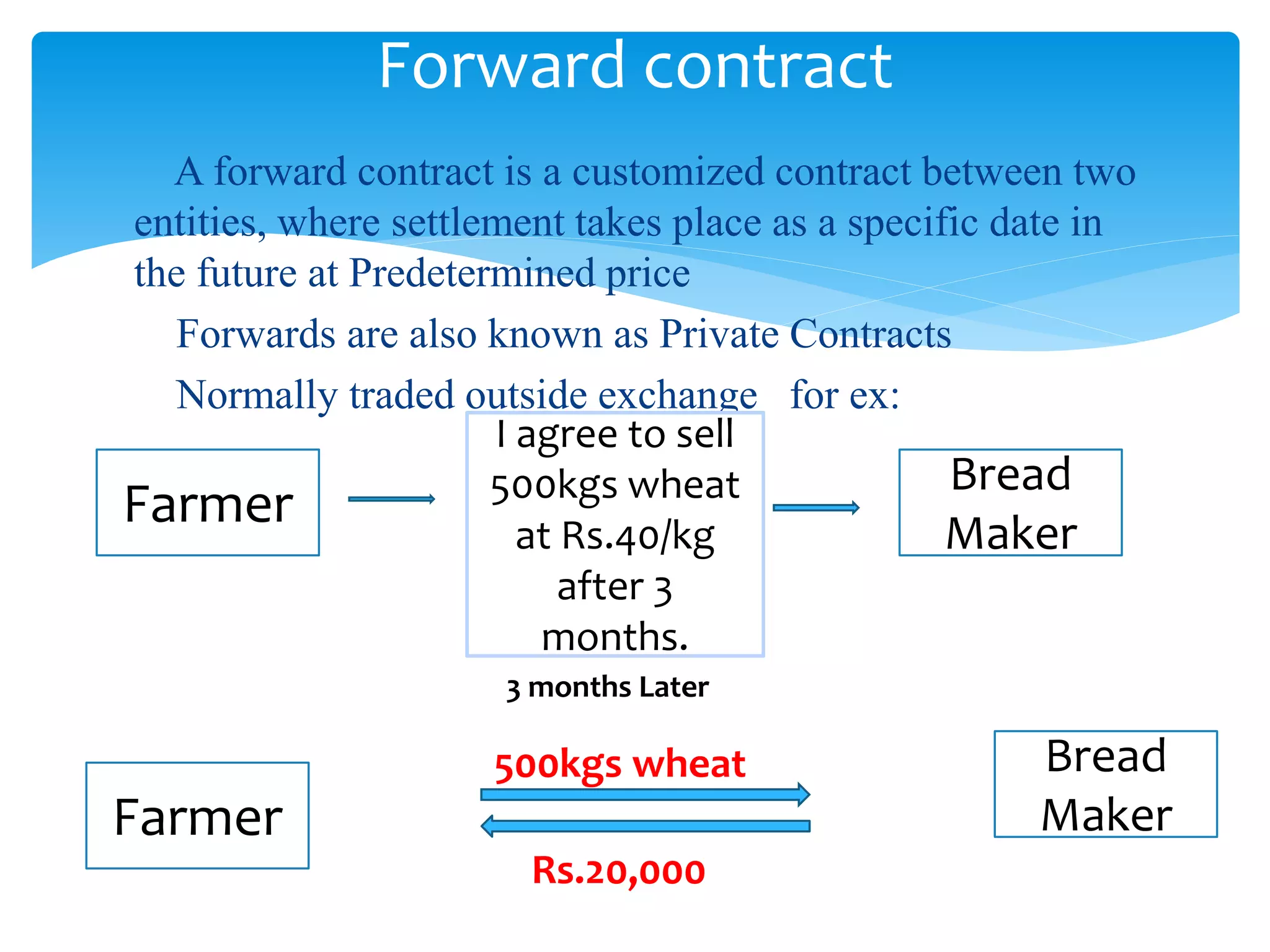
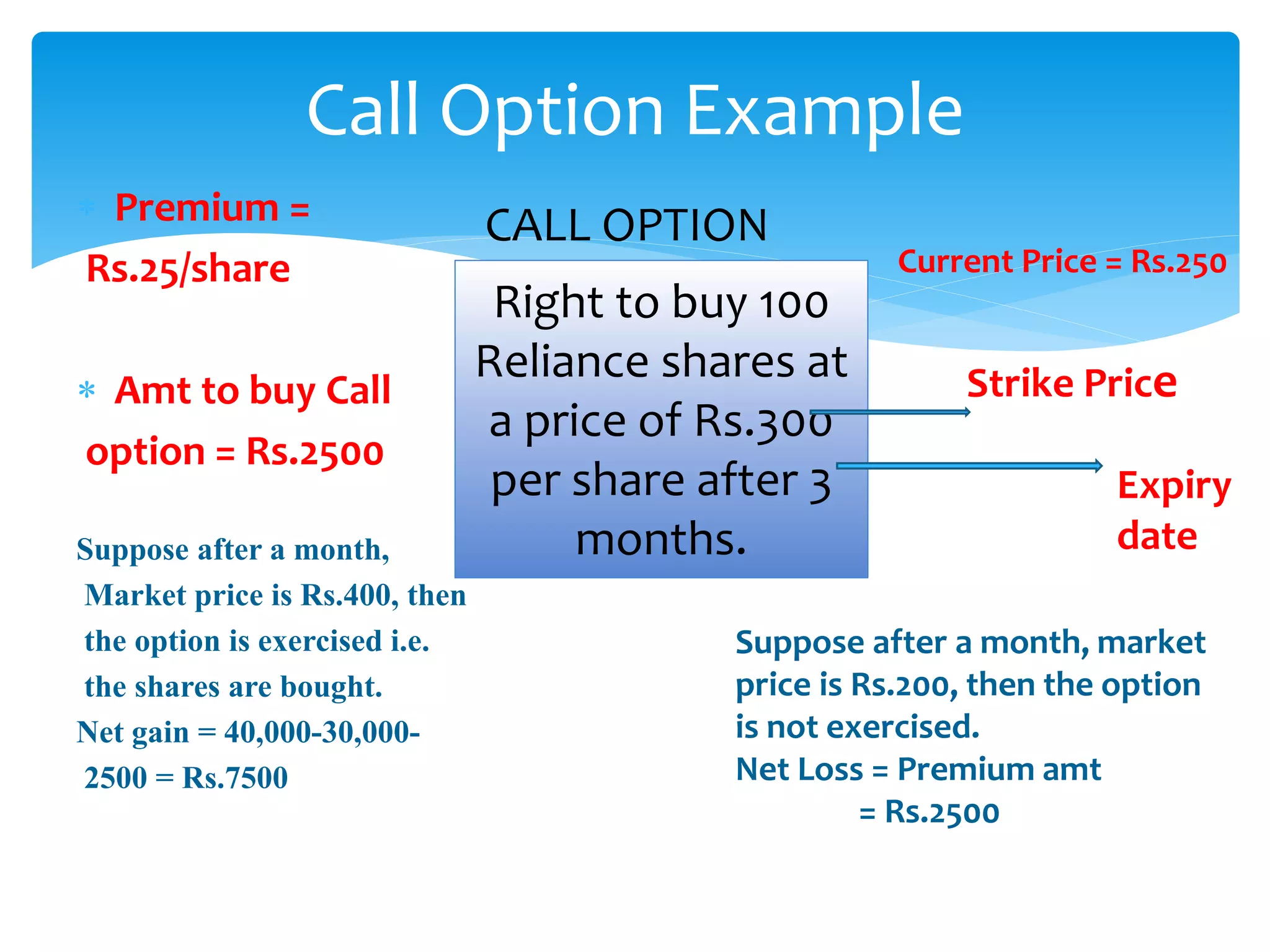
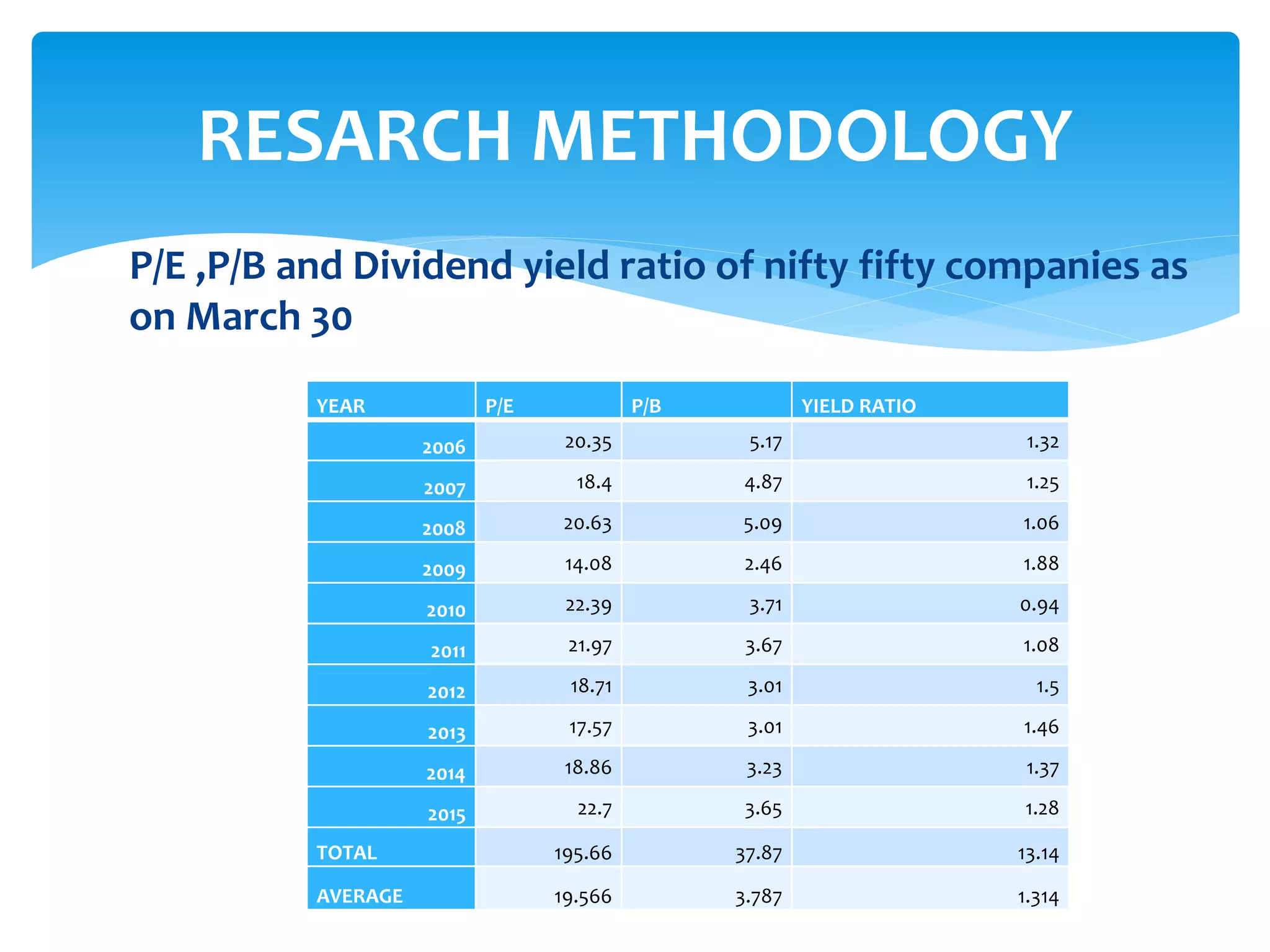
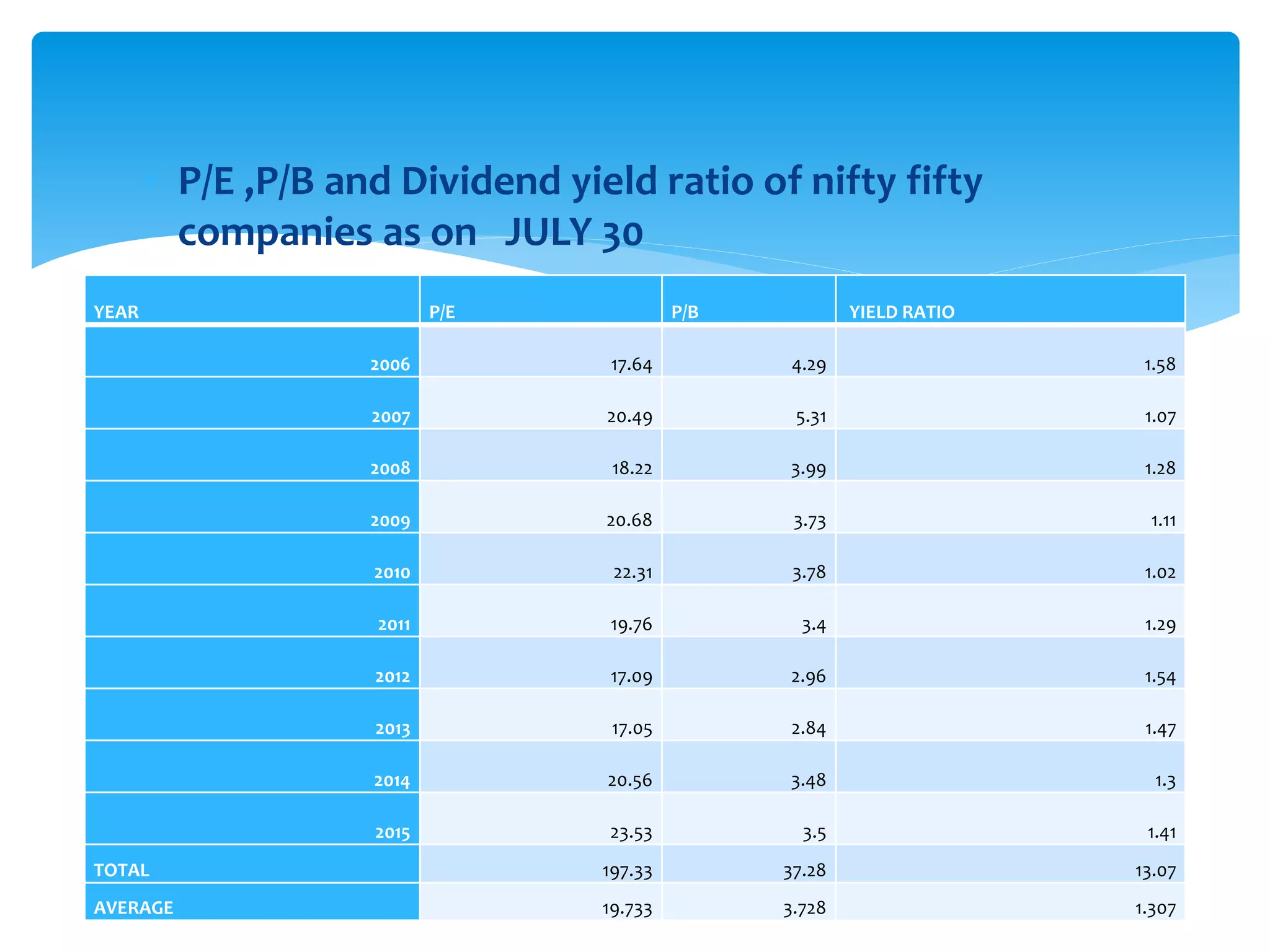
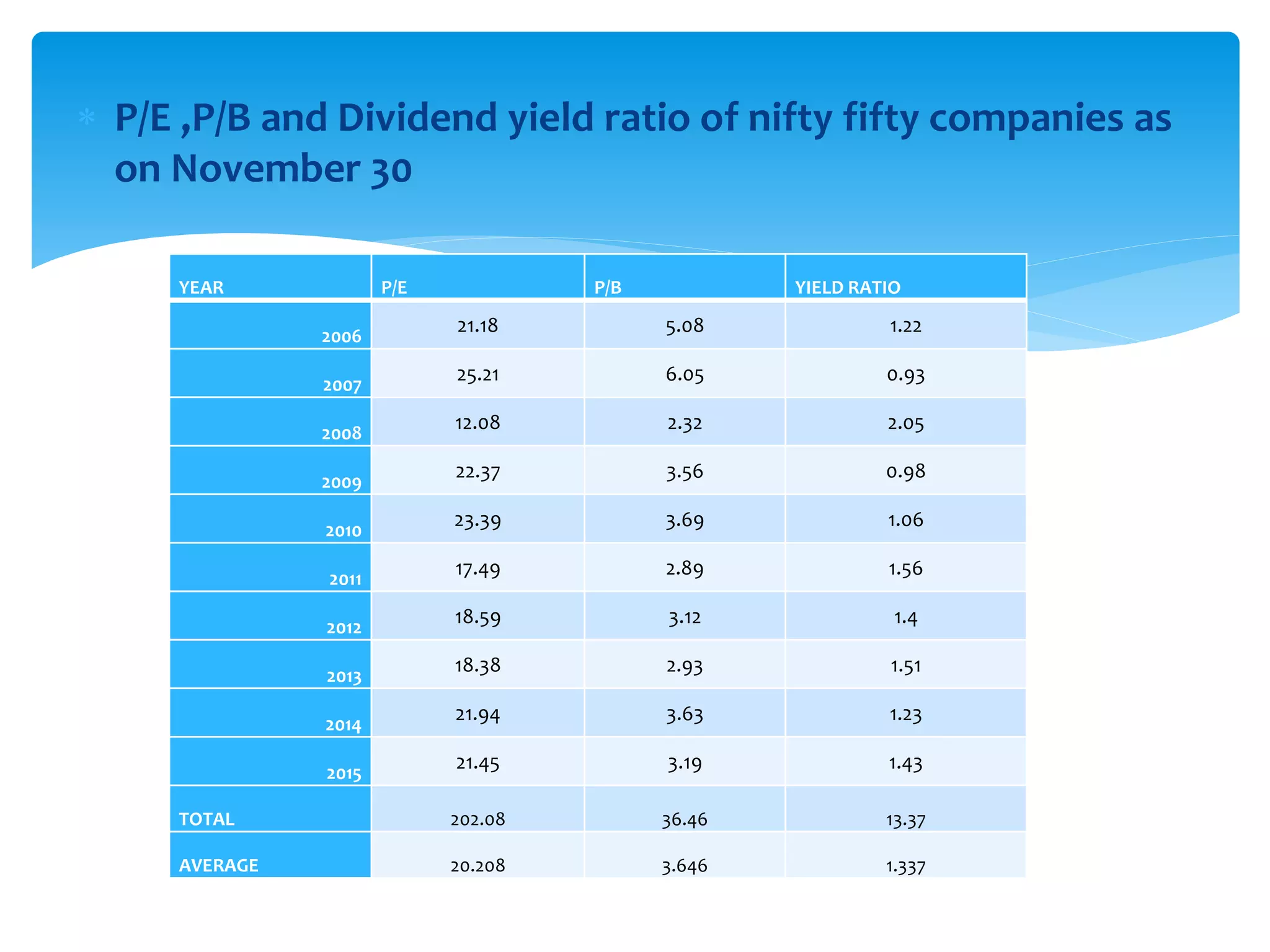
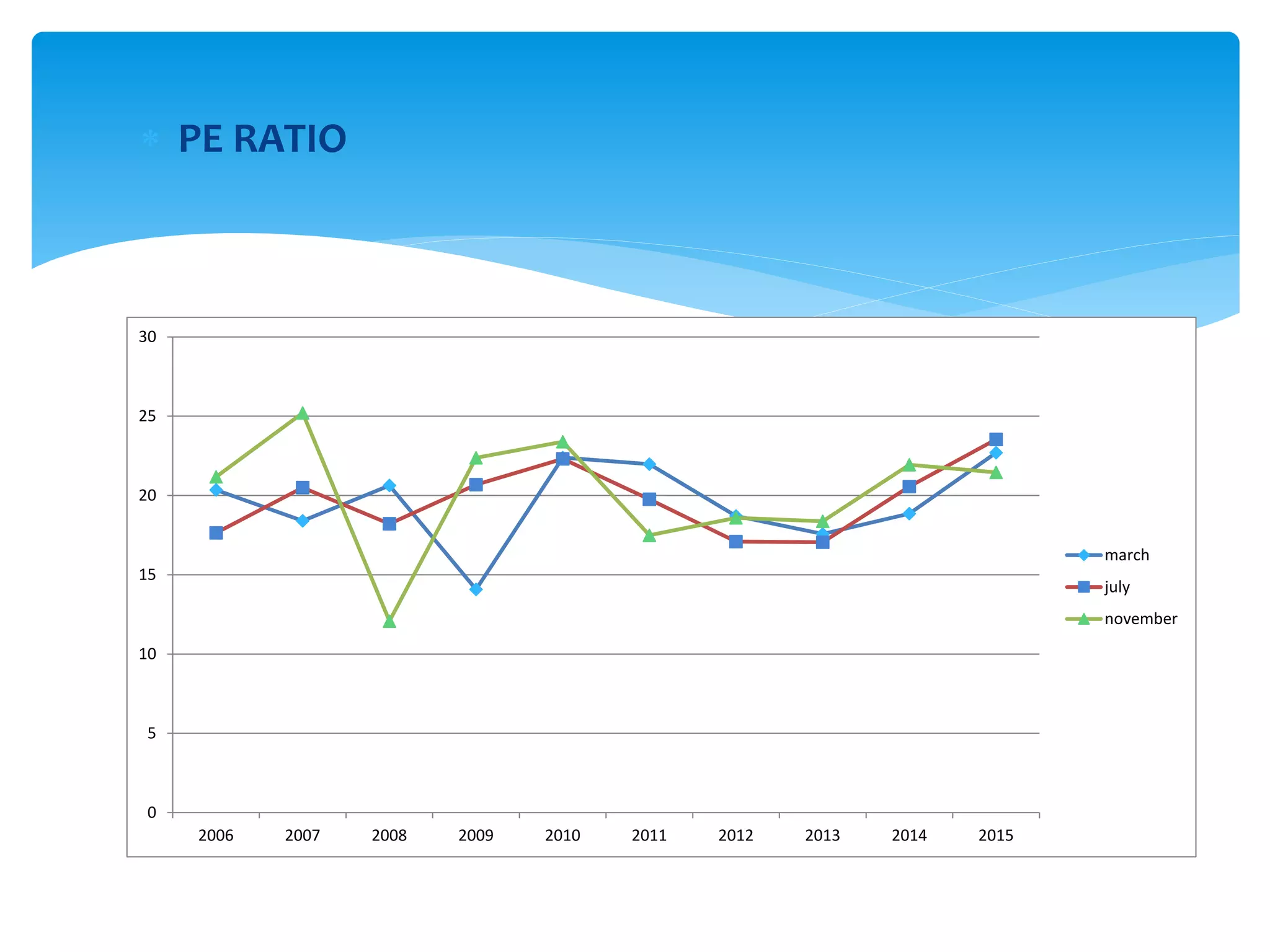
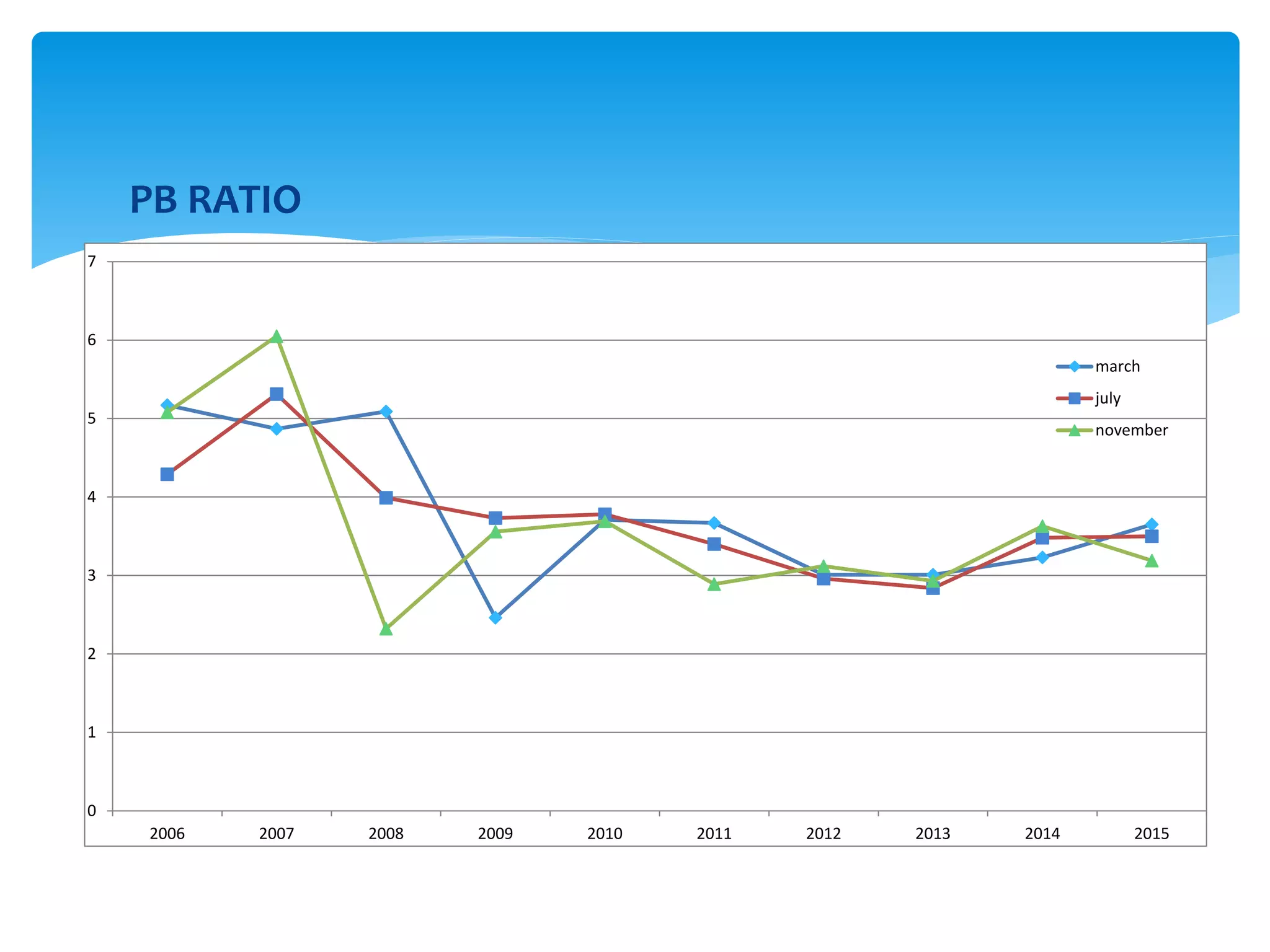
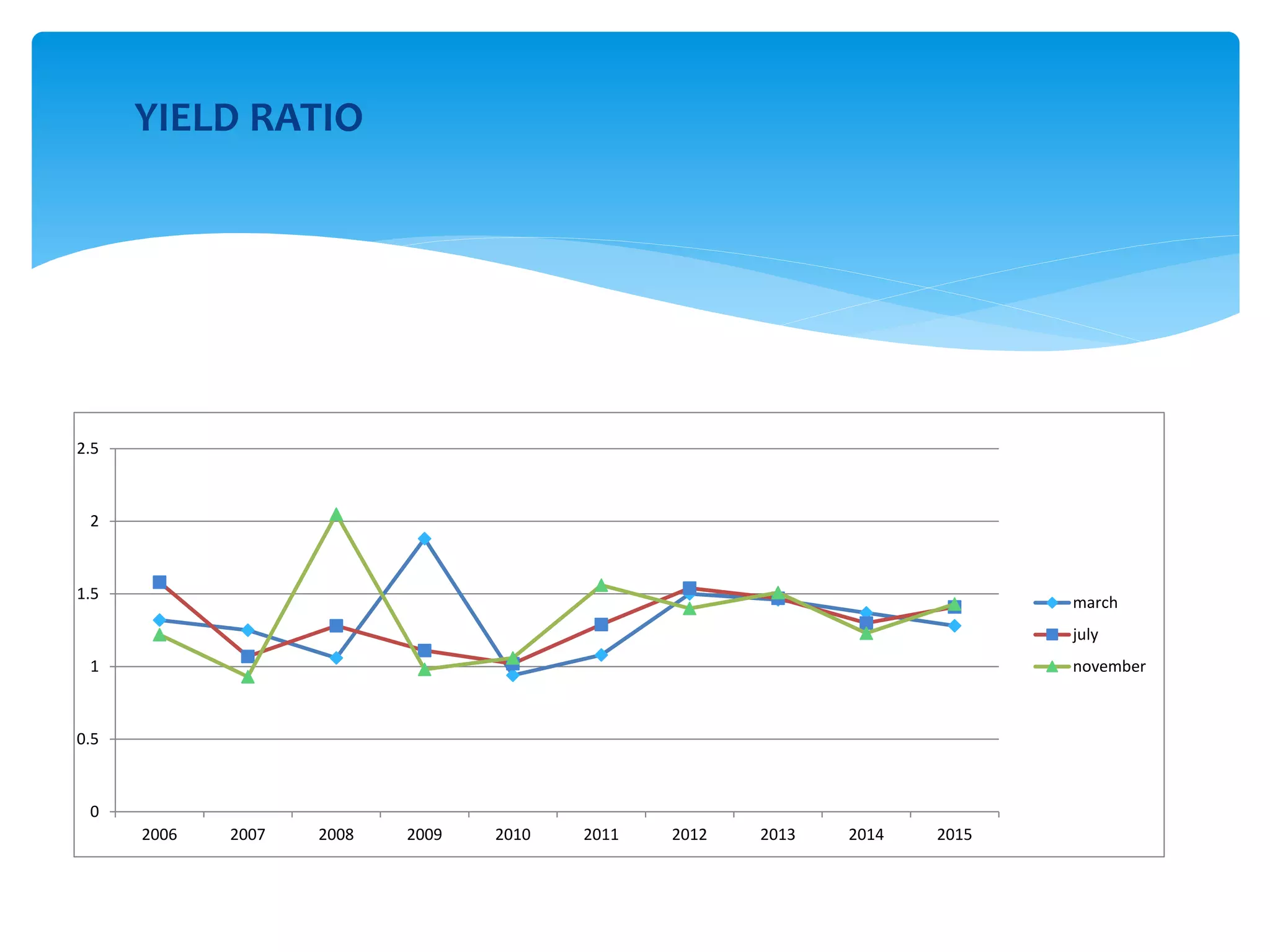
The document discusses various derivatives strategies. It defines a derivative as a security whose price is derived from underlying assets such as stocks, bonds, commodities, currencies, interest rates, and market indexes. The main types of derivatives discussed are forwards, futures, options, and swaps. Forwards and futures are contracts to buy or sell an asset at a future date. Options provide the right but not obligation to buy or sell an asset. Swaps involve exchanging cash flows over time, such as interest rate or currency swaps. The document also analyzes the P/E ratio, P/B ratio, and dividend yield of Nifty 50 companies over different time periods to predict market trends.

![ Smart Equity Brokers Pvt. Ltd. Pvt. Ltd. Brokers Pvt. Ltd.
& Smart Commodity Brokers Pvt. Ltd. was established
on 1st May 2006.
A young Chartered Accountant, Mr. Arun Khera having
a rich experience & exposure to capital, derivative &
commodity market started it. The Company acquired the
membership of:
Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) in 2006
National Stock Exchange [NSE] in 2006
National Commodity & Derivative Exchange [NCDEX] in
2003
Multi Commodity Exchange [MCX] in 2006
About the company](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/astudyofderivativesppt-161002060004/75/A-study-of-derivatives-ppt-2-2048.jpg)