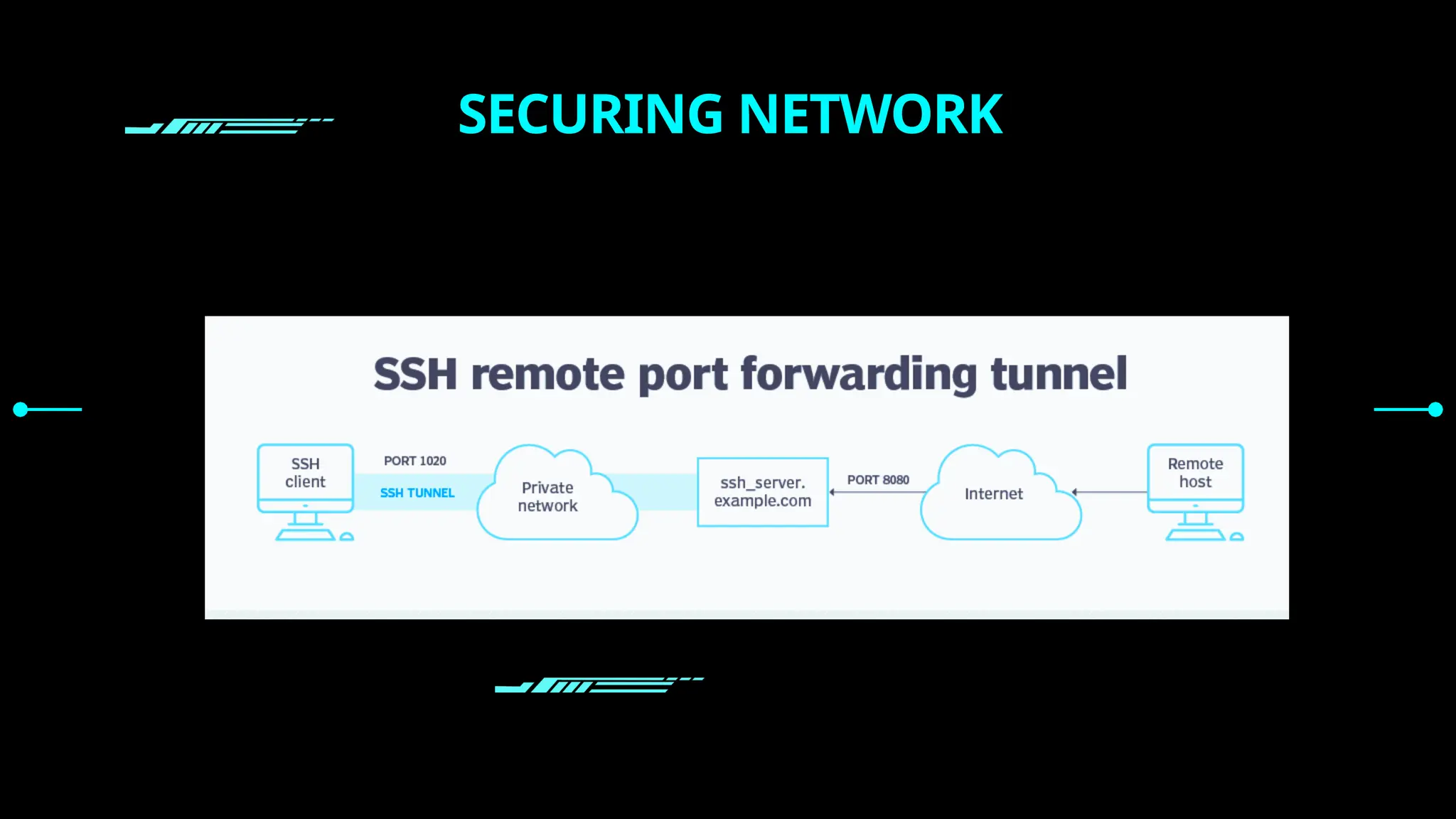
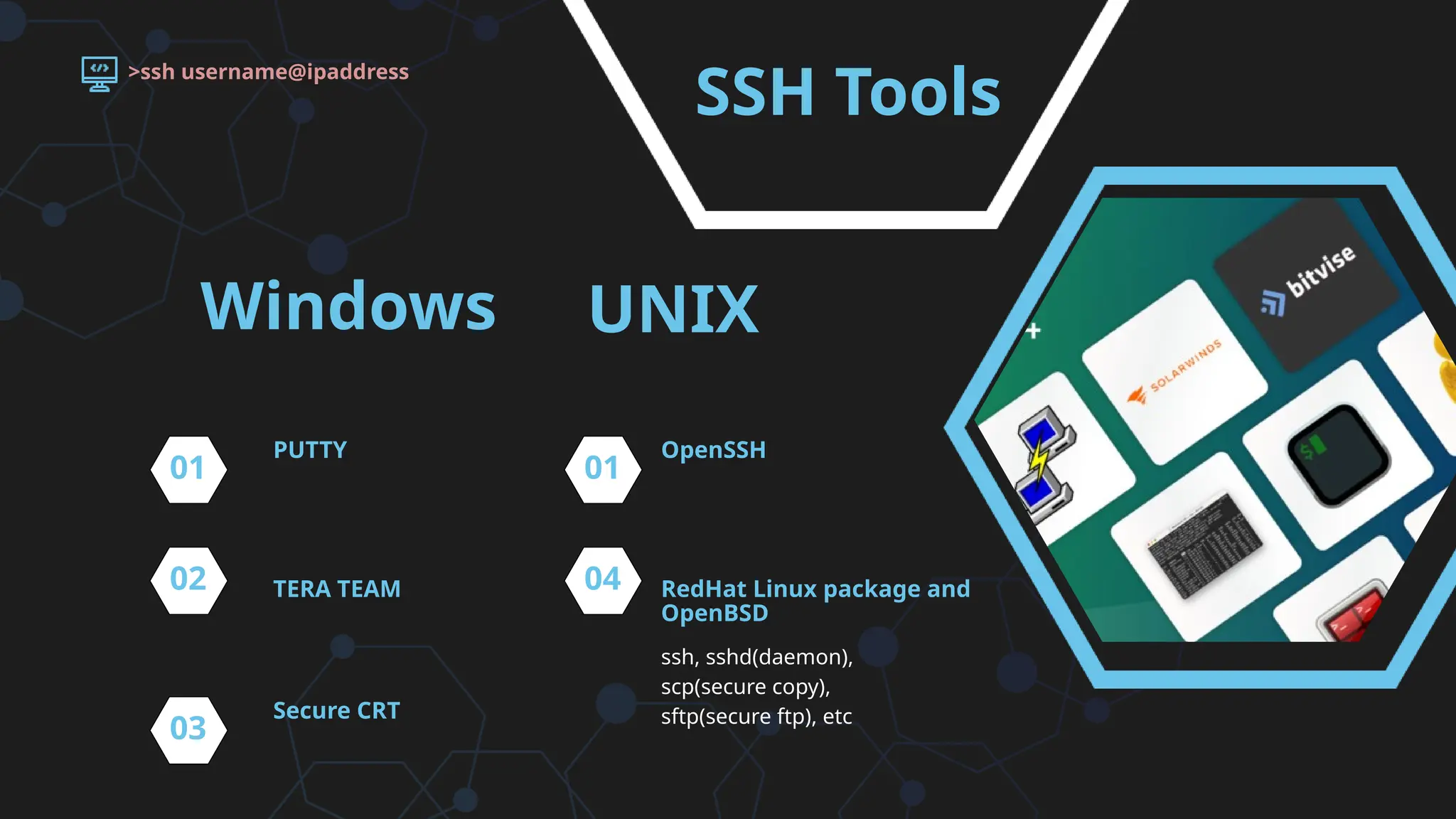
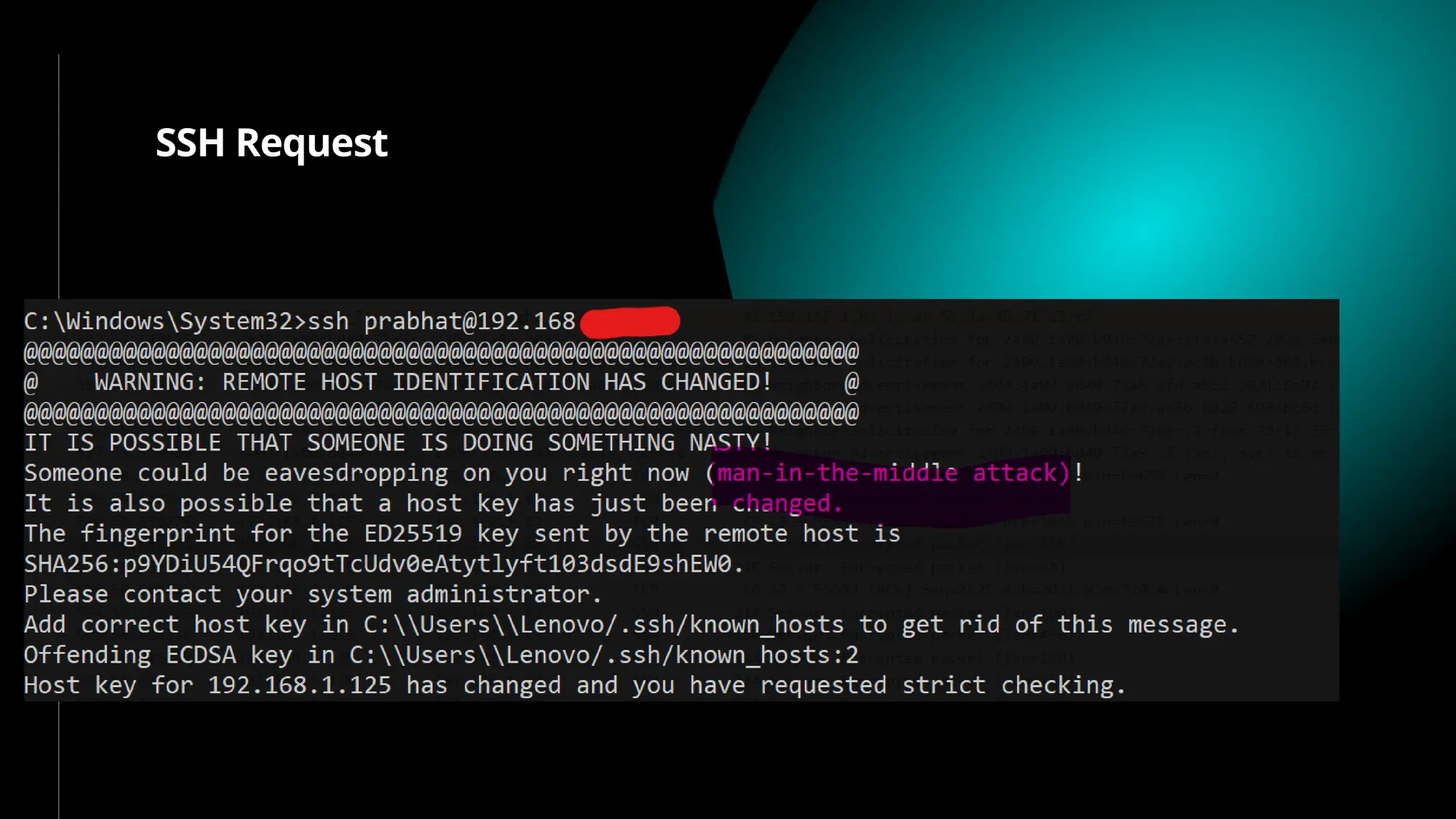
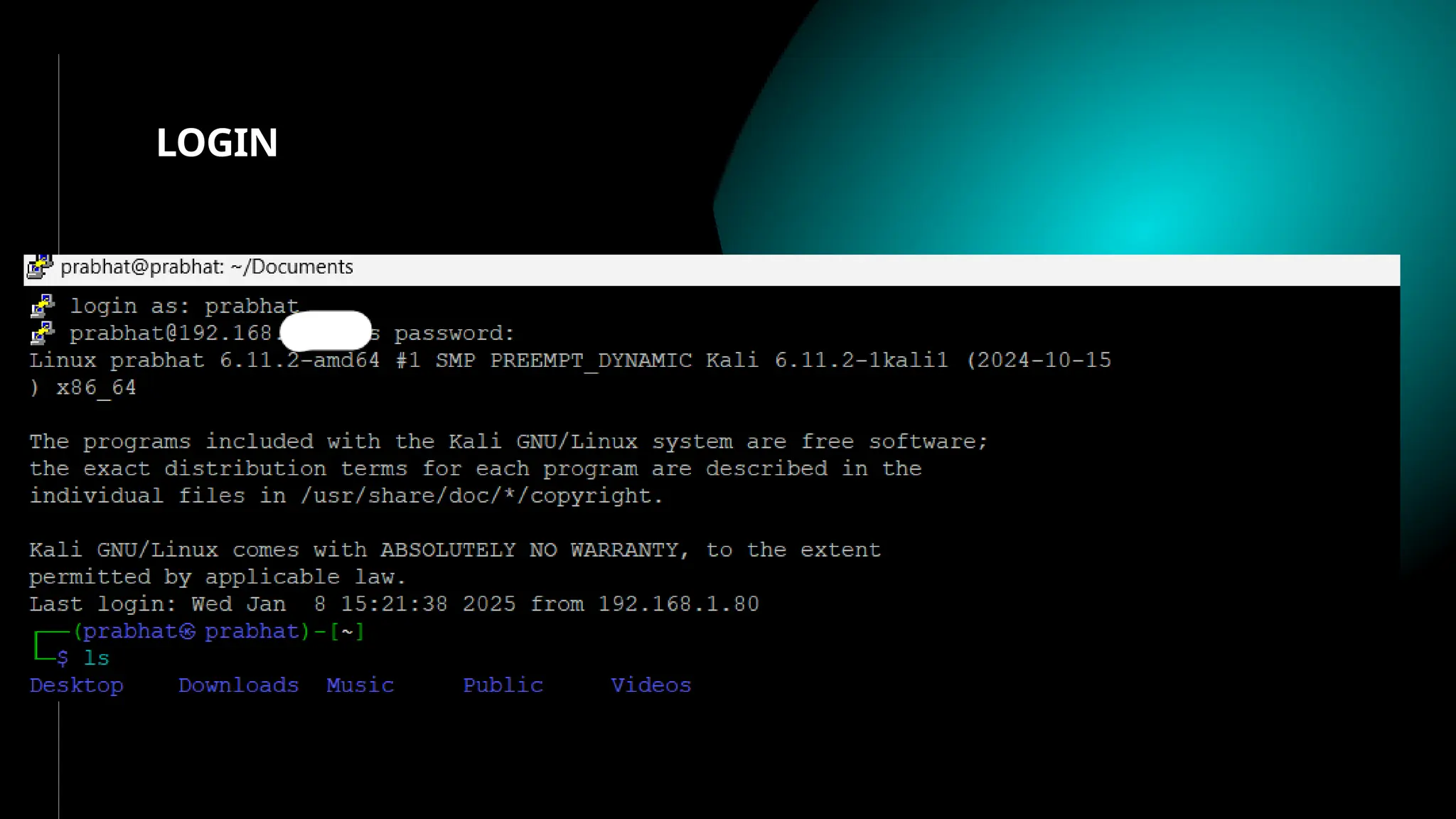
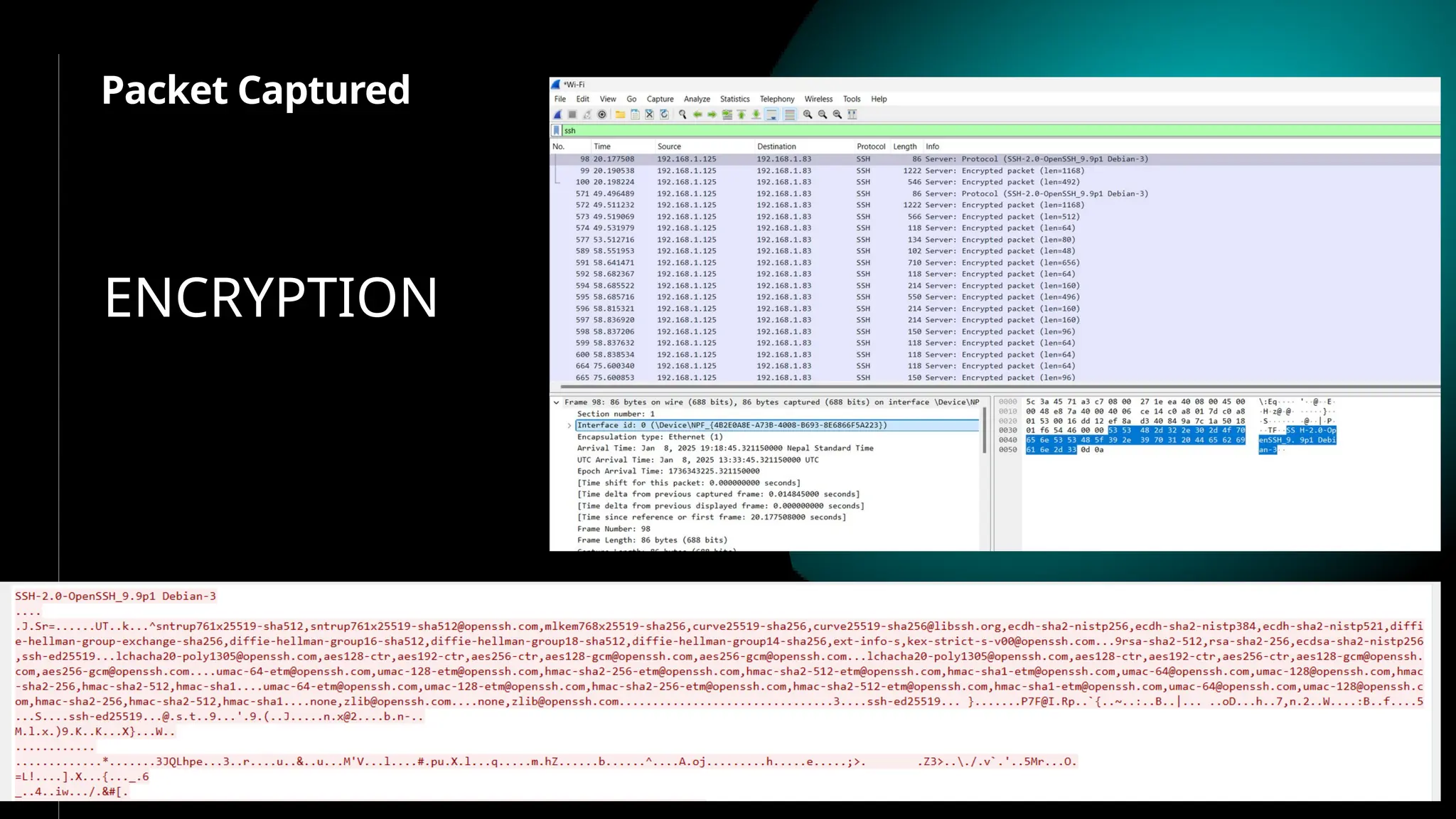
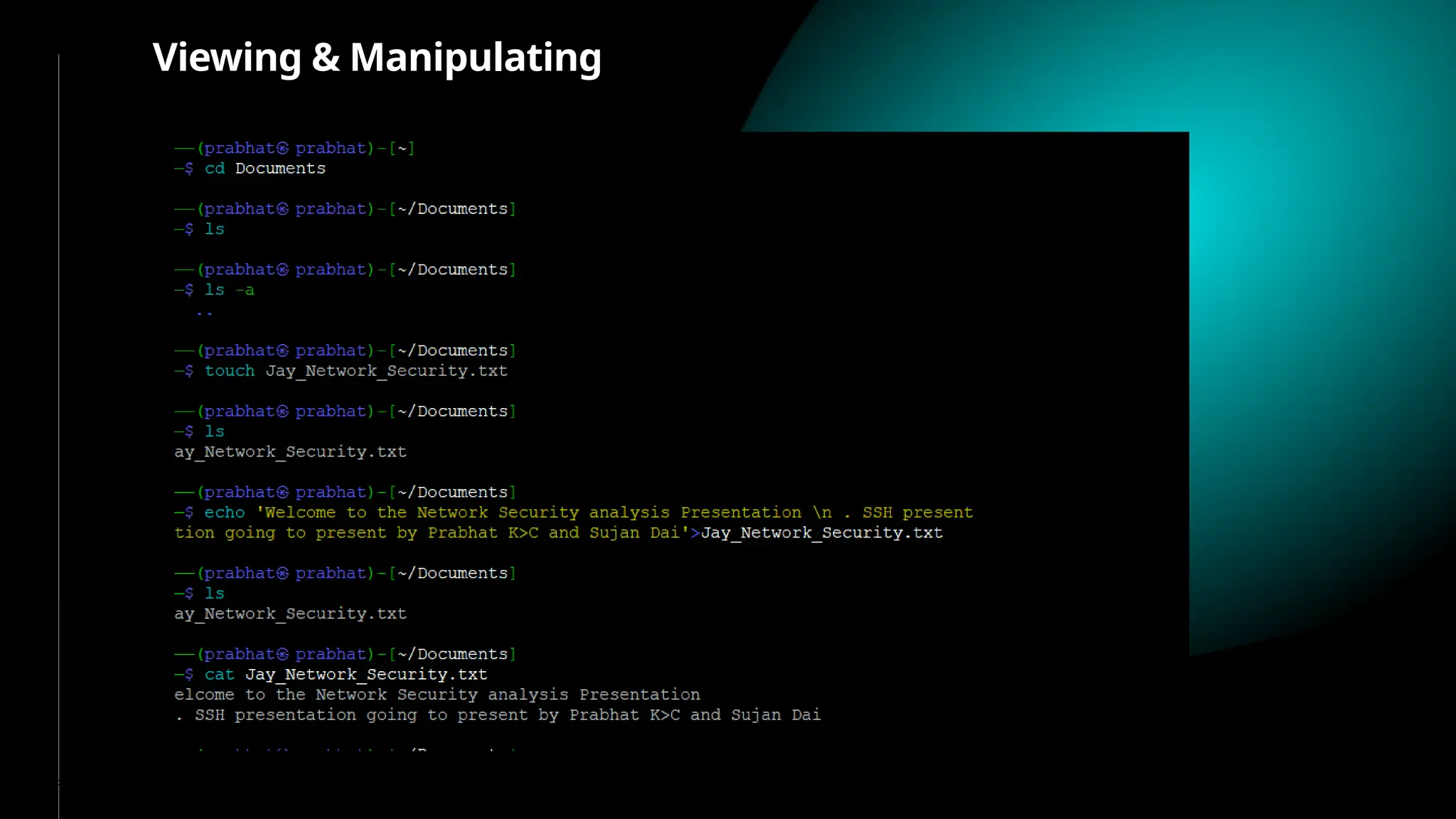
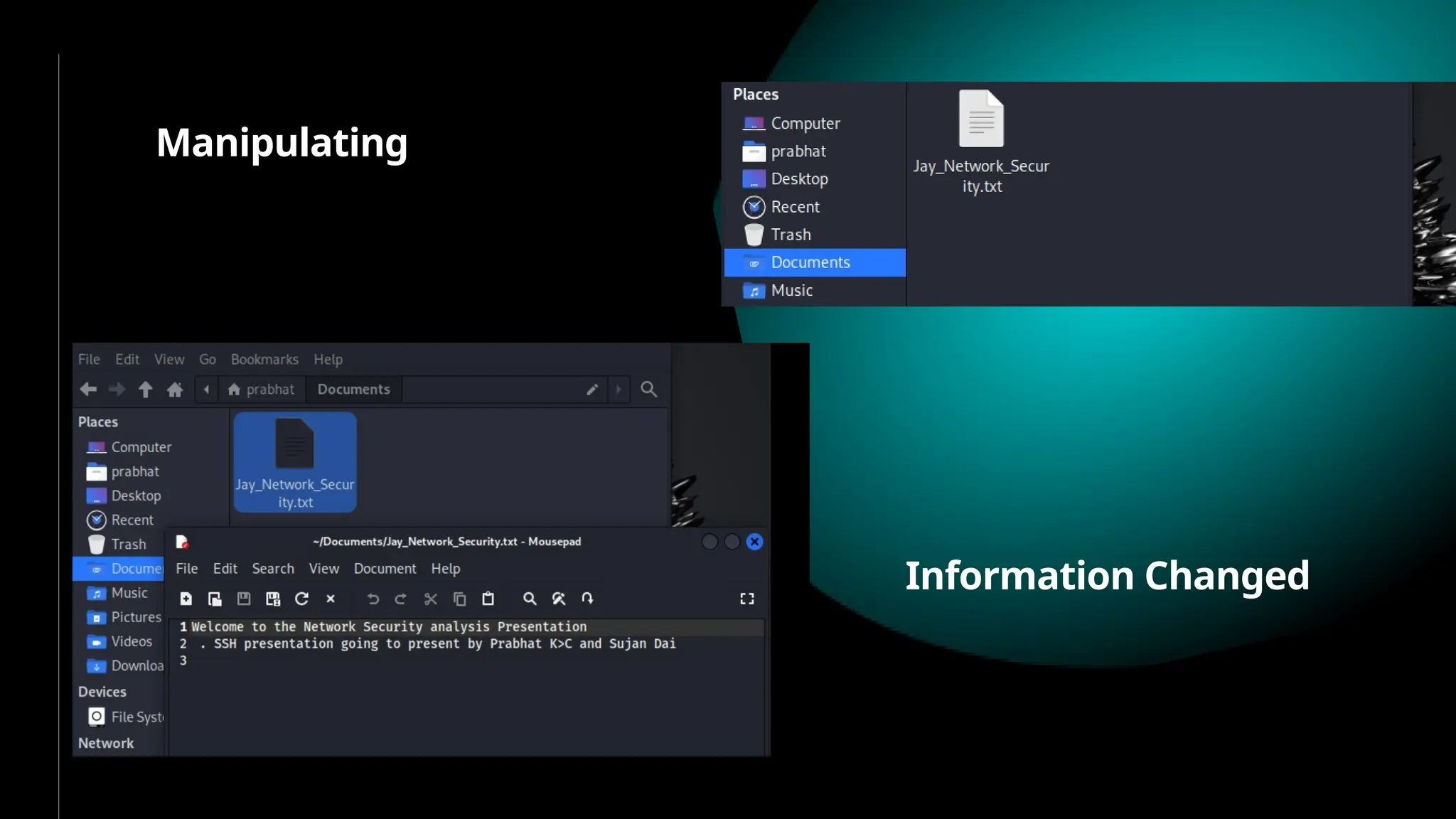
SSH (Secure SHell) is a secure replacement for TELNET, rcp, rlogin, rsh (for login, remote execution of commands, file transfer). Security-wise SSH provides confidentiality (nobody can read the message content), integrity (guarantee that data is unaltered in transit) and authentication (of client and server)
![INTRODUCTION TO
SSH
UNDERSTANDING THE BASICS
• ‘Secure shell is a de facto standard for remote logins and
encrypted file transfers.’ [SSH communications inc.]
• It provides authentication and encryption for business
critical applications to work securely over the internet.
• Originally introduced for UNIX terminals as a
replacement for the insecure remote access “Berkeley
services" , viz. rsh, rlogin, rcp, telnet, etc.
• It is a layer over TCP/IP and runs on the port 22.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sshpresentation-250215035944-10f6505a/75/A-presentation-on-SSH-Secure-Shell-or-Secure-Socket-Shell-2-2048.jpg)