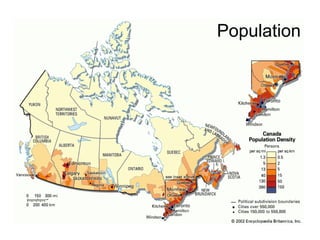
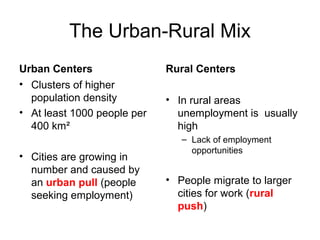
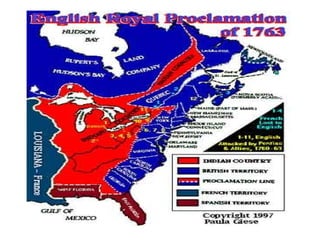
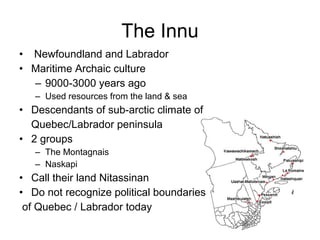
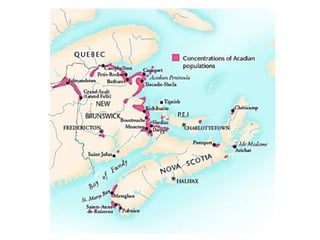
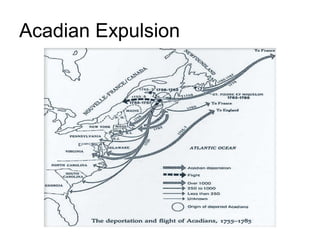
The document summarizes population patterns and settlement in Atlantic Canada. It notes that the population is not evenly distributed across the four provinces, with Nova Scotia and Prince Edward Island having higher population densities. It discusses the original Indigenous inhabitants, including the Mi'kmaq, Maliseet, Passamaquoddy, Inuit, and Beothuk peoples. It then outlines the major waves of European settlement, including the French in the 1600s, Acadian settlers, and British settlers in the 1700-1800s, many of whom were Loyalists fleeing the American Revolution.