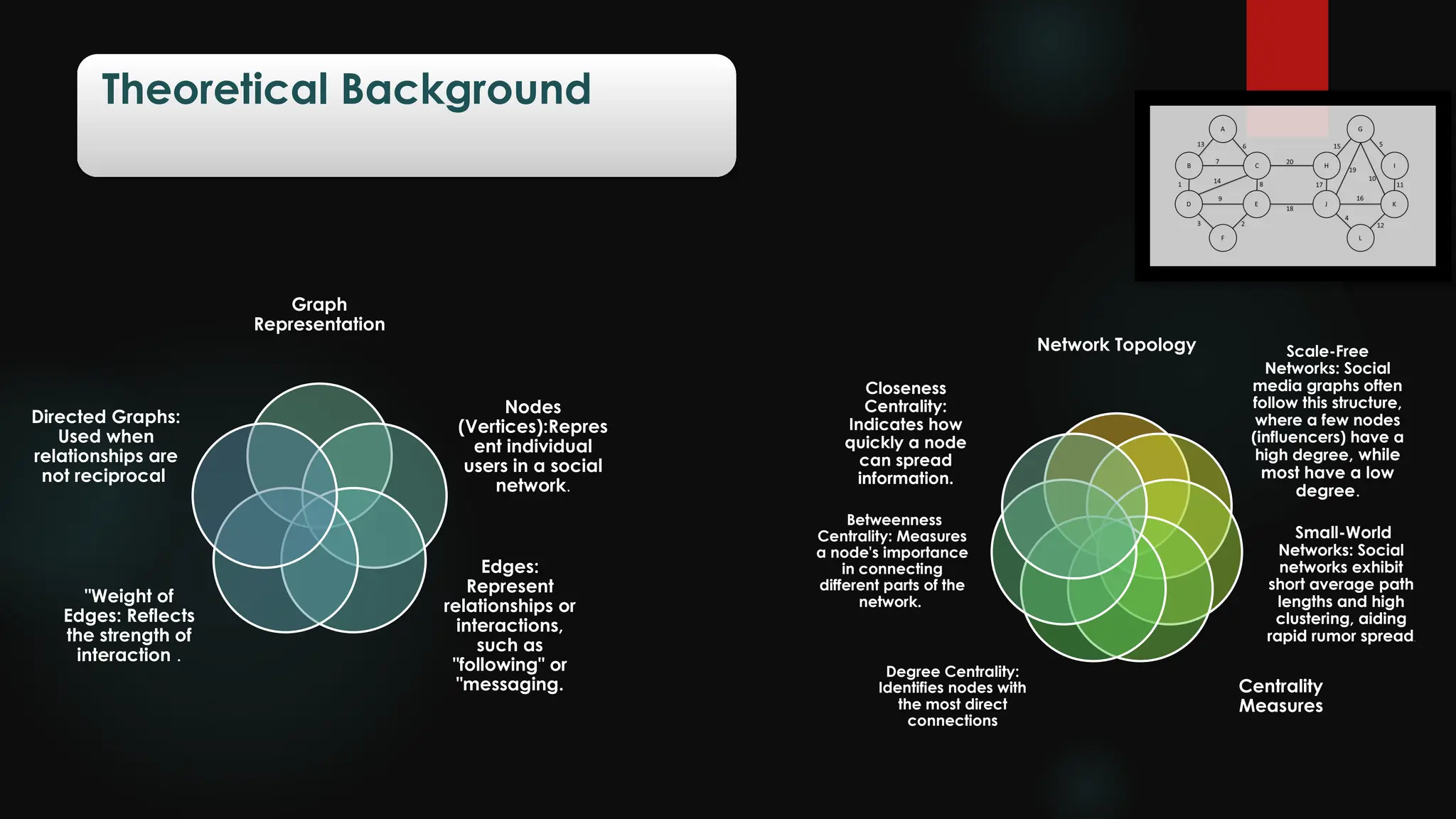
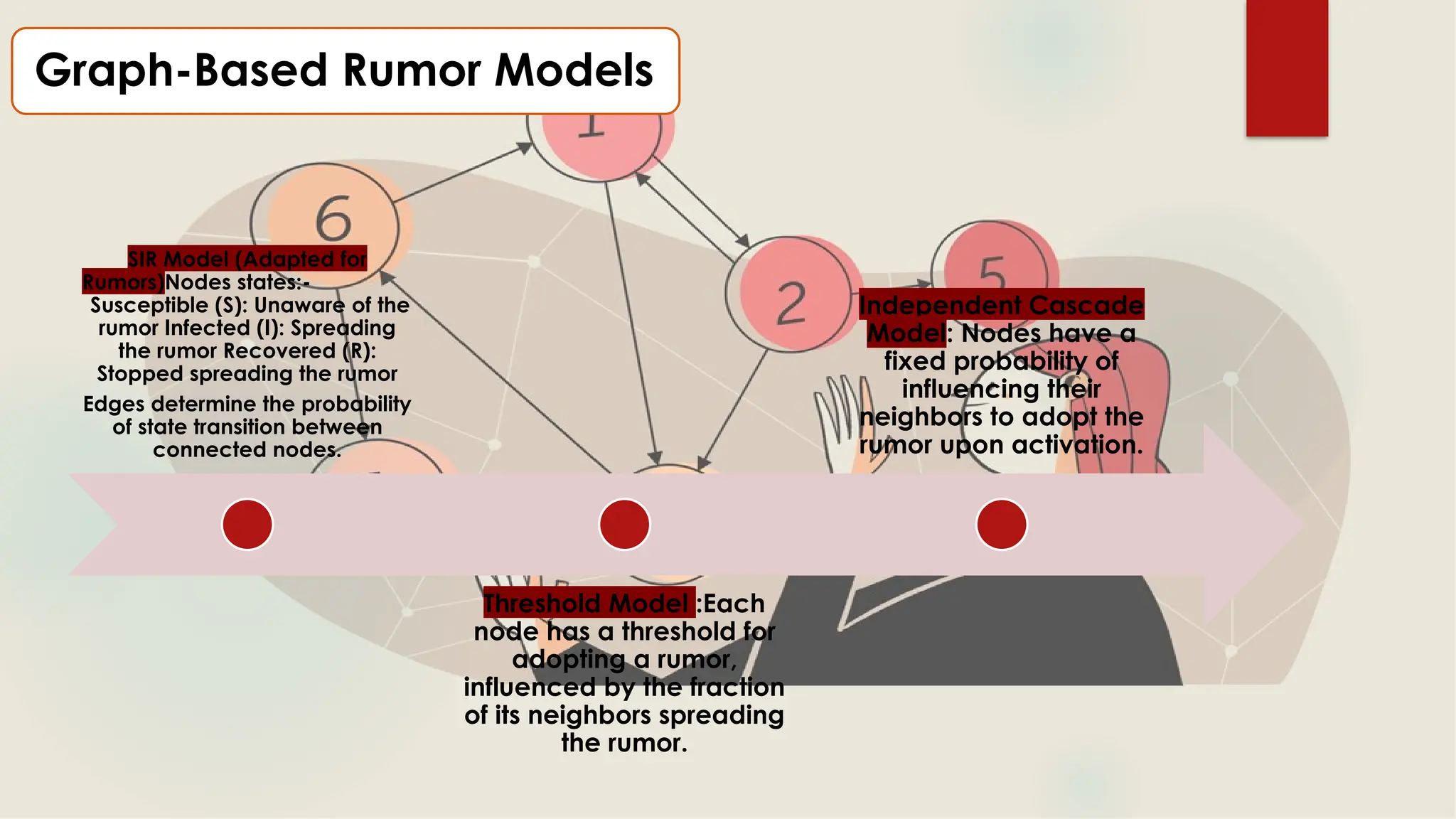
The document explores the spread of rumors on social media through a mathematical lens using graph theory. It discusses various graph-based models, such as the SIR model and the threshold model, to analyze rumor dynamics, as well as strategies for countering their spread. The conclusion highlights the rapid transmission of rumors influenced by individual beliefs and sharing behaviors.