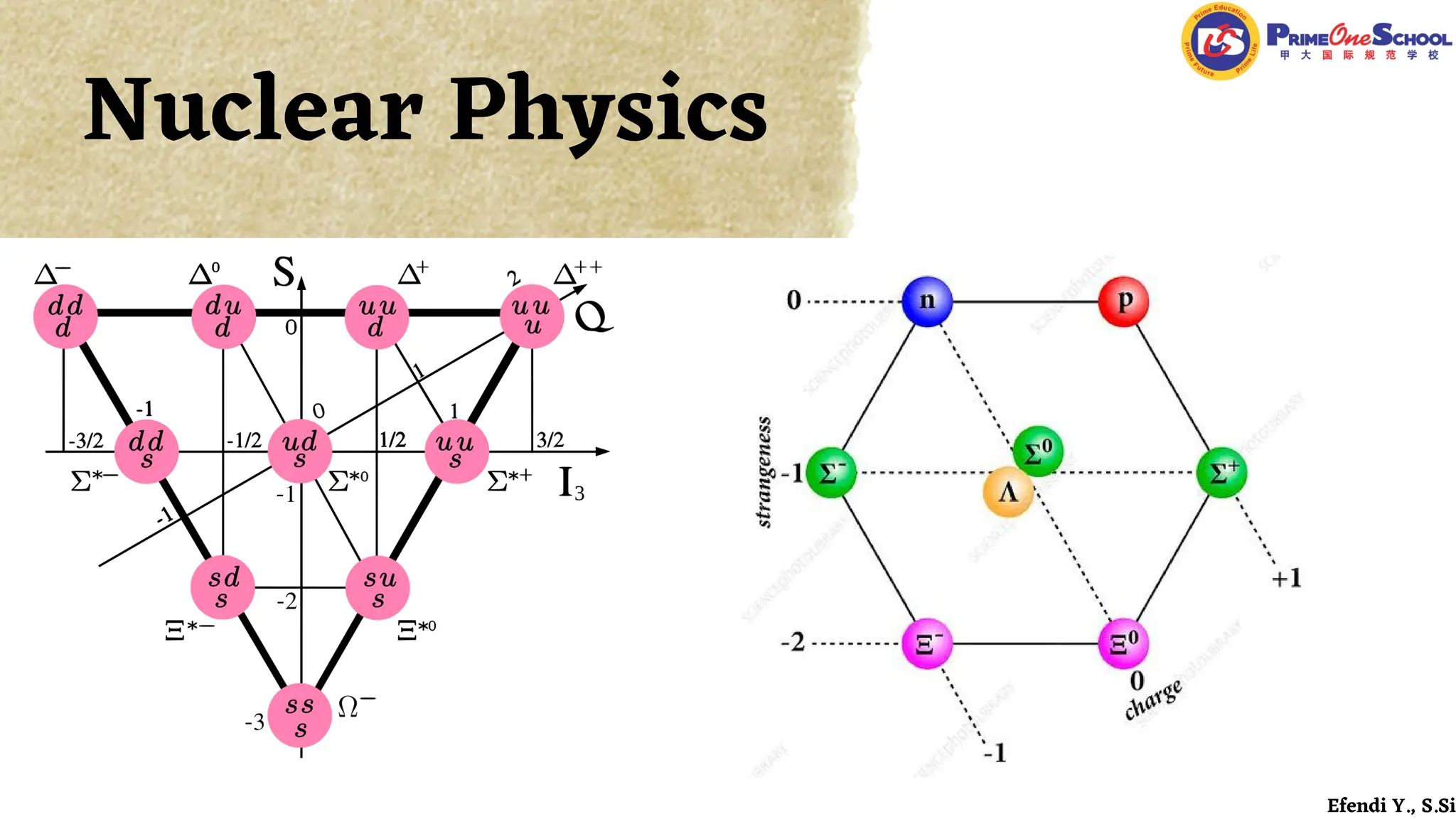
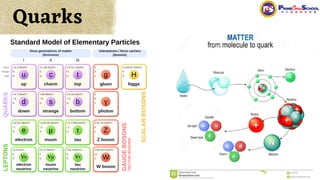
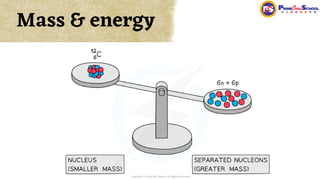
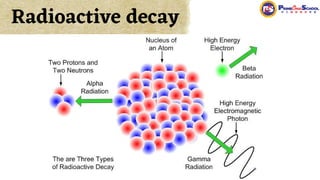
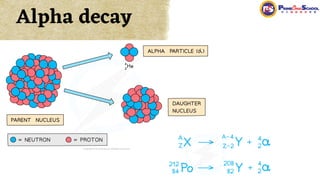
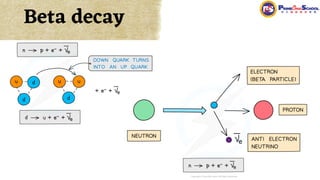
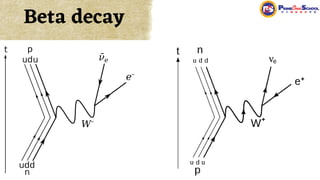
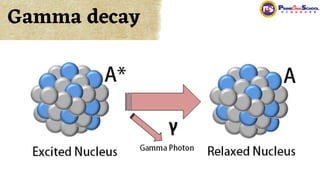
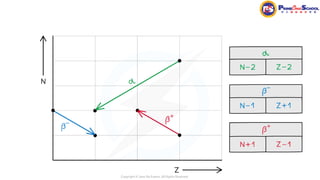
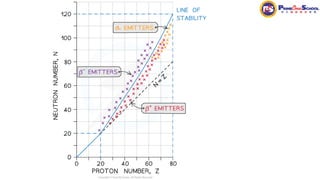
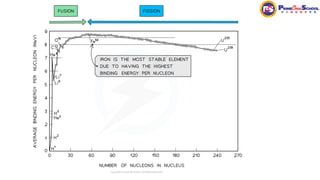
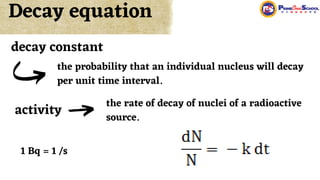
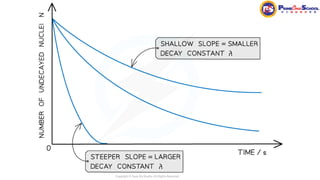
The document covers fundamental concepts in nuclear physics, detailing particle families such as hadrons and leptons, and the forces acting upon them. It discusses processes like radioactive decay, fission, and fusion, including their mechanisms and related equations. Key terms include binding energy, decay constant, and activity related to the decay rates of radioactive sources.