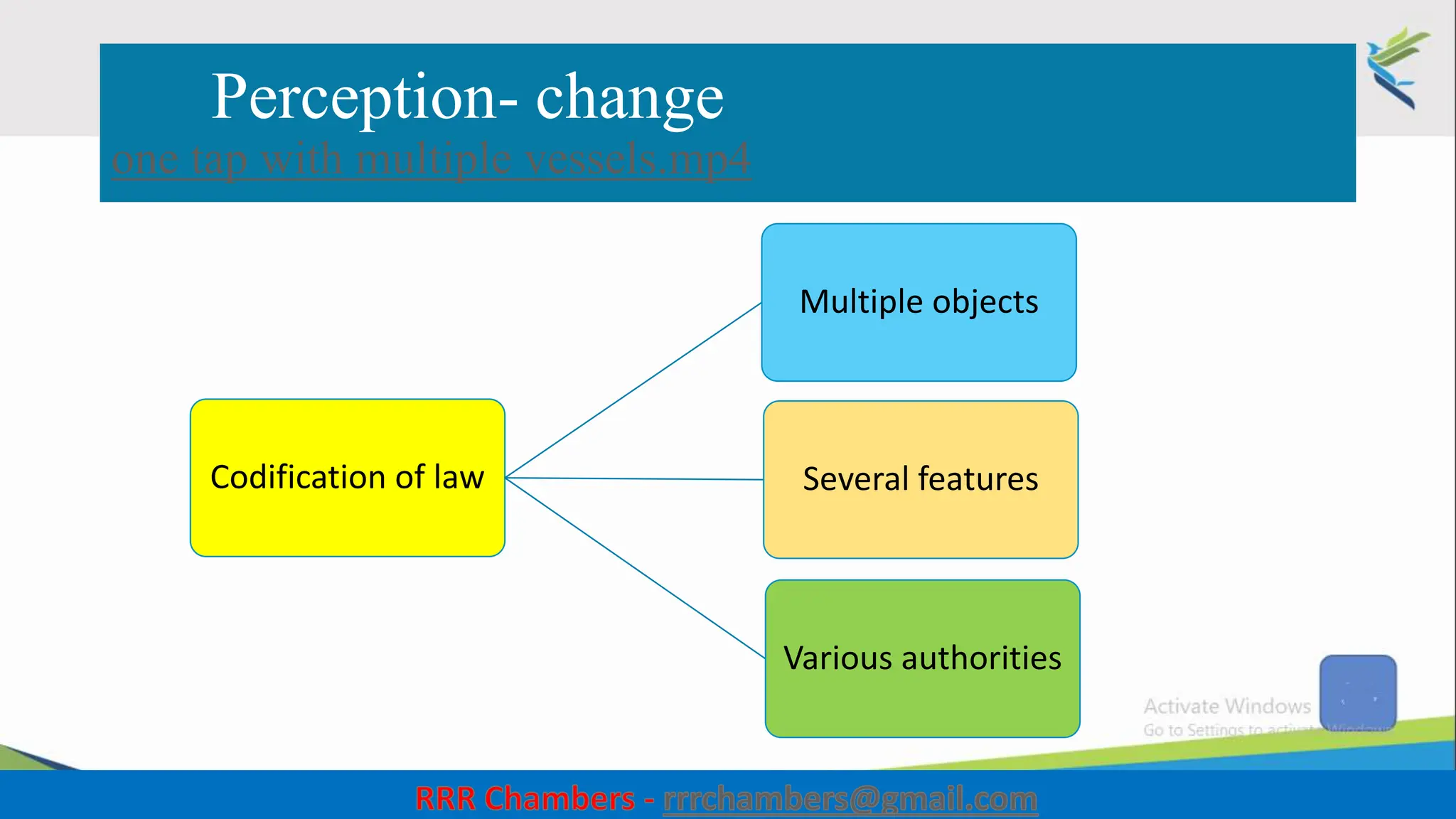
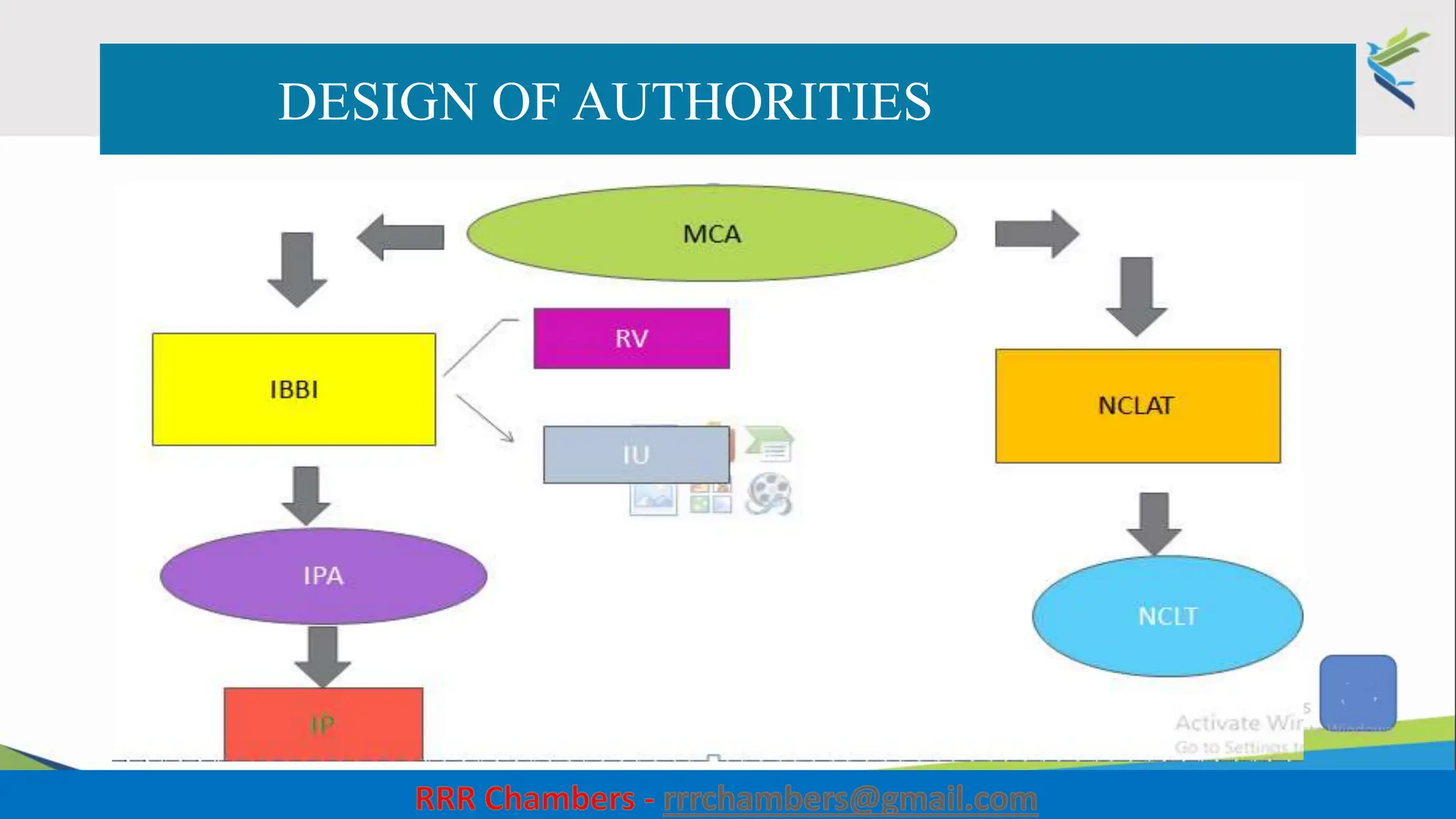
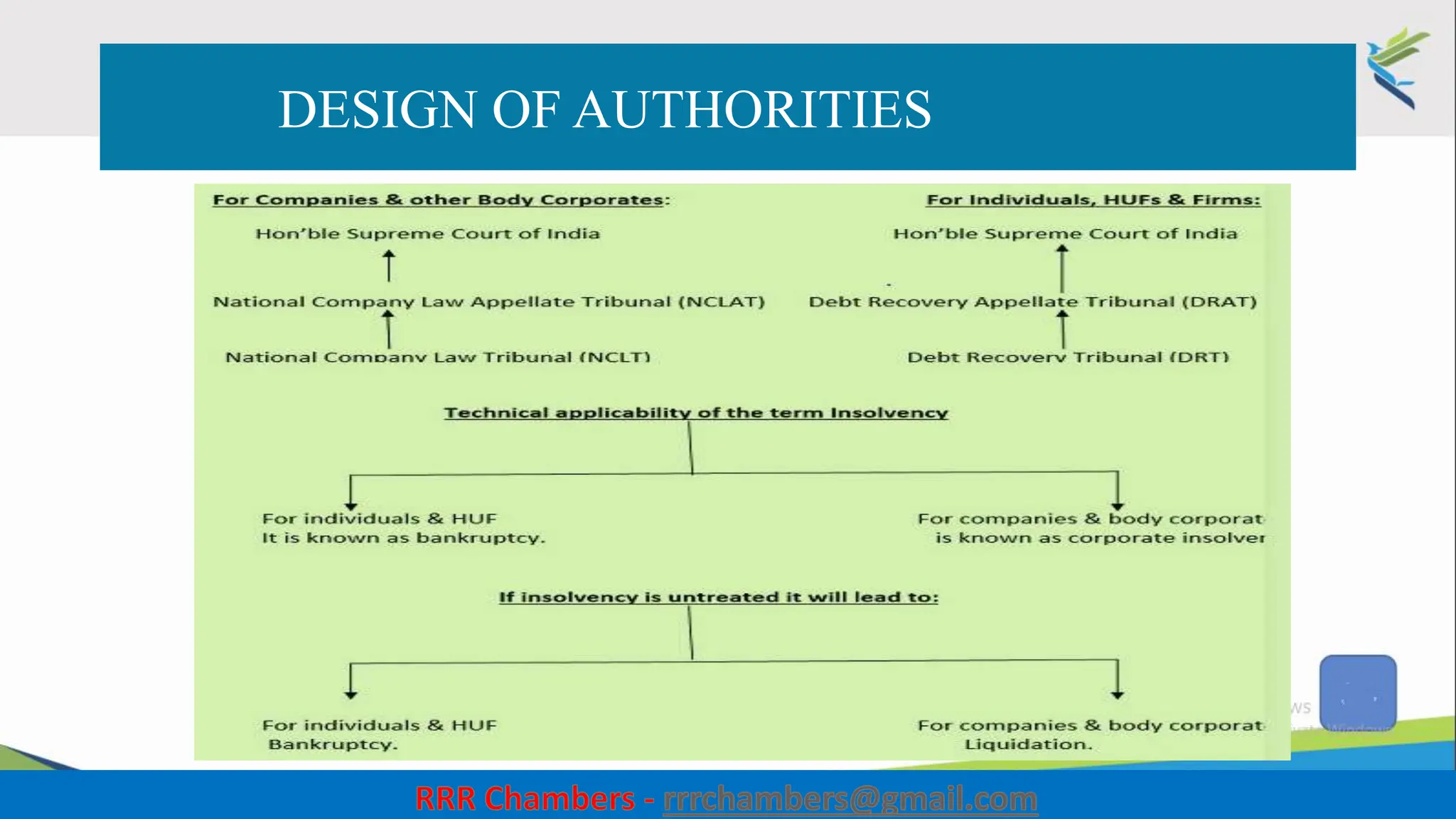
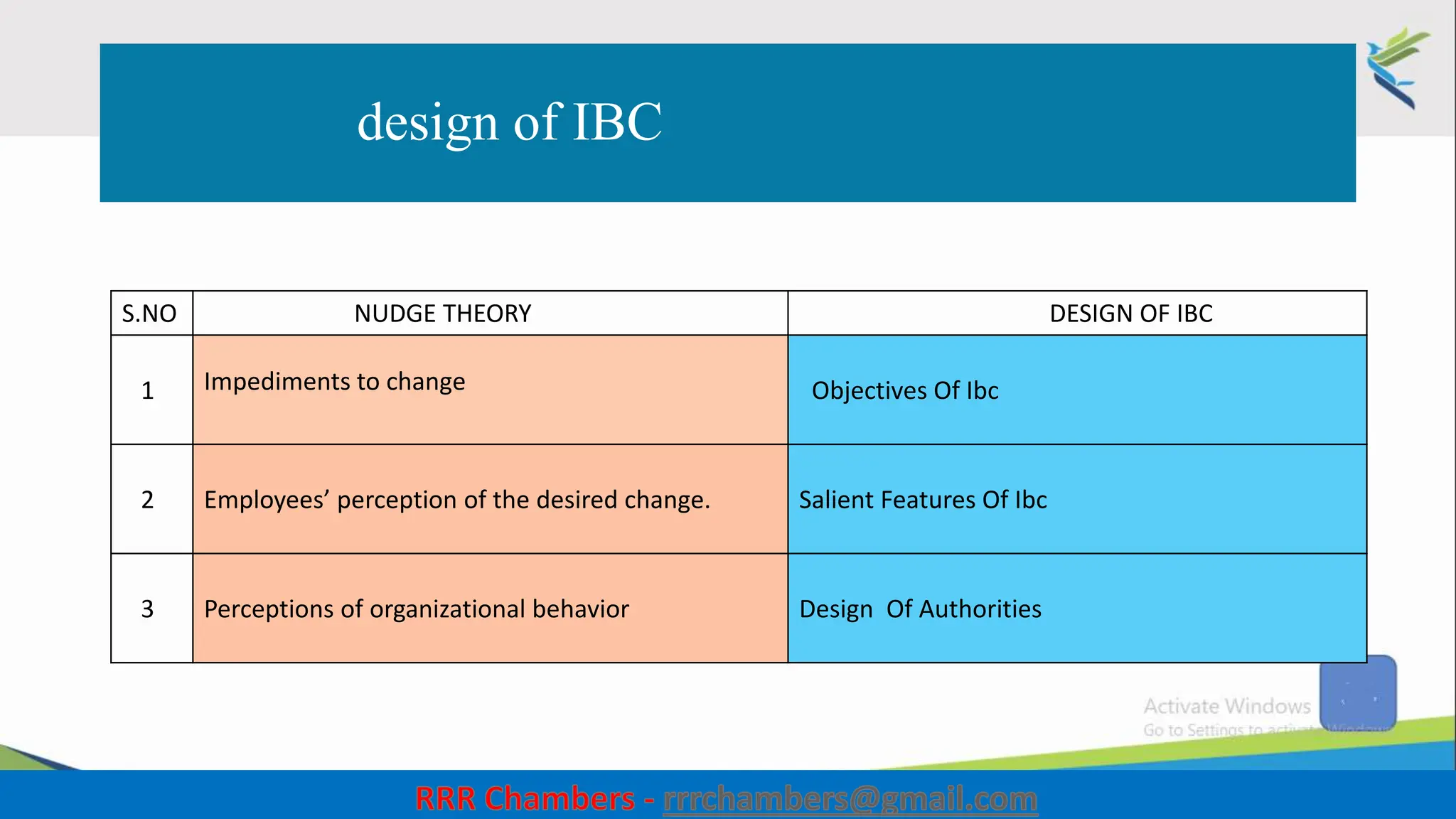
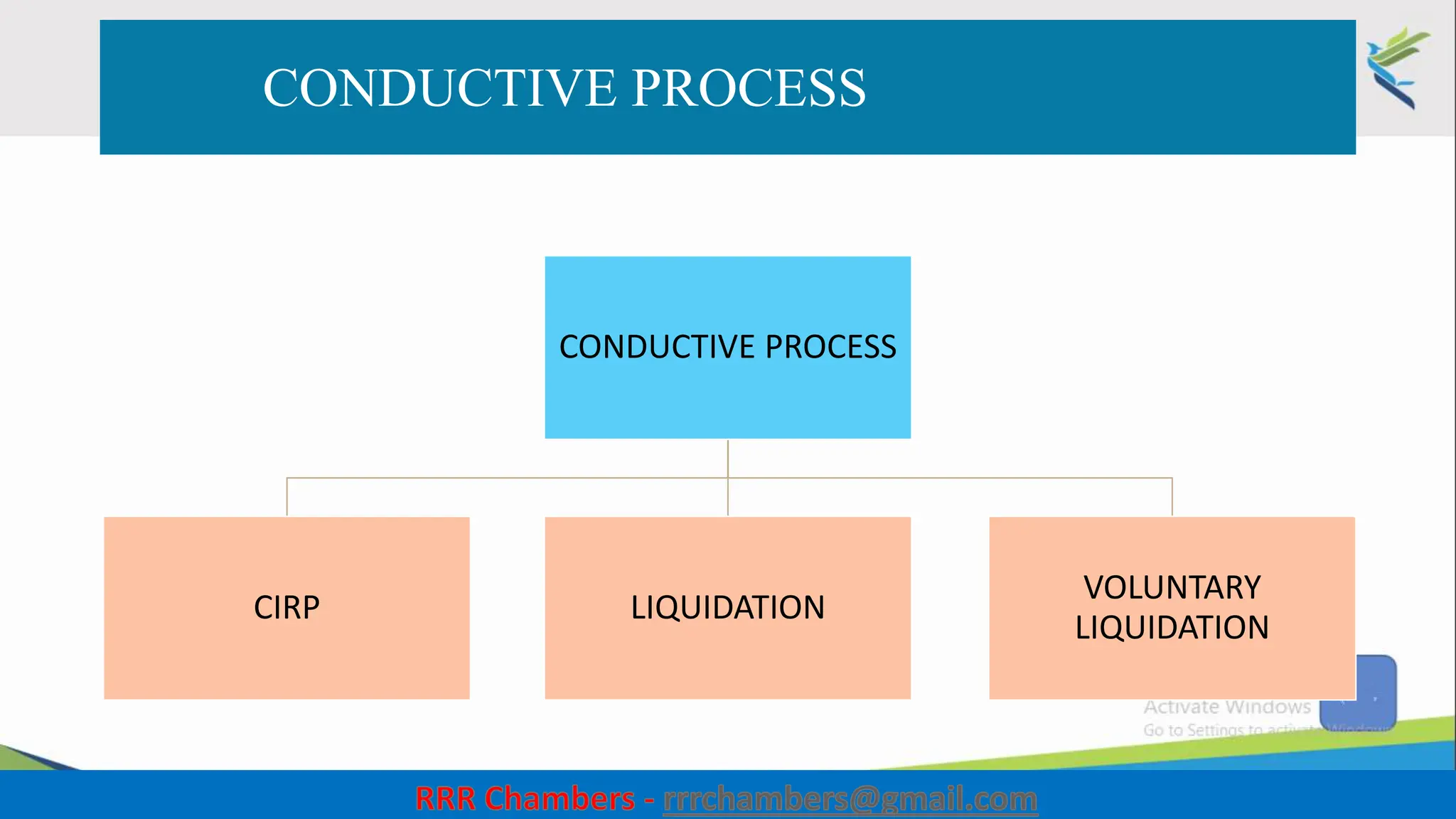
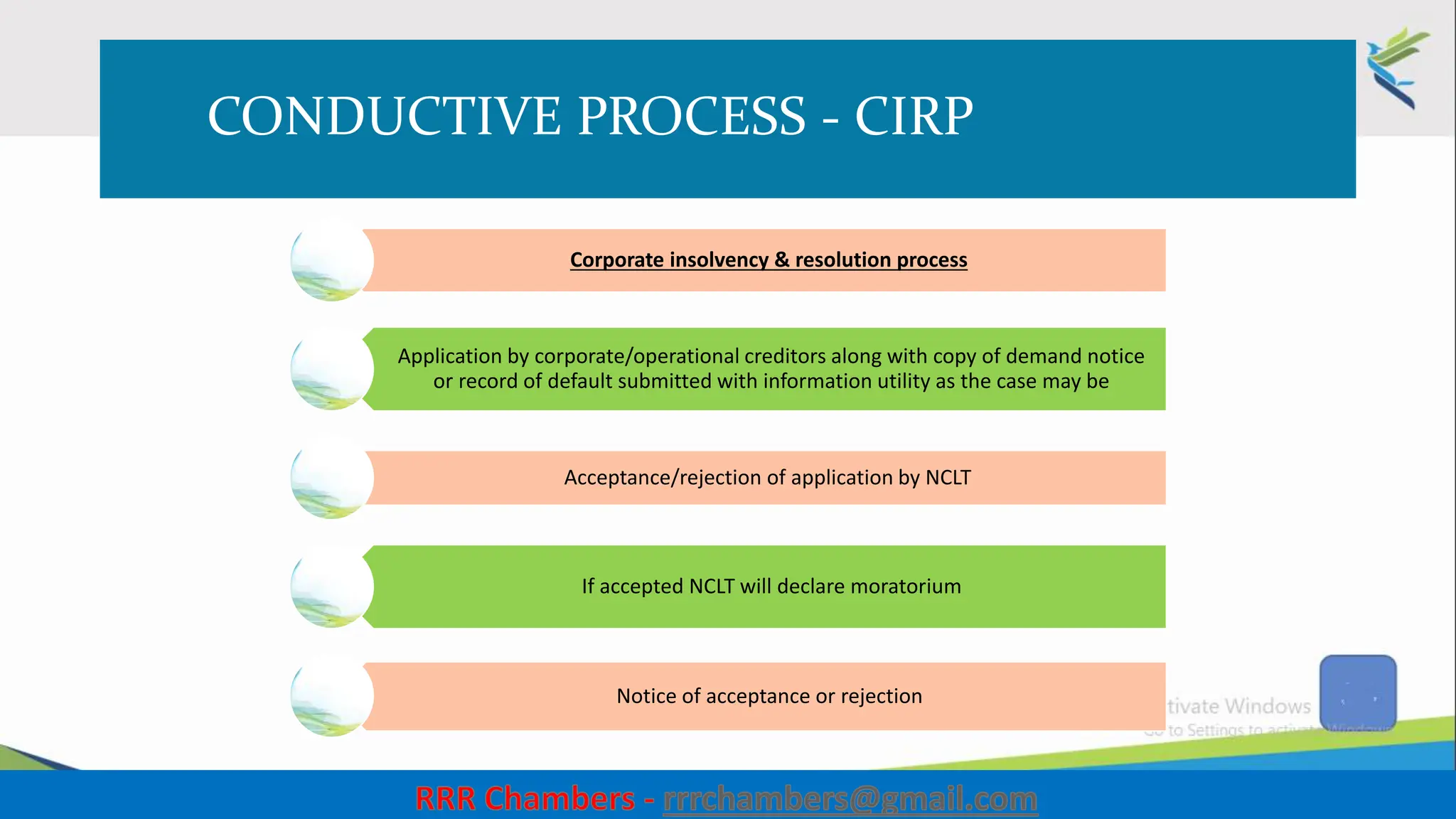
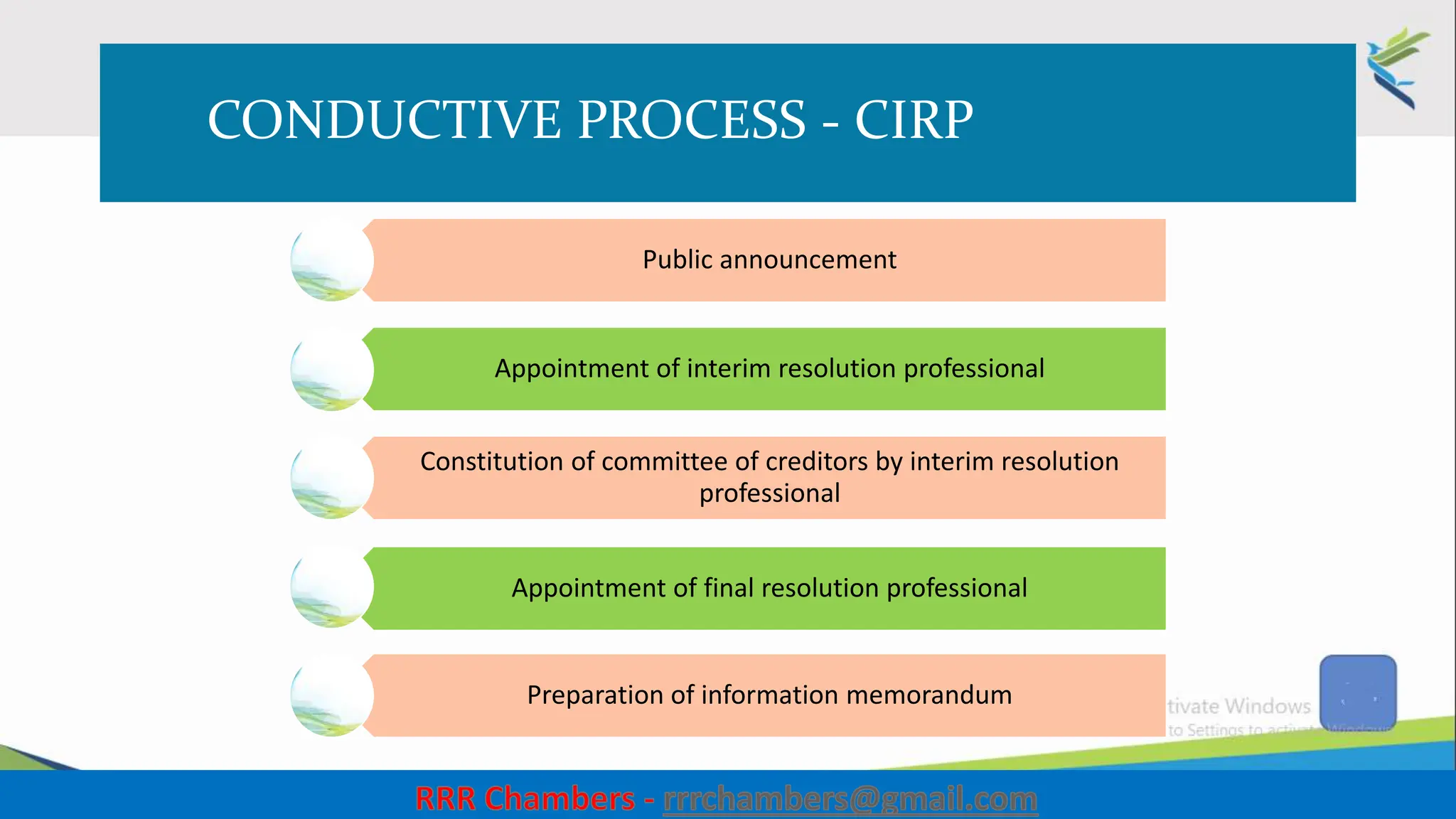
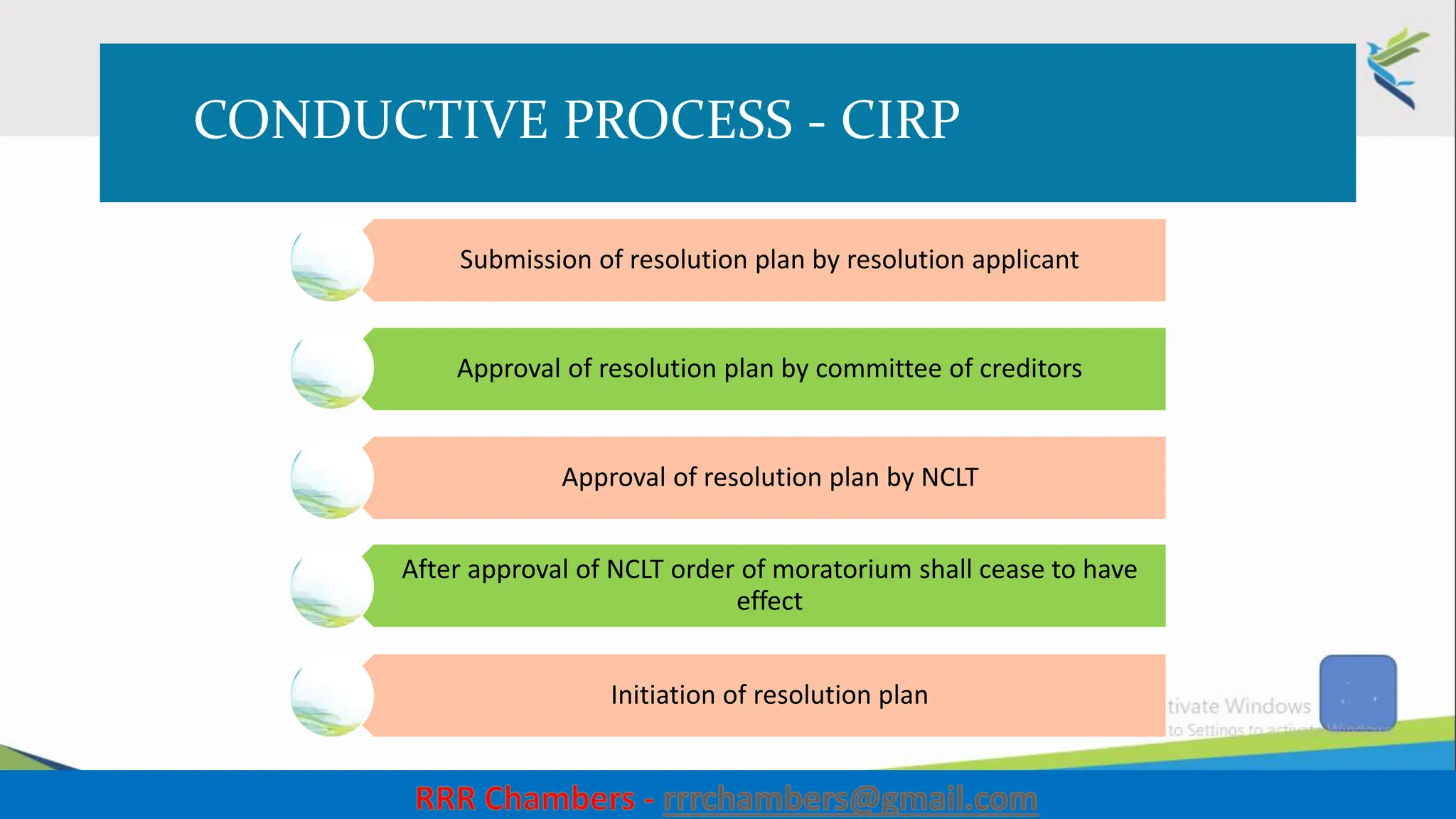
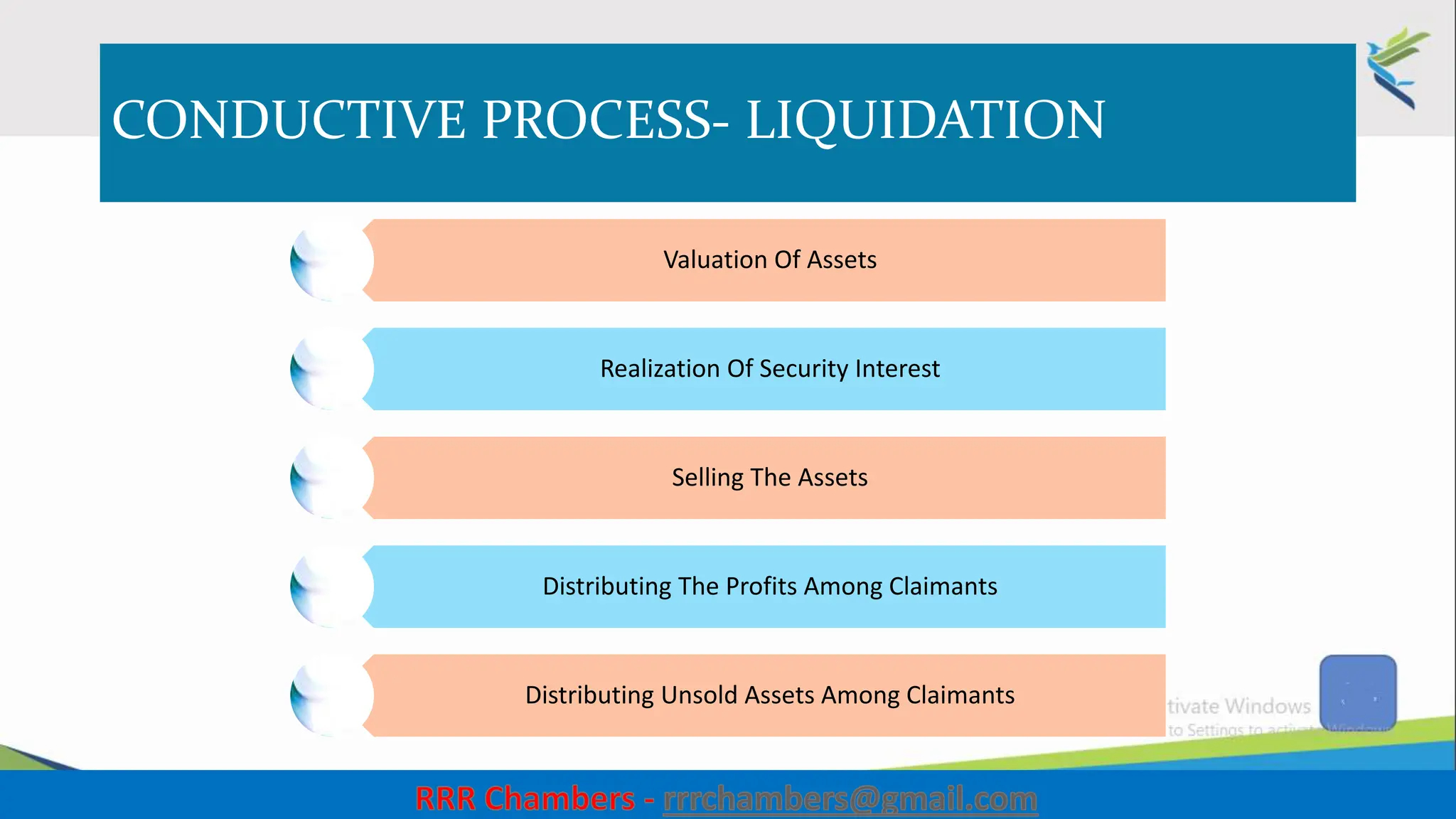
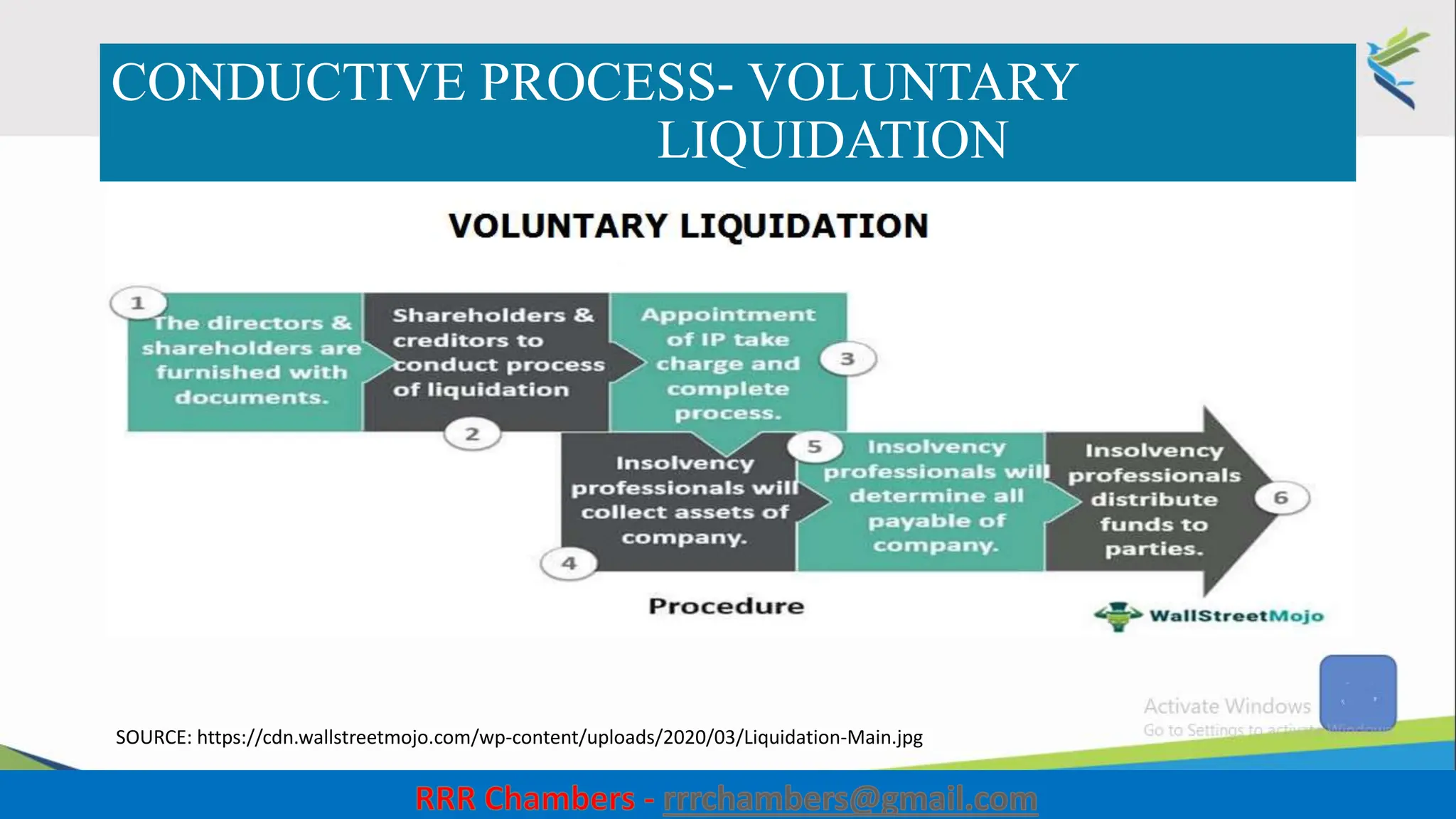
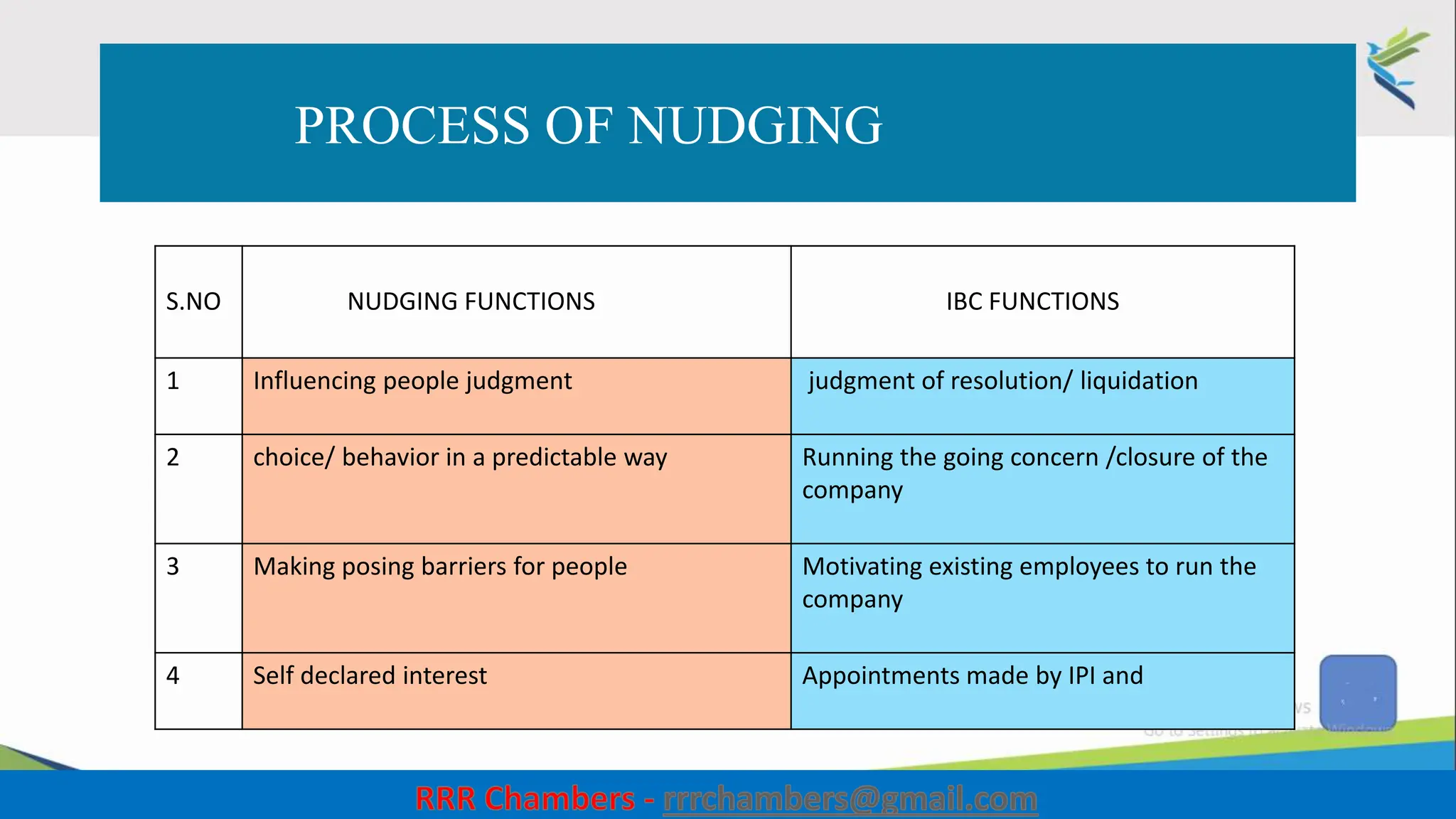
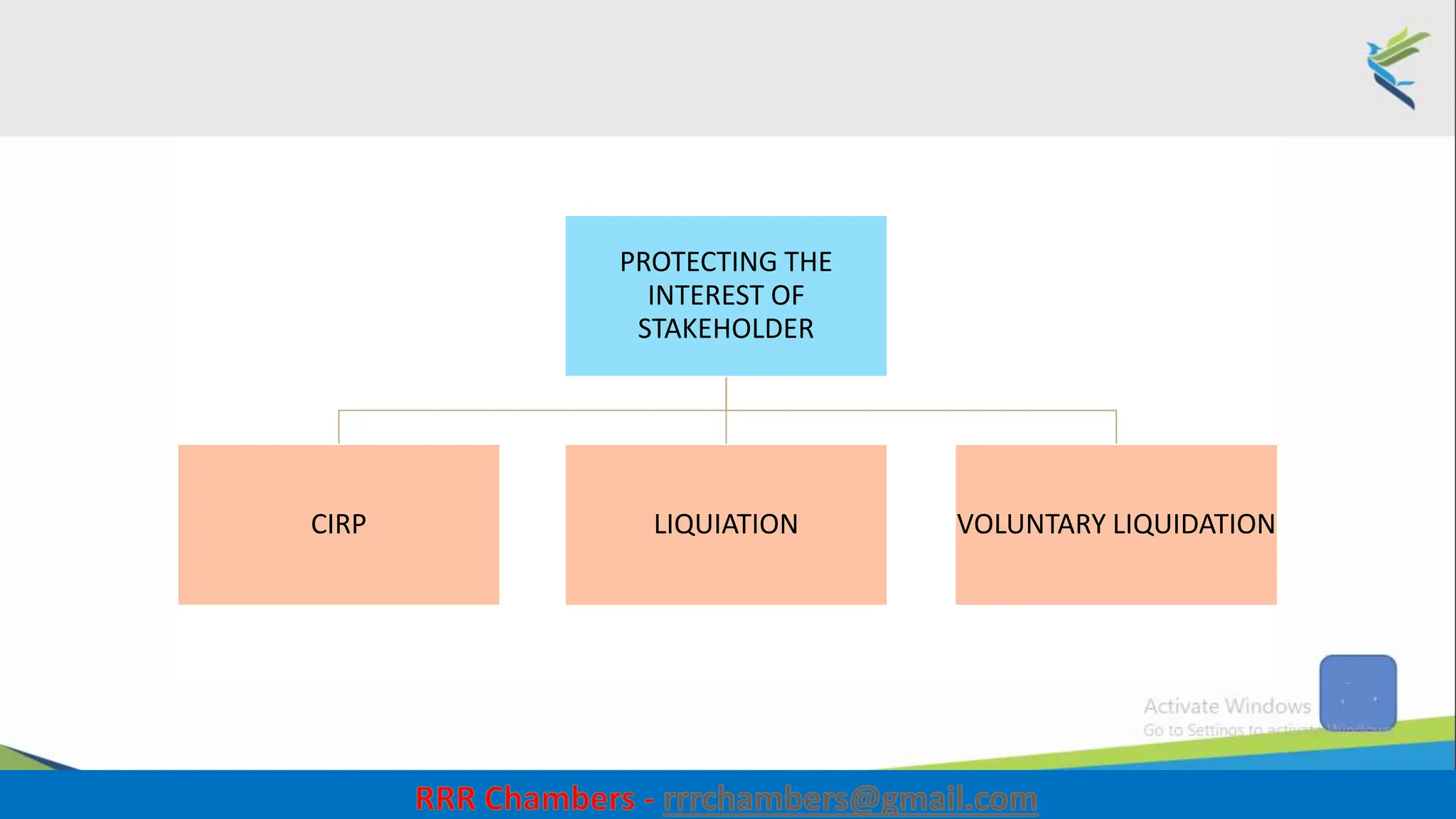
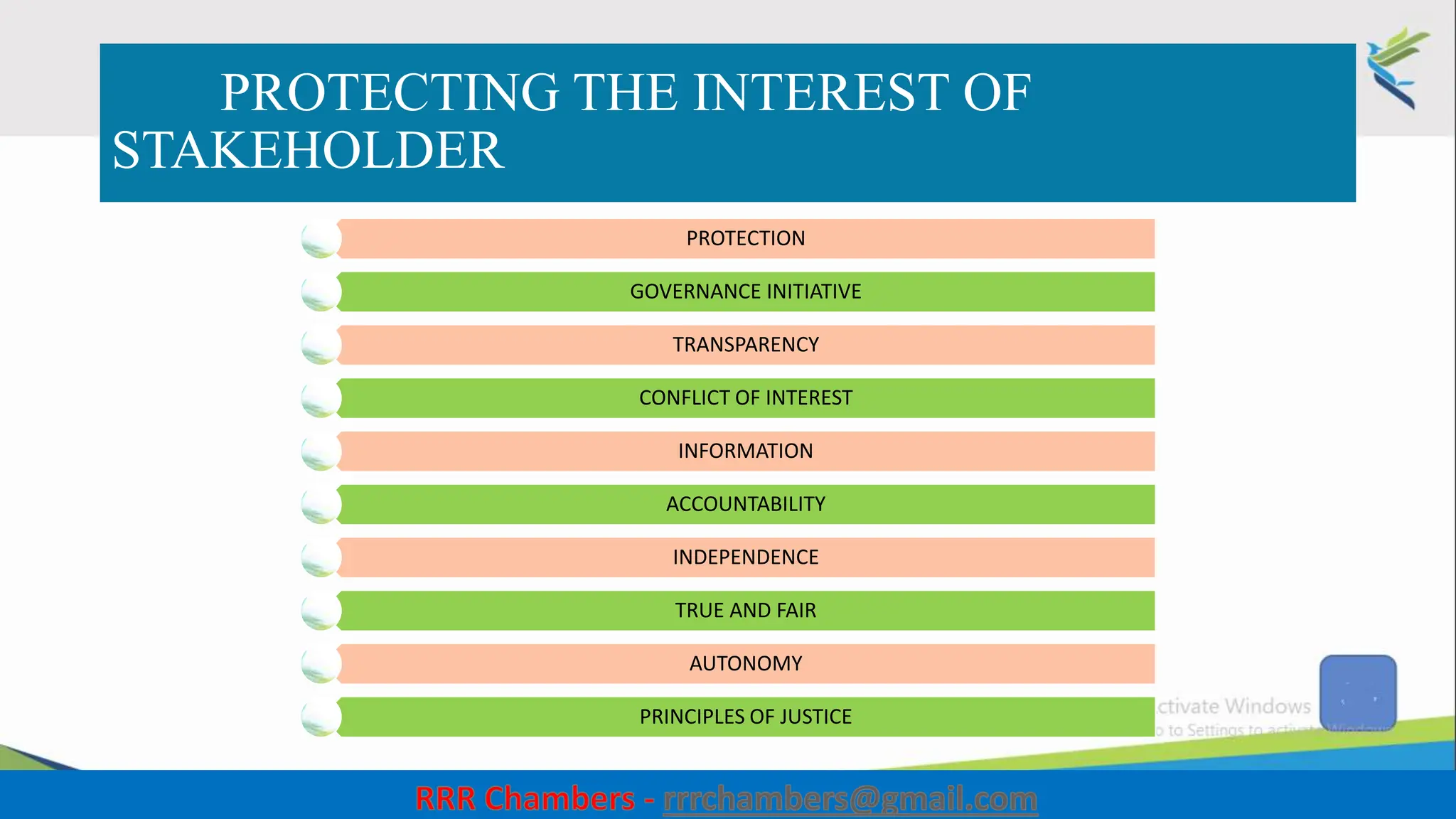
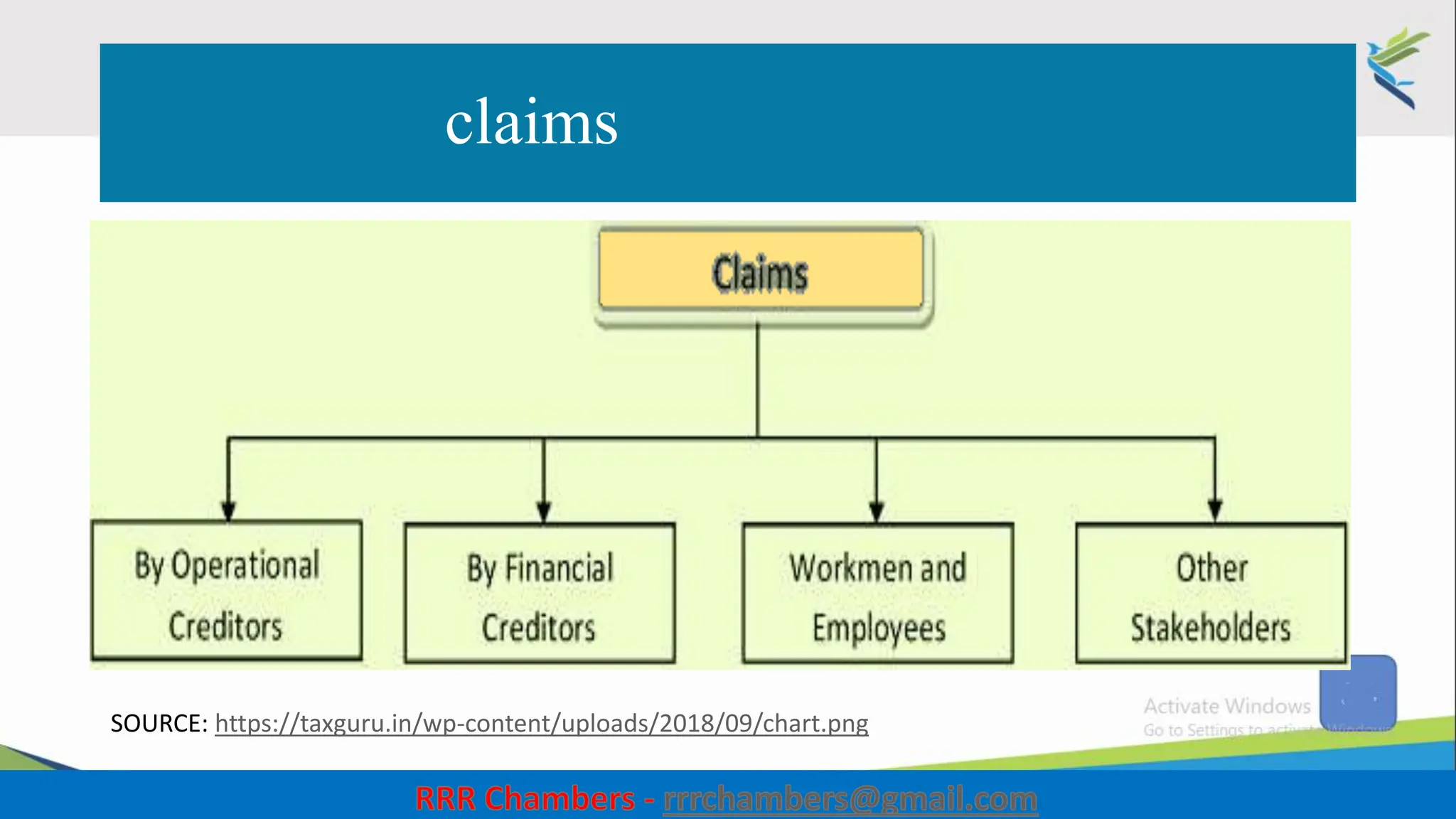
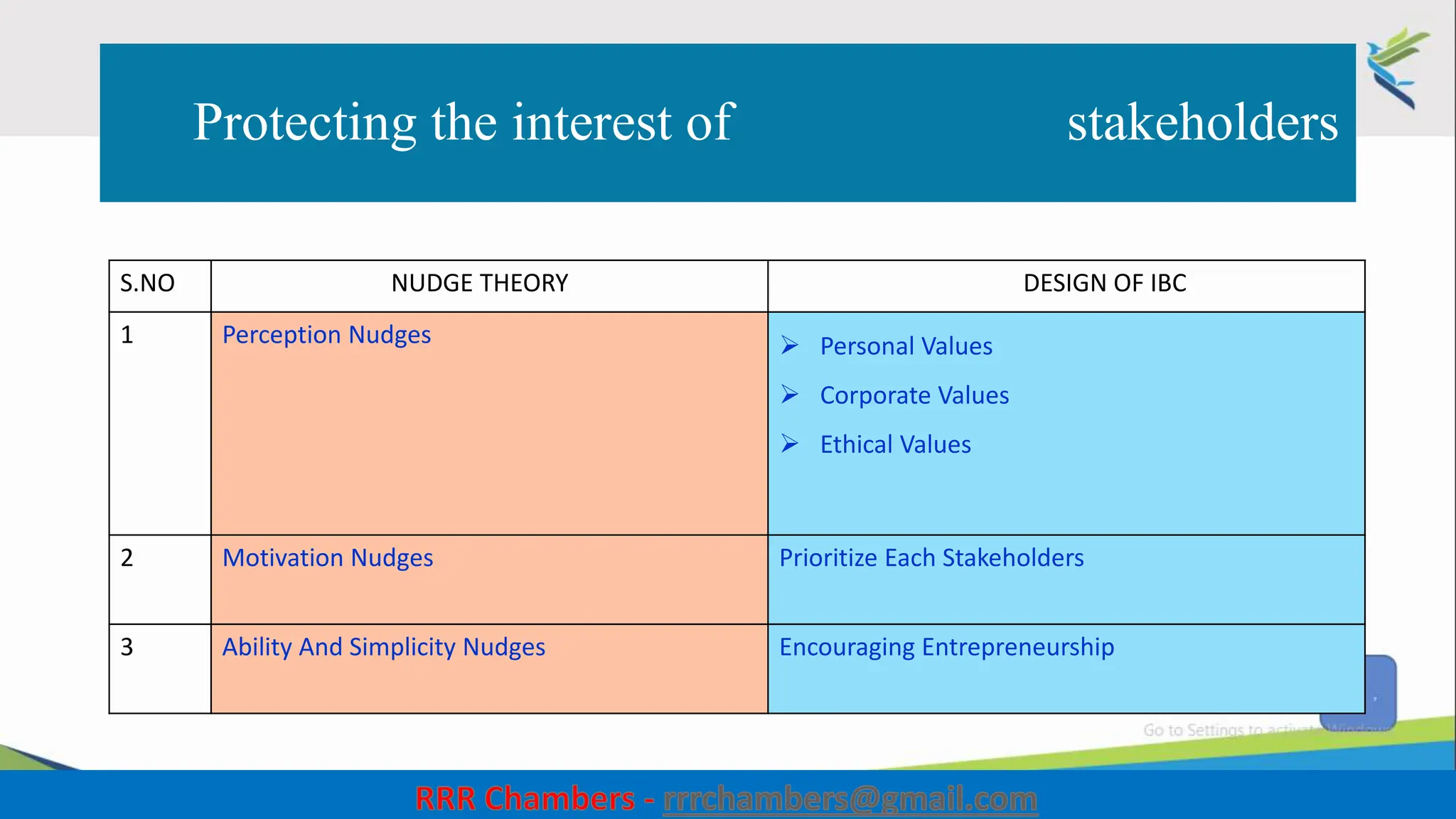
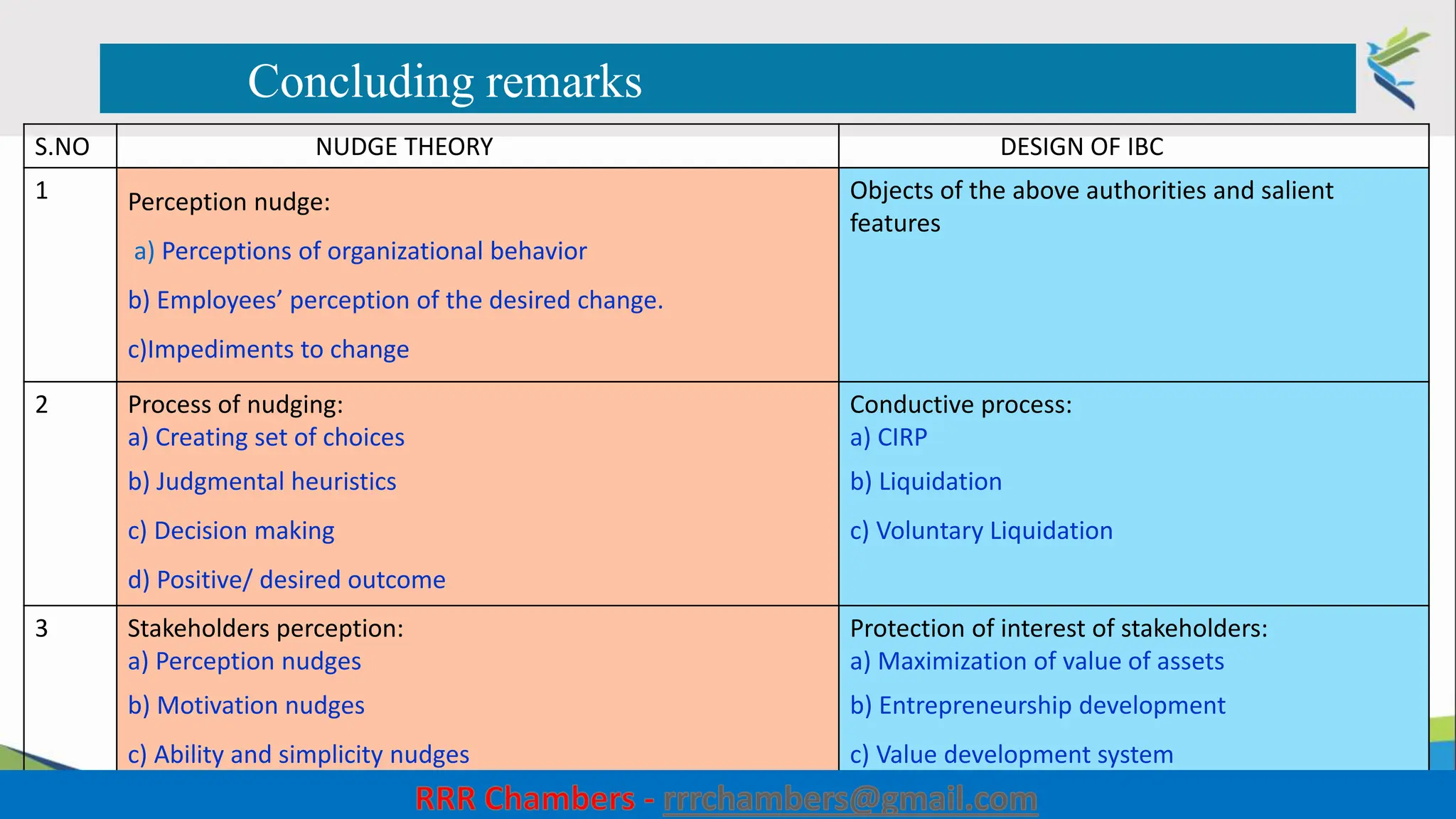
The document outlines the design of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) as a process for protecting stakeholder interests in India. It discusses nudging theory and its application in changing perceptions and behaviors within organizations, focusing on enhancing corporate governance and promoting entrepreneurship. Key objectives include fixing timelines for insolvency resolution, maximizing asset value, and balancing stakeholder interests through a structured and transparent approach.