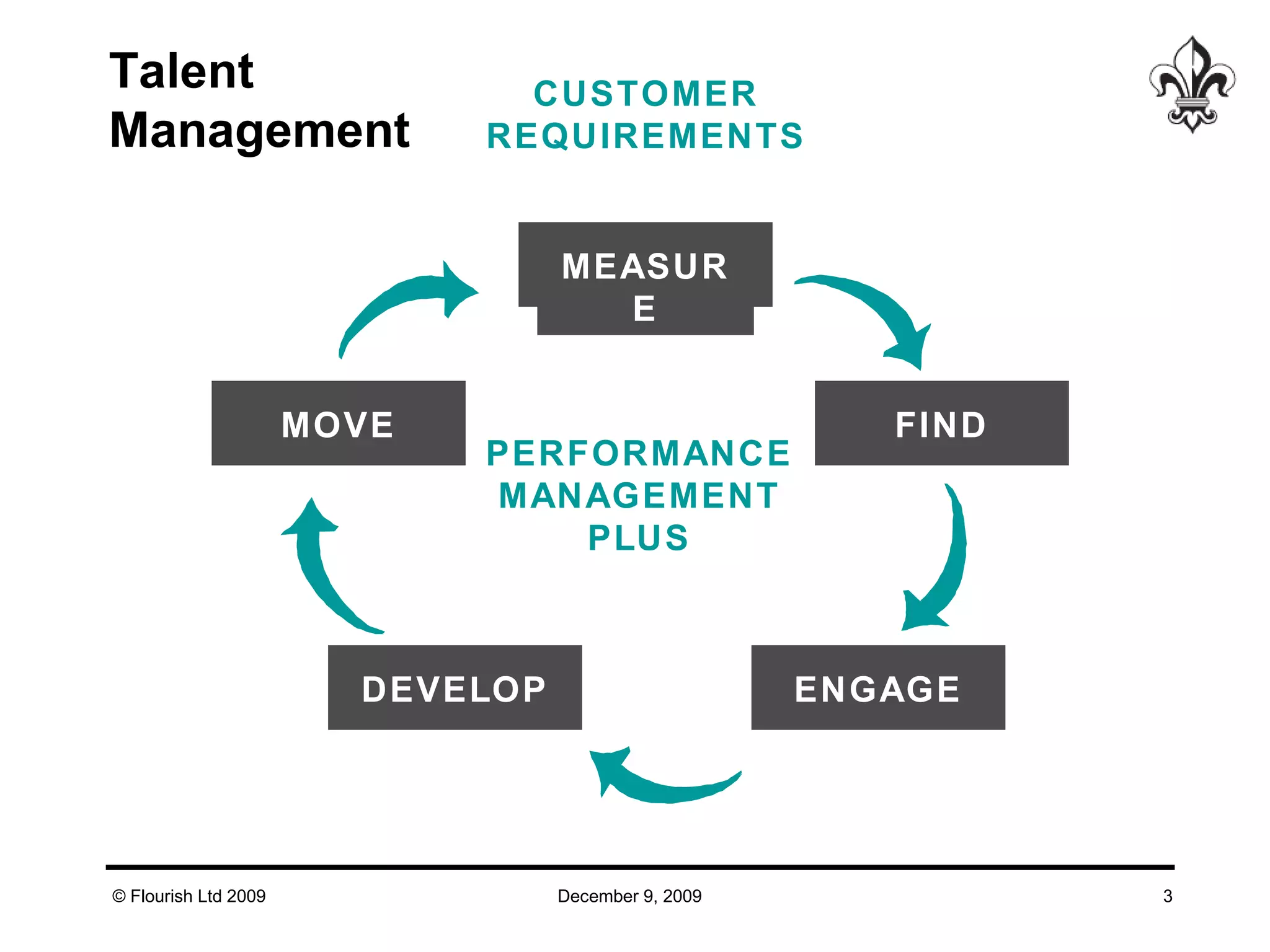
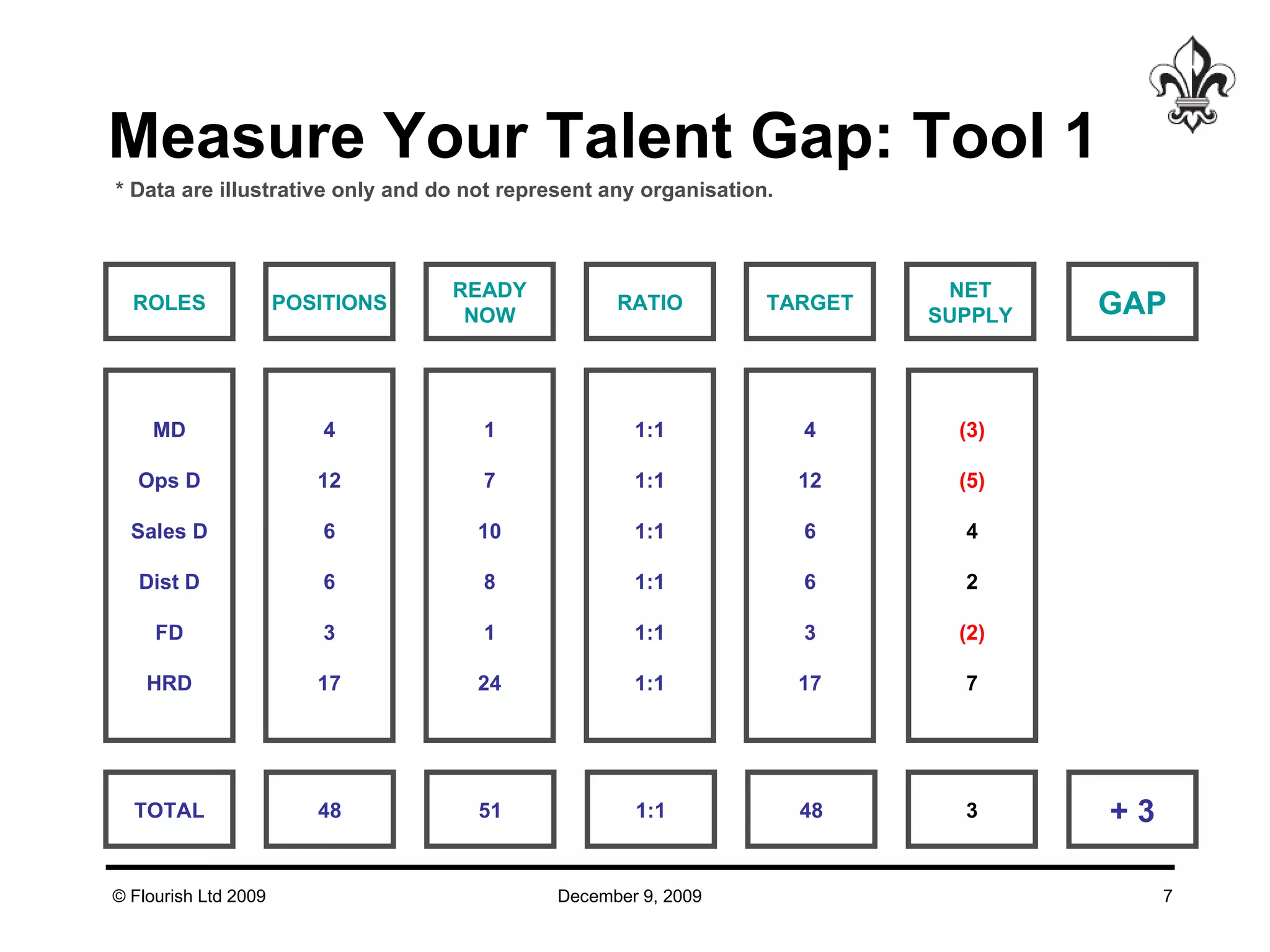
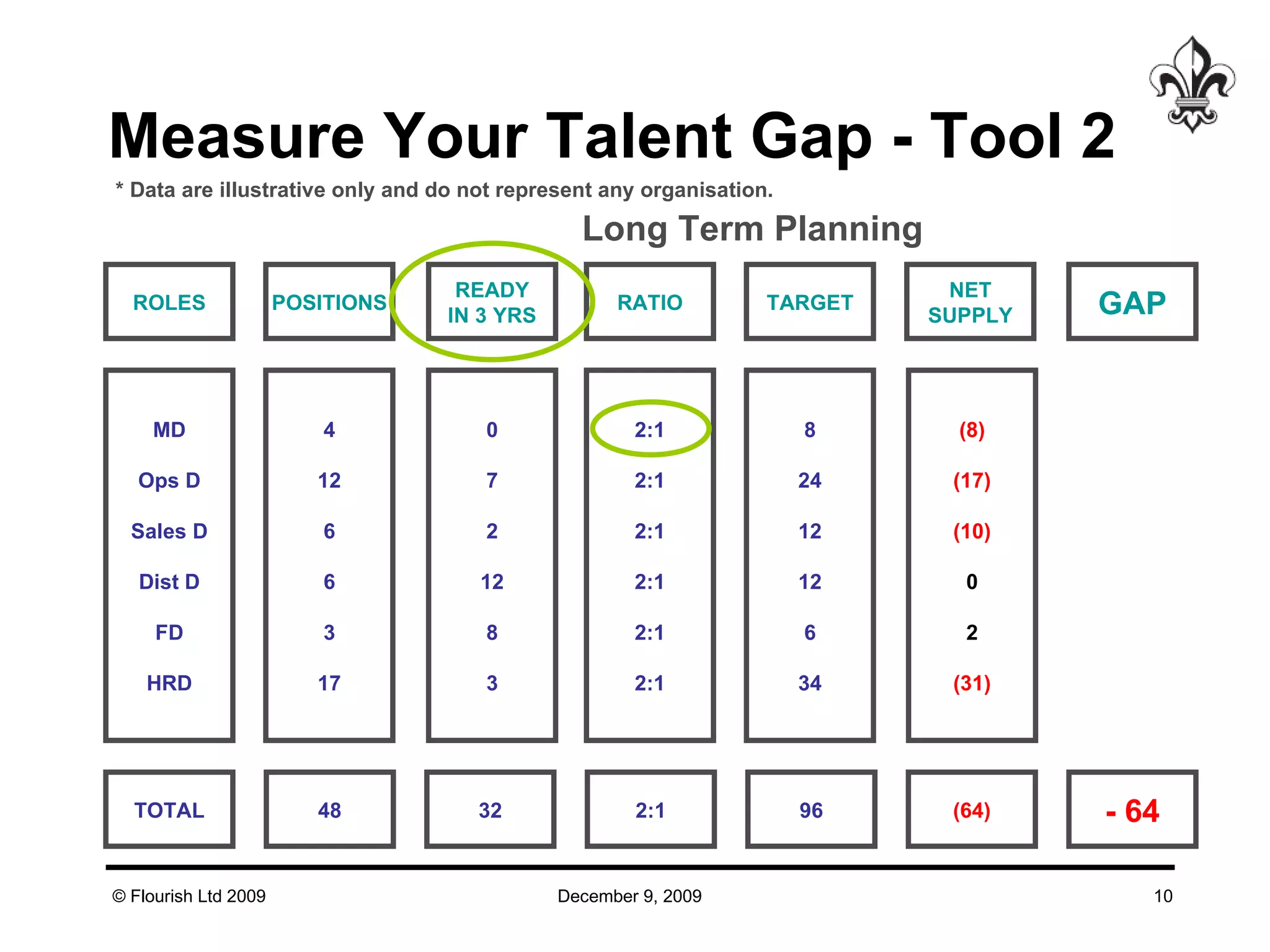
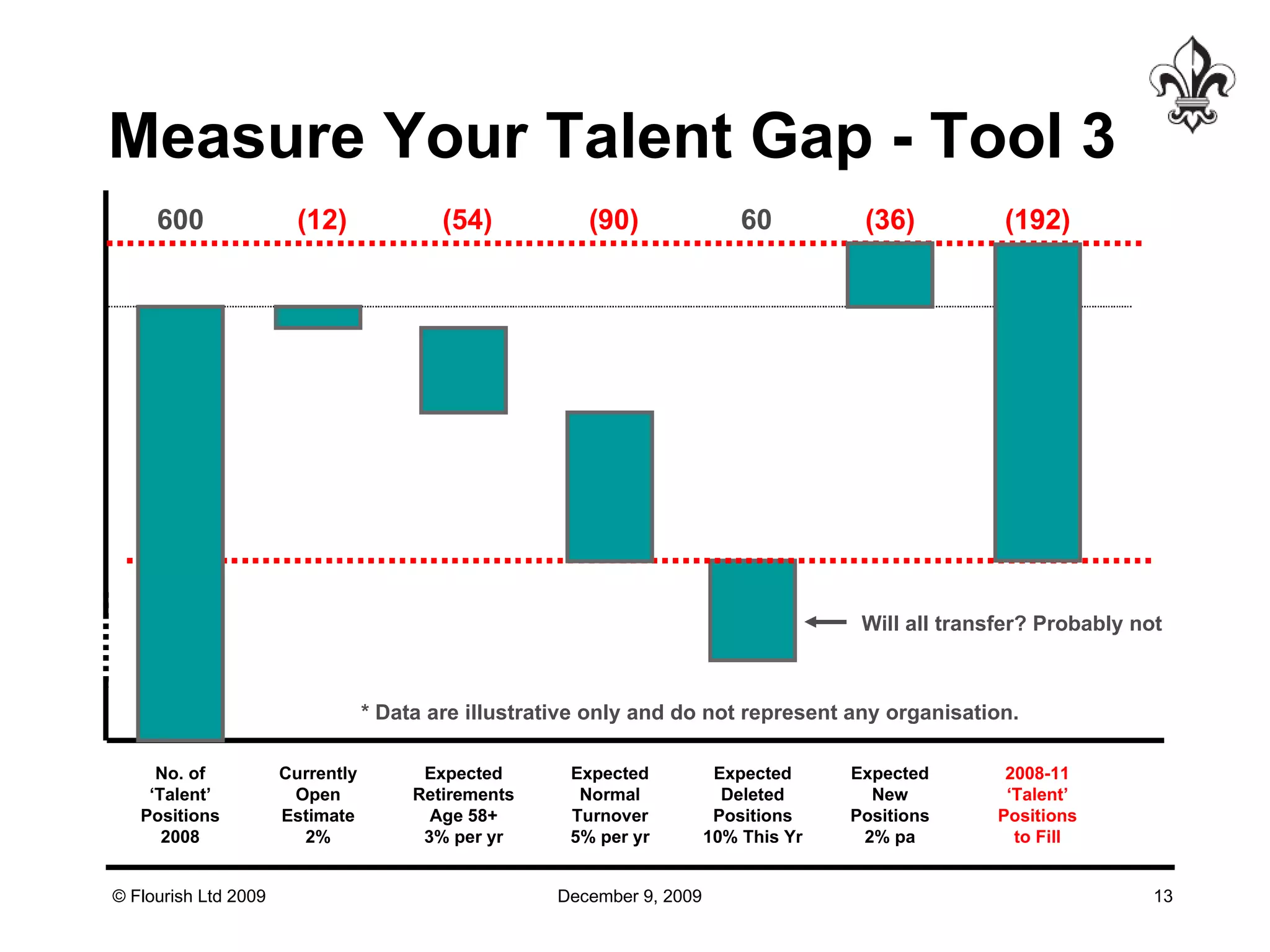
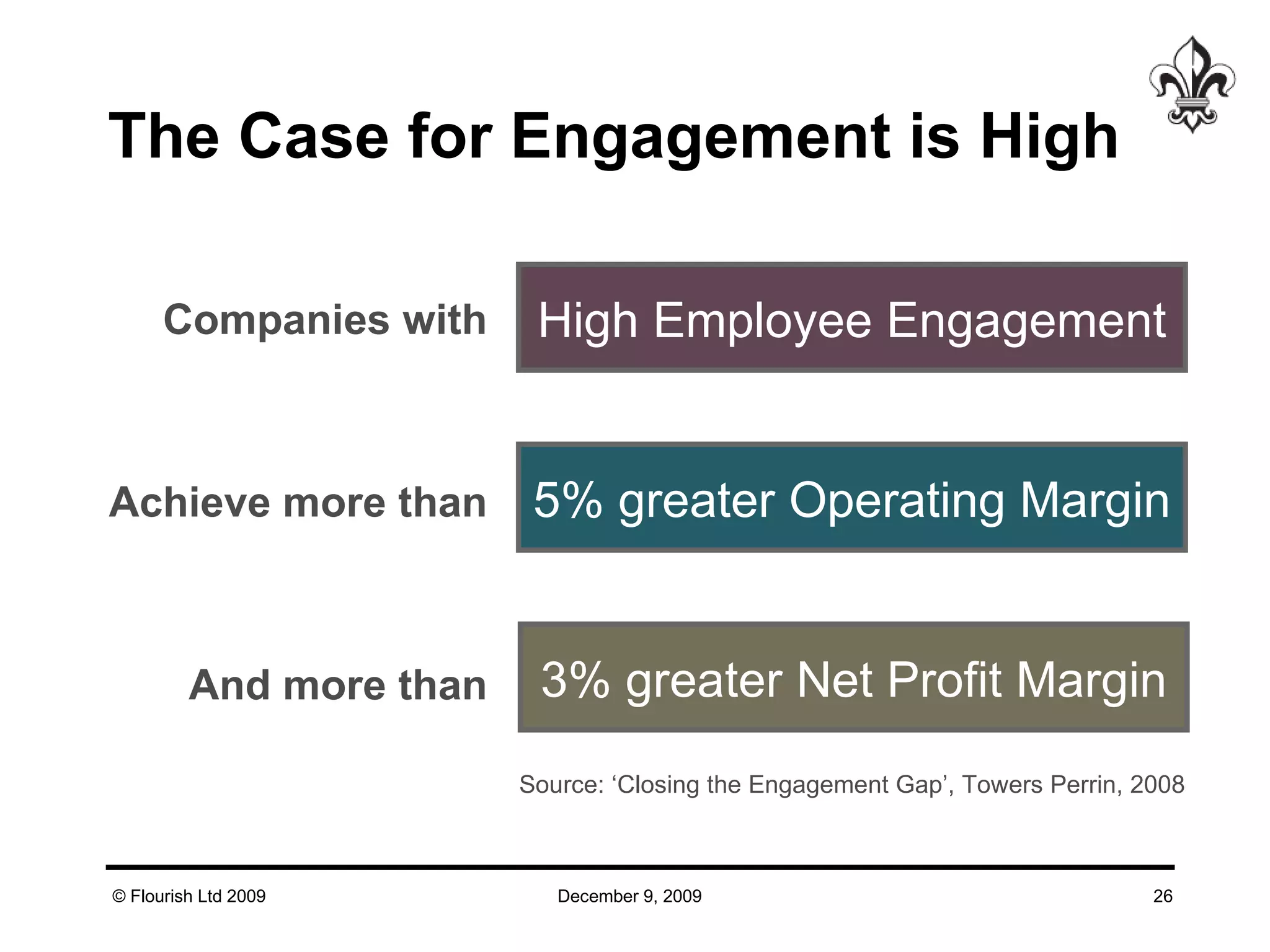
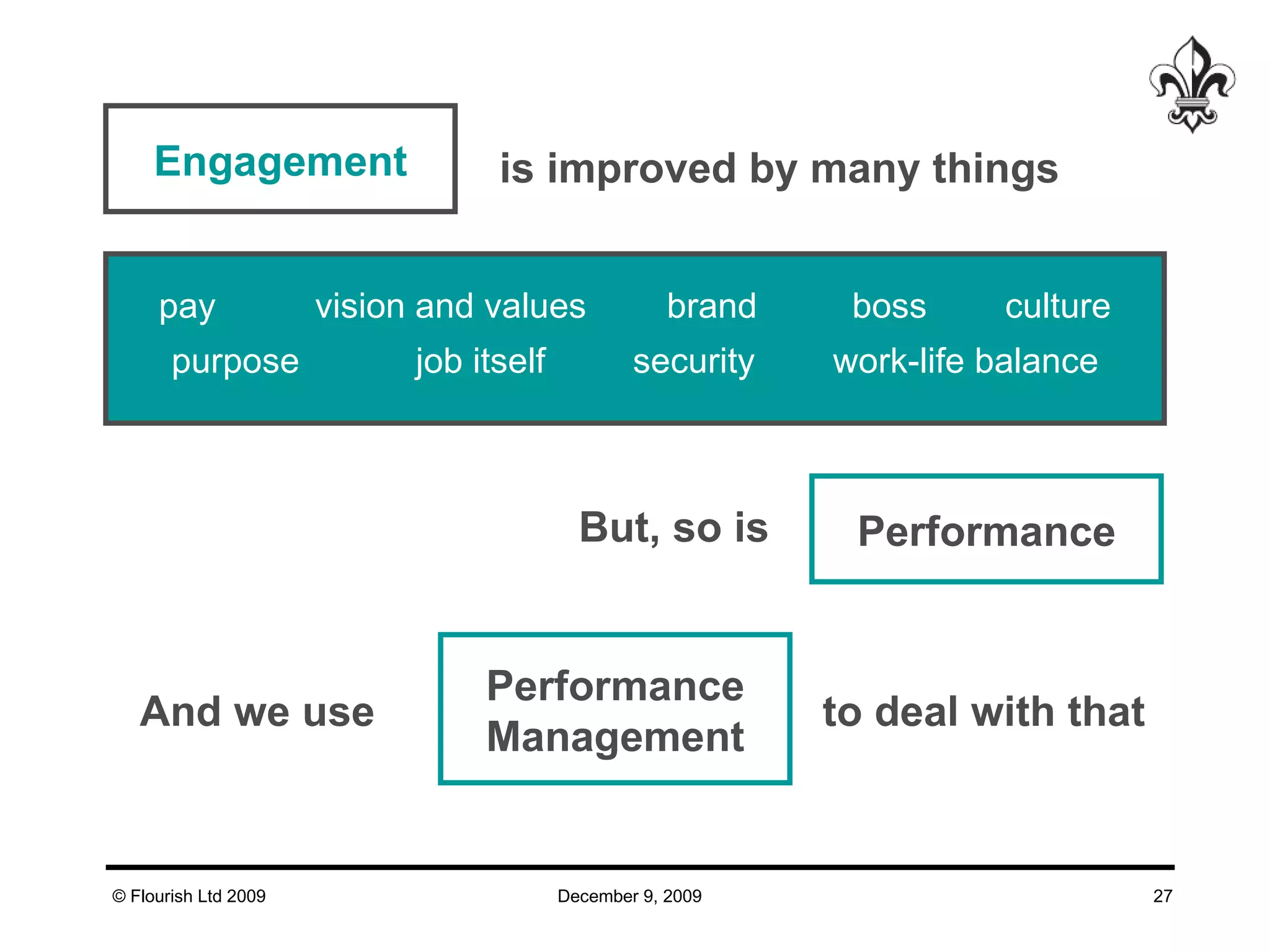
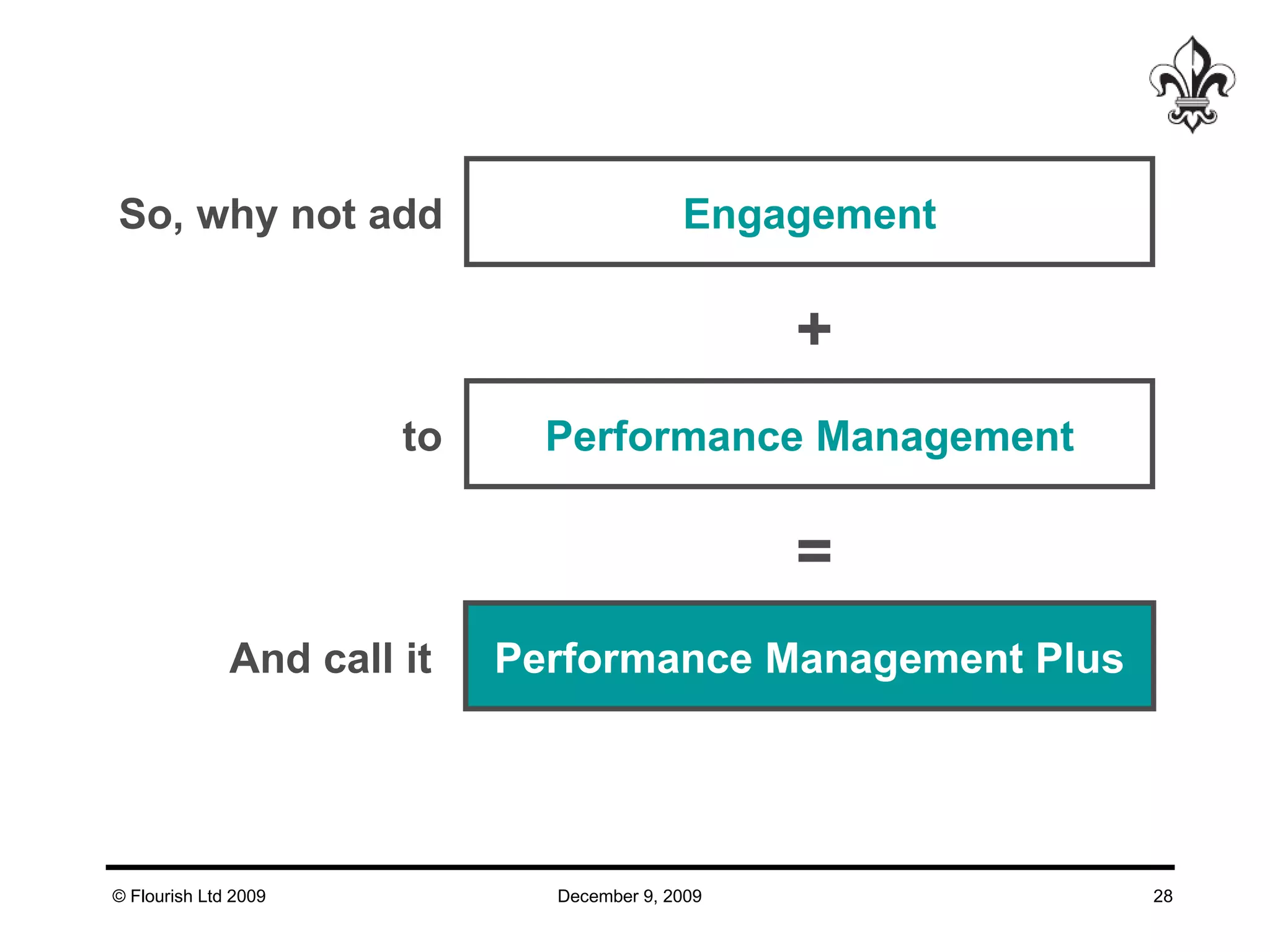
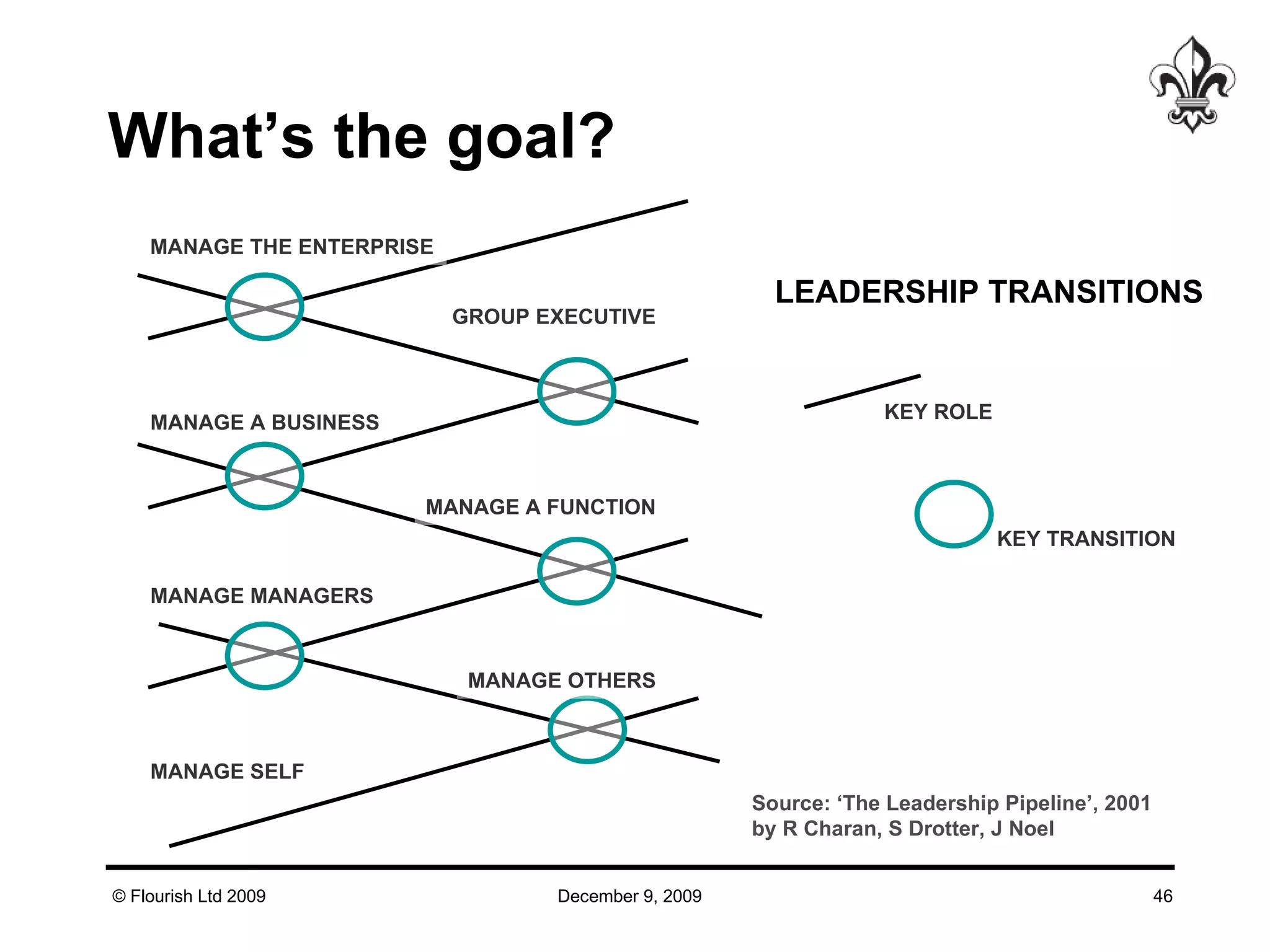
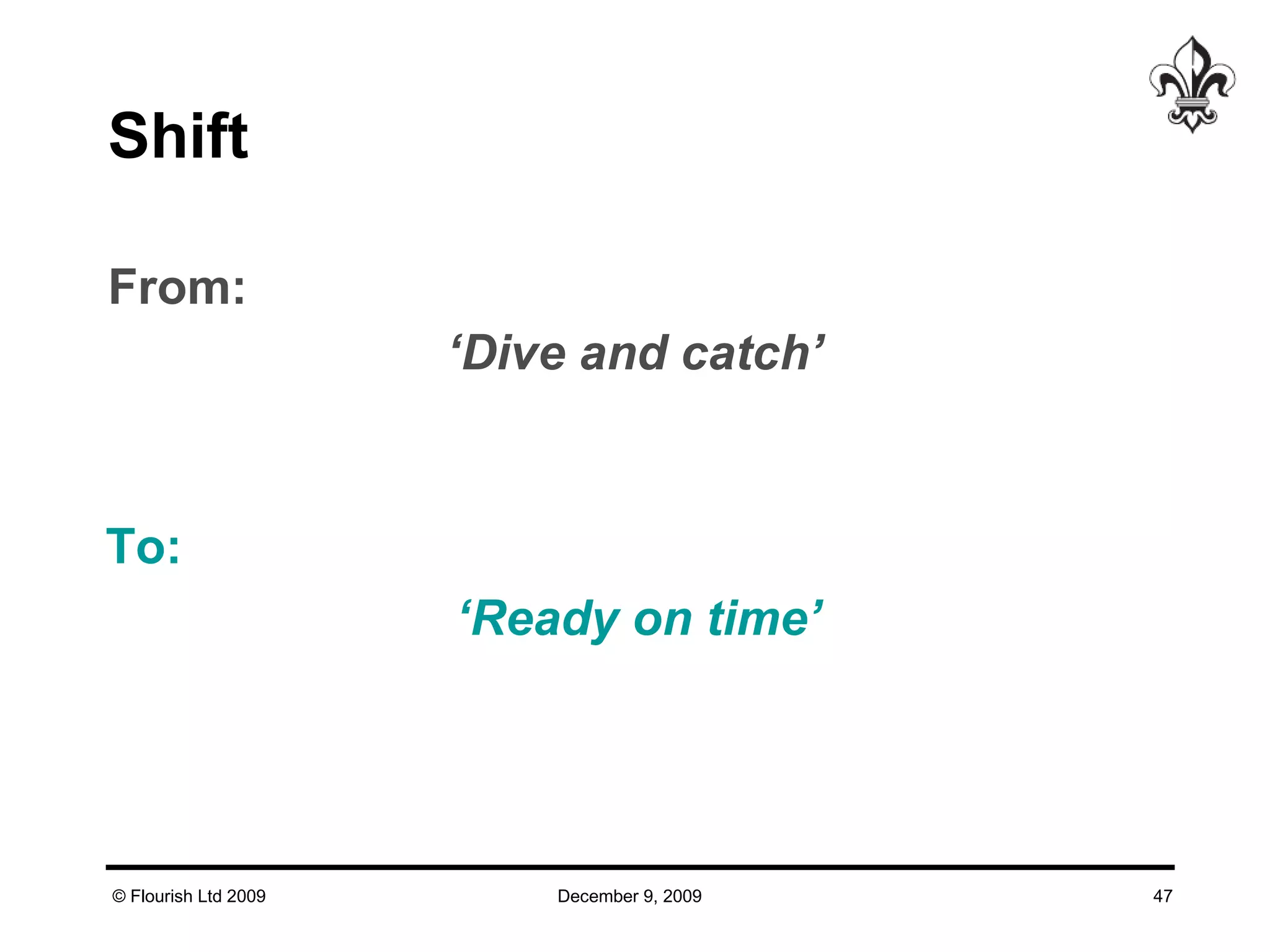
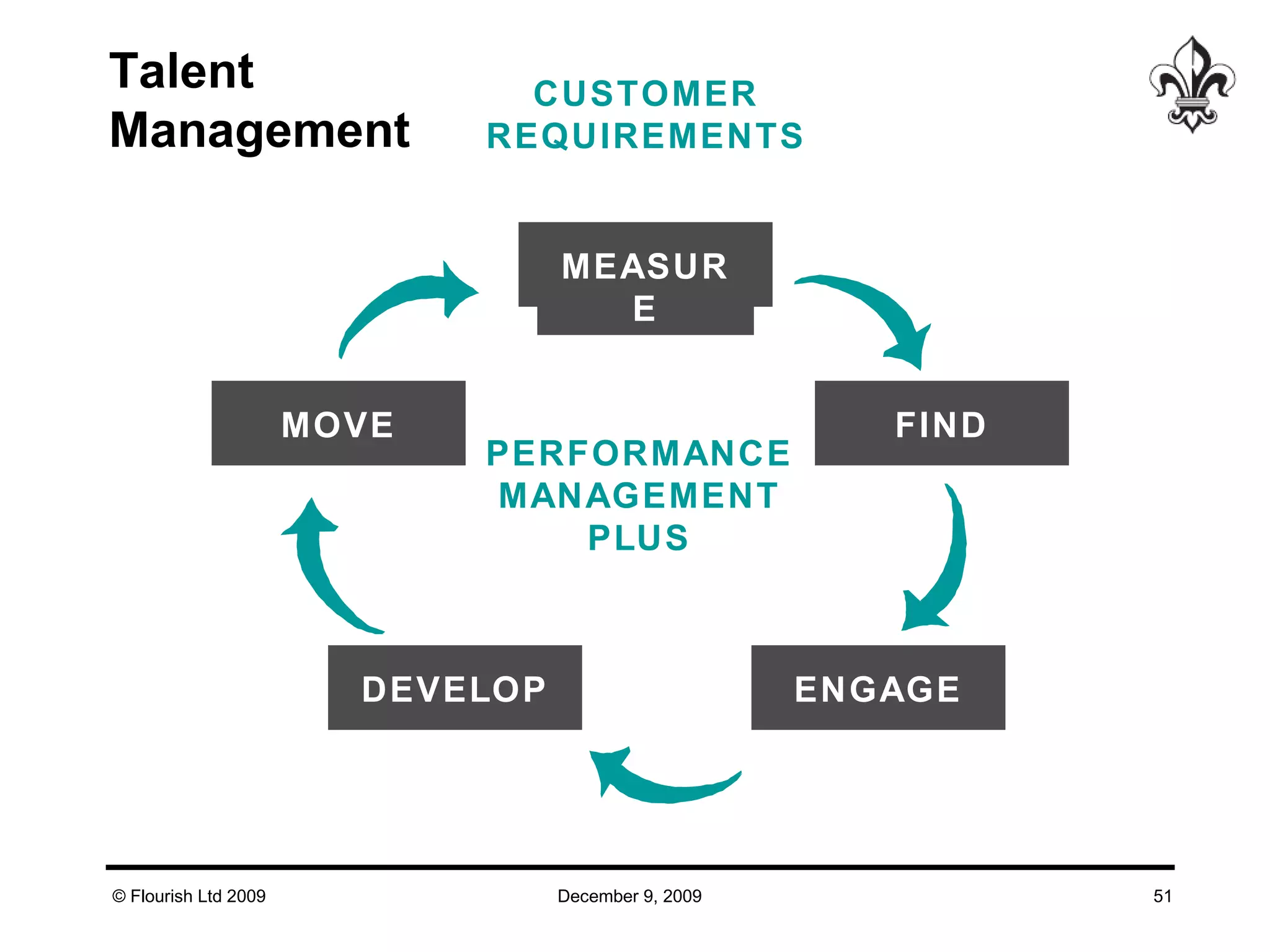
The document discusses effective strategies for managing leadership talent, offering practical tools to assess and bridge talent gaps within organizations. It emphasizes the importance of engagement, measurement, and aligned development methods to elevate performance management. Additionally, it highlights the responsibilities of line management in talent management and ways to foster a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability in leadership roles.






































![For more information: www. flourishltd .com tim . [email_address] .com Flourish provides solutions for: Executives Leaders HR business partners Consultants, coaches and facilitators We have expertise in: Leadership Development Talent Management Employee Engagement Organisation Development Tim Coburn has more than 20 years experience in senior positions at the BBC, Motorola and Rolls-Royce in talent management, leadership development, OD and learning and development. He is Managing Director of Flourish, a specialist provider of high value performance and development solutions. He is a Visiting Fellow at the International Centre for Talent Management and Development at Nottingham Business School, England.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ManagingLeadershipTalent-123660735148-phpapp01/75/Managing-Leadership-Talent-58-2048.jpg)