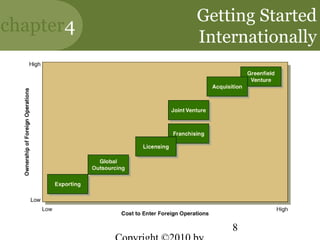
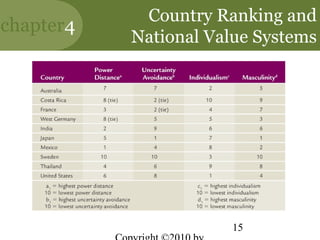
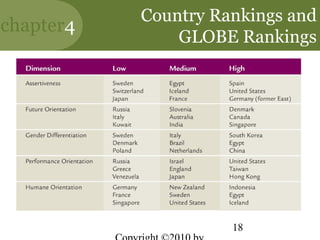
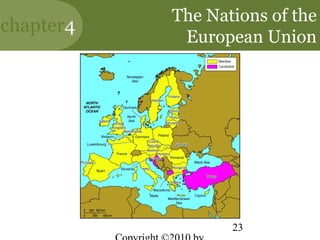
This chapter discusses managing in a global environment. It describes how the world is becoming increasingly borderless and globalized. Managers need cross-cultural skills and a global mindset. The chapter outlines different strategies for entering international markets and factors of the international environment that managers must consider, such as economic, sociocultural, and legal-political differences between countries. It also discusses trade alliances, multinational corporations, and developing cultural intelligence to manage successfully across cultures.