Embed presentation
Downloaded 36 times



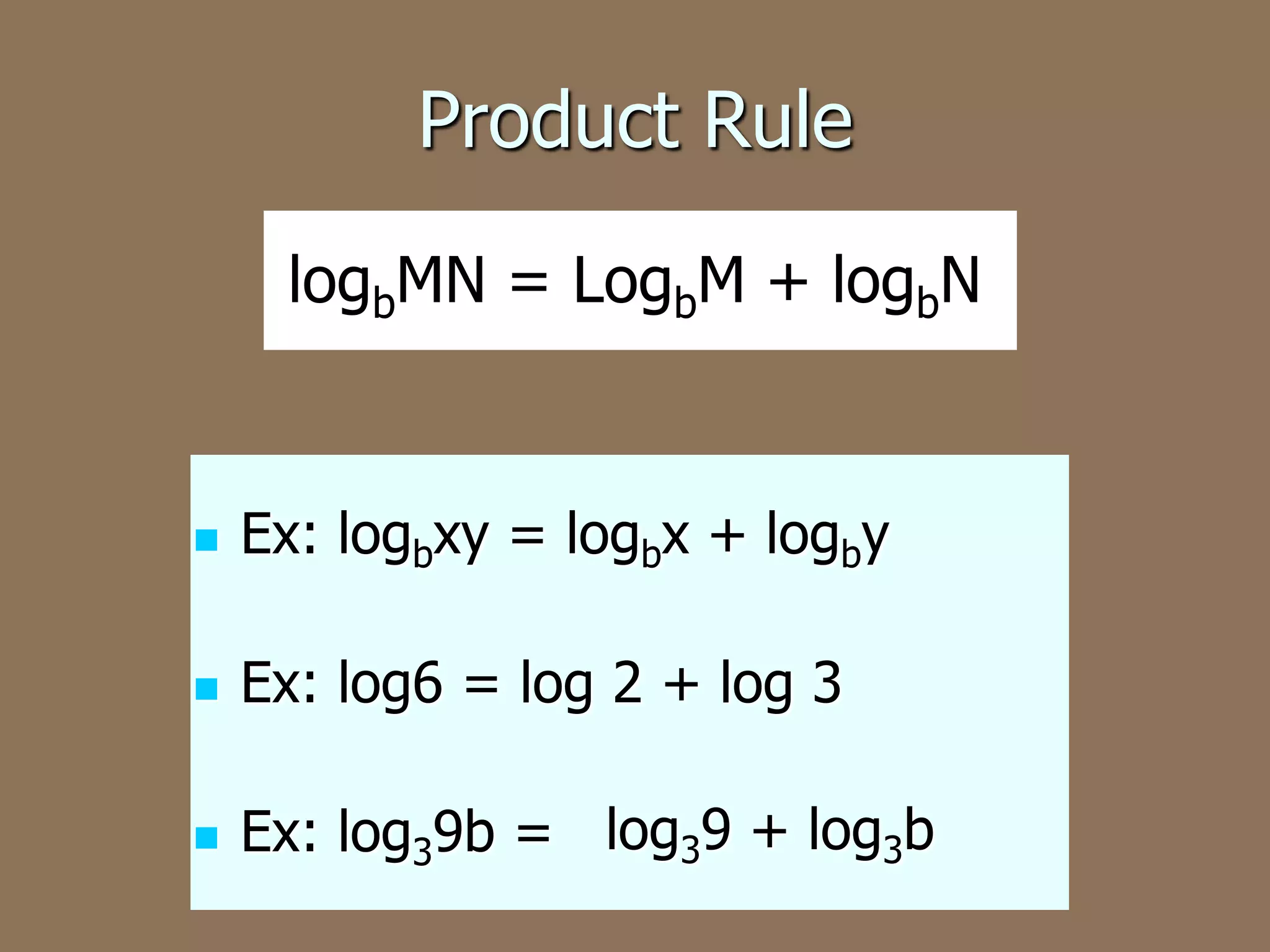
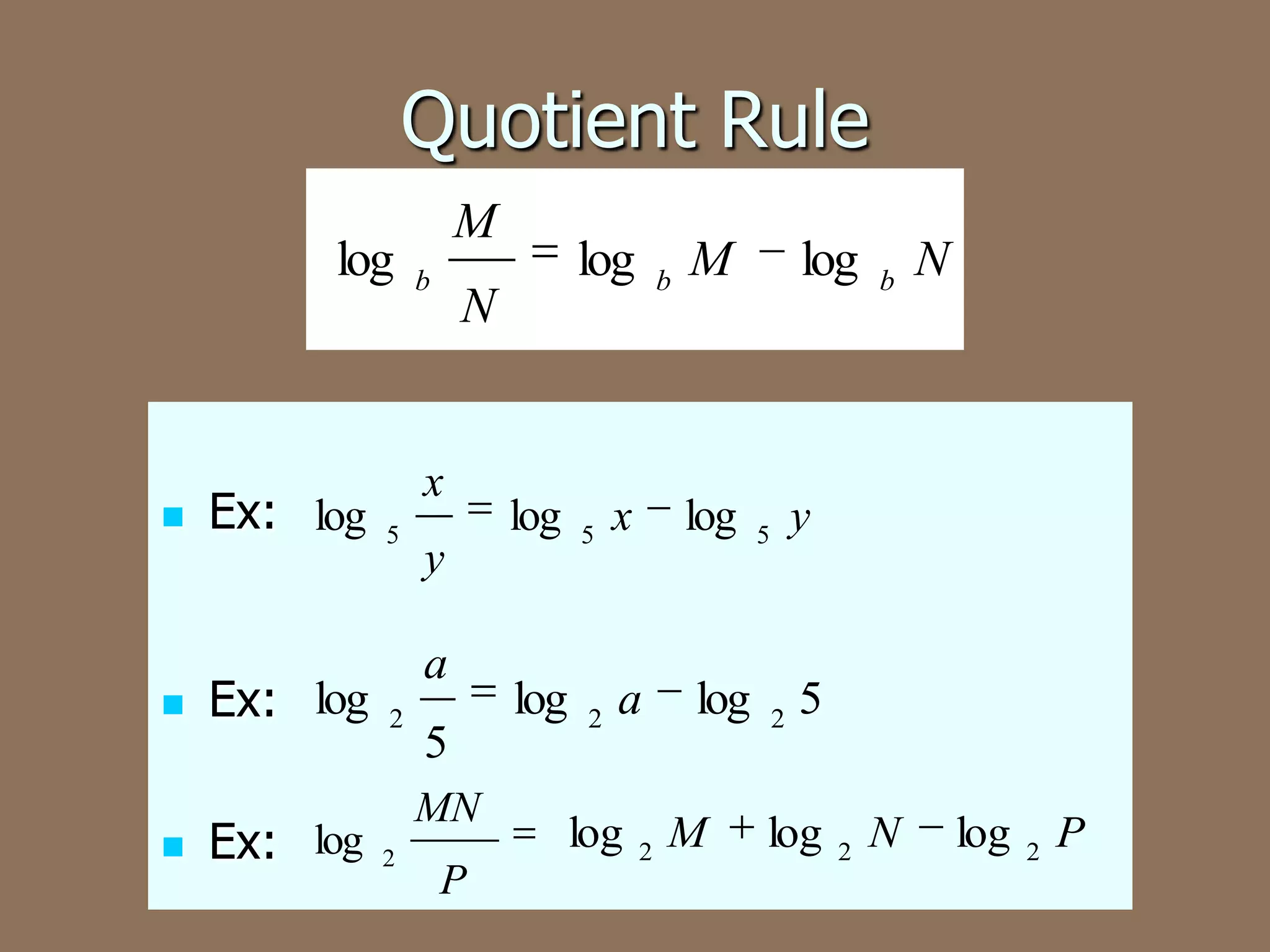
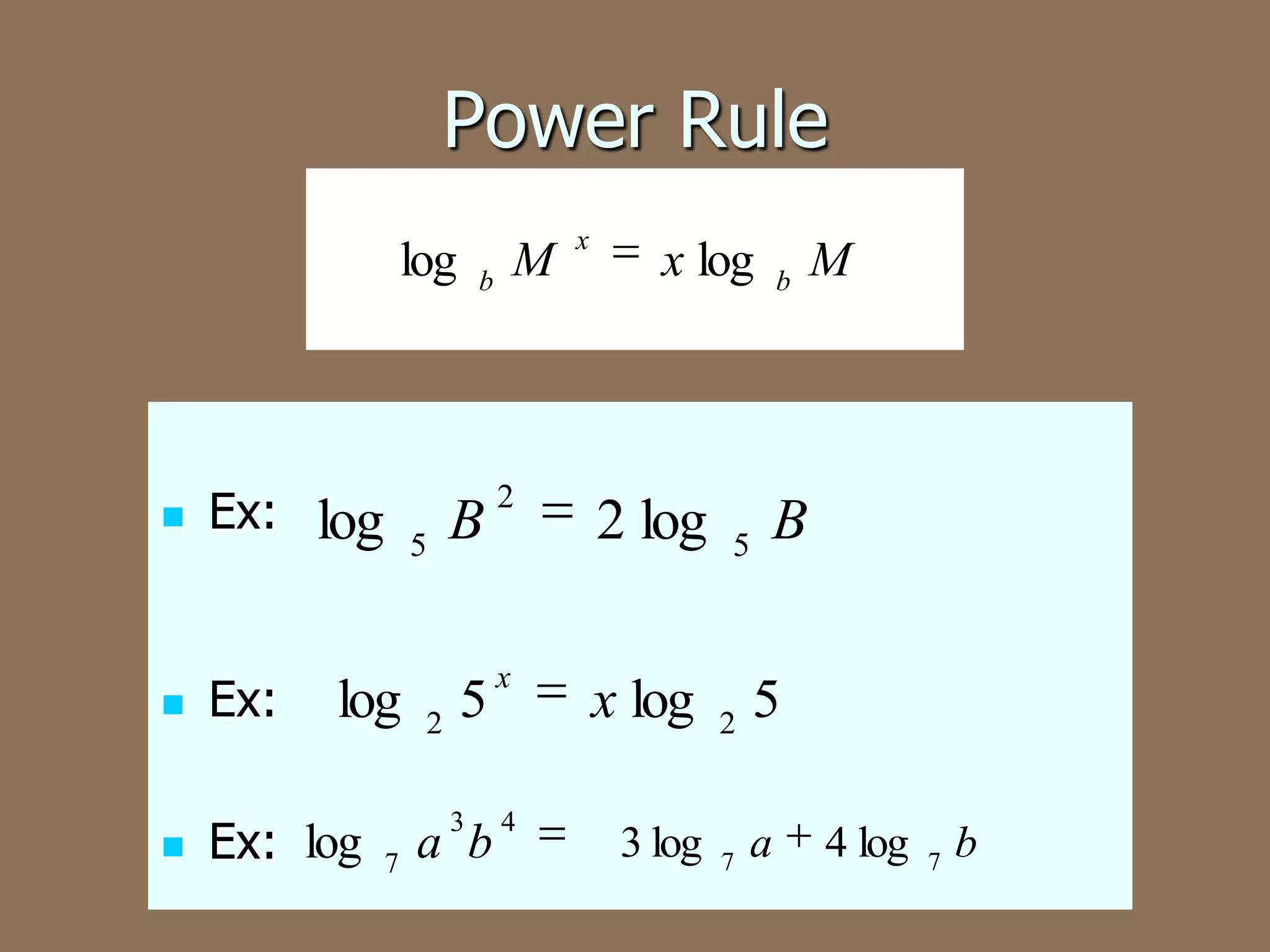




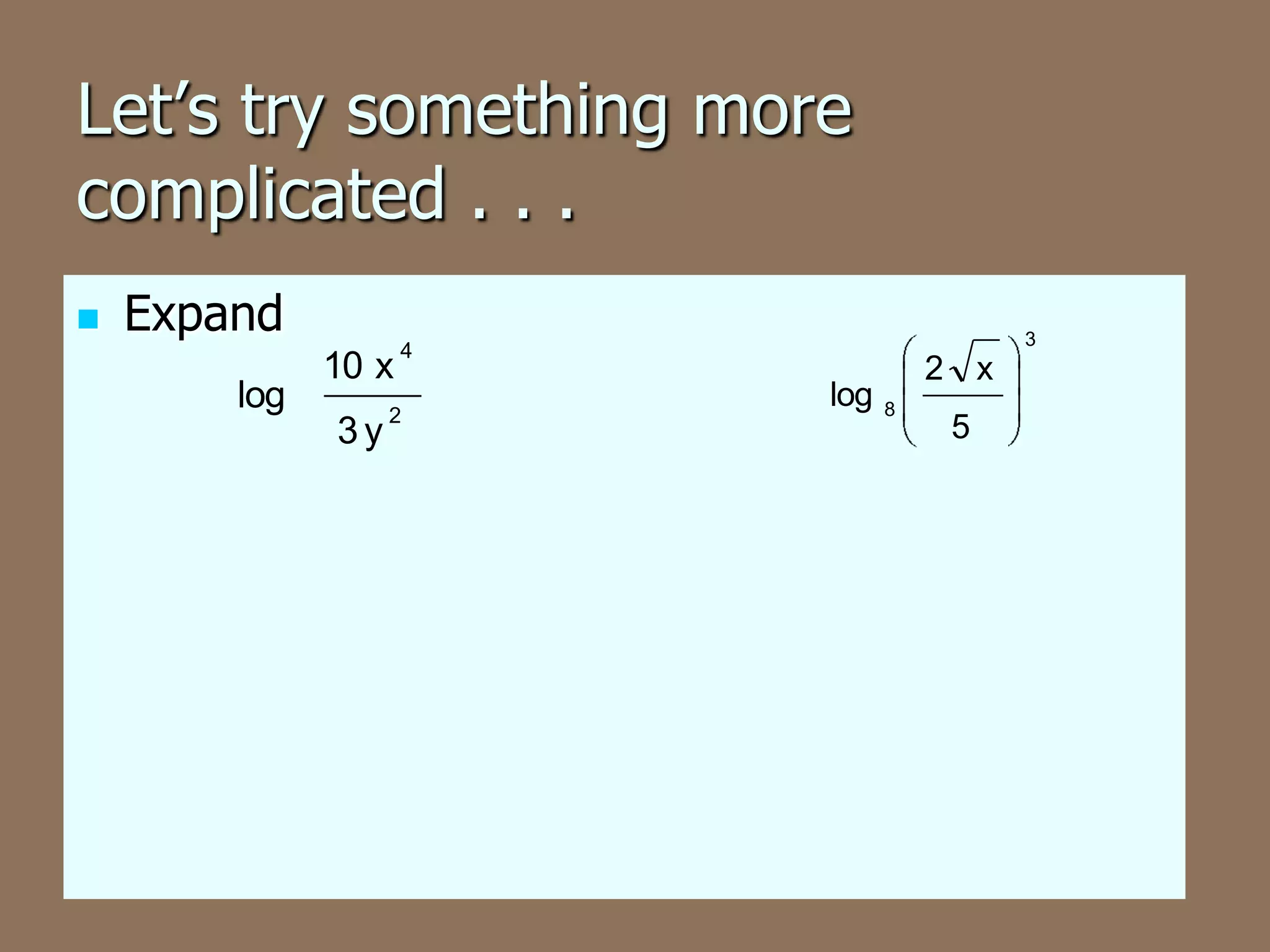
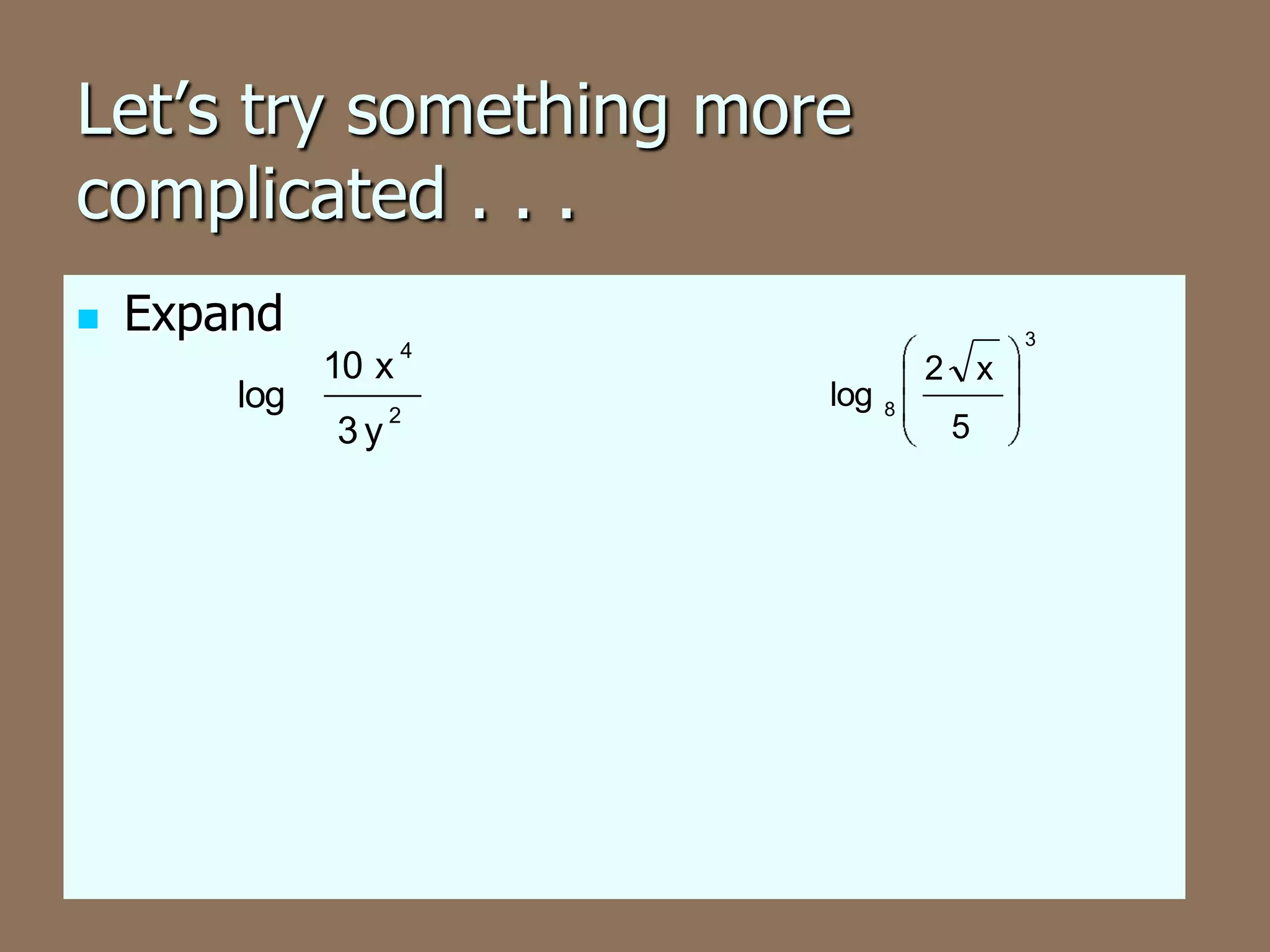
This document discusses the four basic properties of logarithms: the product rule, quotient rule, power rule, and examples of applying each rule to write logarithmic expressions as single logarithms or expand logarithmic expressions. More complex examples show condensing multiple logarithms using properties and expanding a logarithm using the rules.











