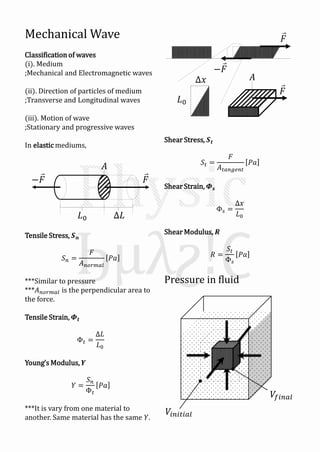
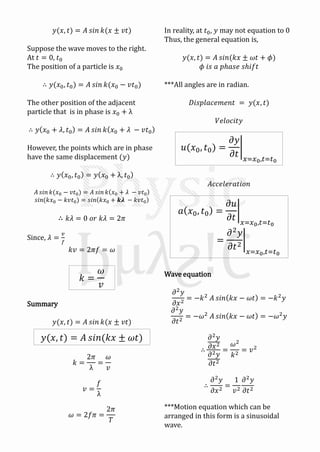
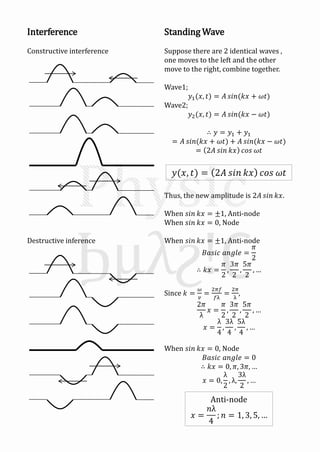
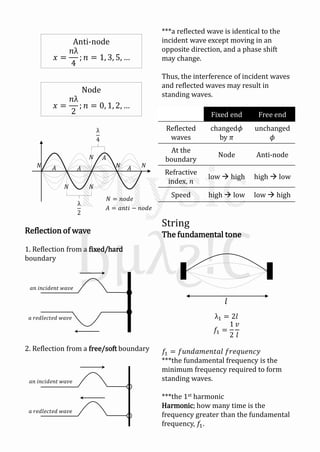
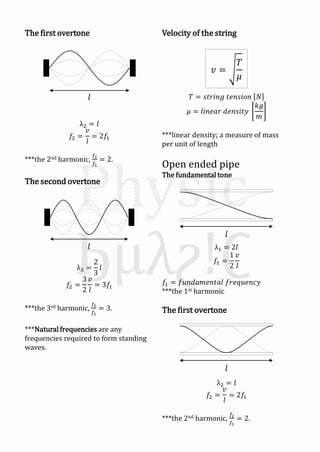
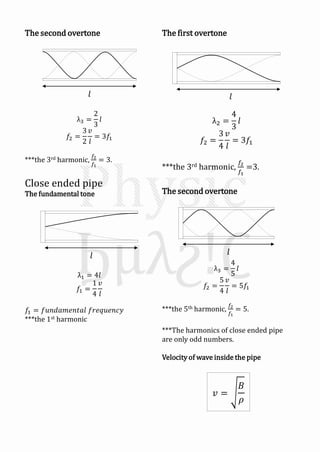
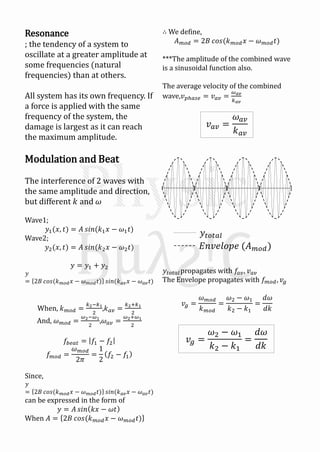
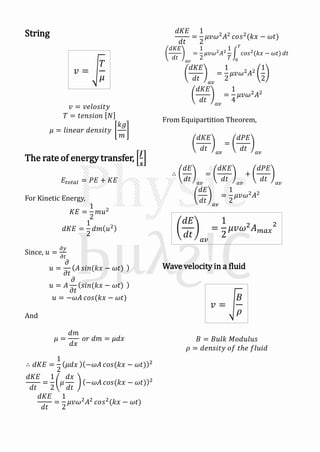
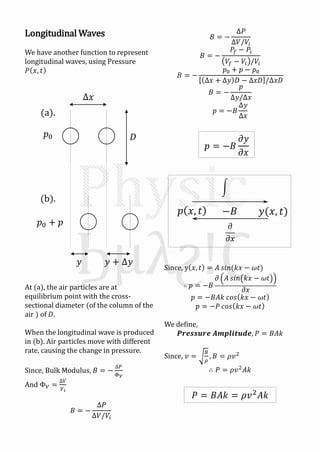
Mechanical waves can be transverse or longitudinal depending on the direction of particle motion in the medium. A sinusoidal wave equation describes mechanical waves as y=Asin(kx±ωt), where y is displacement, A is amplitude, k is wave number, x is position, t is time, and ω is angular frequency. The speed of the wave v is related to its wavelength λ and frequency f by v=fλ. When two identical waves traveling in opposite directions combine, they form a standing wave with antinodes and nodes fixed in space described by y=2Asinkx cosωt.