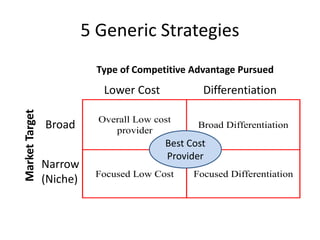
This document discusses competitive strategies that firms can pursue, including developing a cost advantage or differentiation advantage over competitors. It describes five generic strategies of overall low cost, differentiation, focused low cost, and focused differentiation. Key aspects of developing a cost advantage include controlling cost drivers through economies of scale, learning curves, and reconfiguring the value chain. Differentiation strategies involve focusing activities to meet customer needs better than competitors. Focused strategies target a niche market segment with either lower costs or a differentiated product.