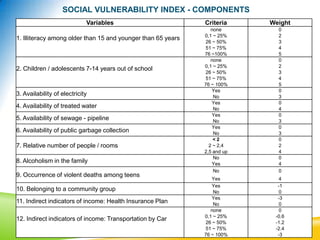
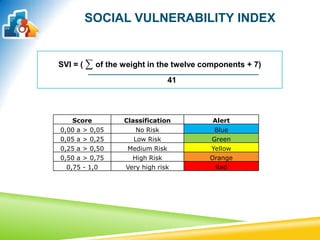
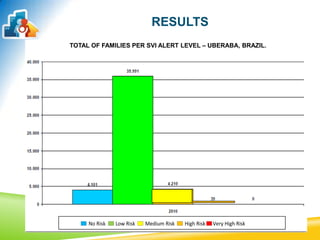
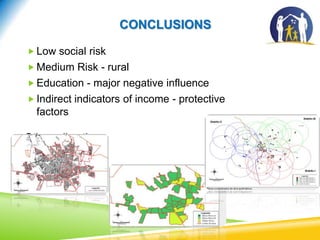
This document discusses using the Social Vulnerability Index (SVI) to analyze the population served by Family Health Teams in Brazil. It analyzed data from 50 Family Health Teams in Uberaba, Brazil serving 156,720 people. The results showed most families had low or no social risk, while rural areas faced medium risk. Education level and indirect income indicators like health insurance and car ownership were the most influential factors on social vulnerability. The SVI can help identify at-risk groups and target resources to improve health equity.