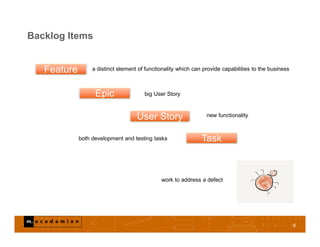
This document discusses Agile requirements management. It provides an overview of key Agile concepts like the product backlog, backlog items, acceptance criteria, and how requirements work in Scrum. The product backlog is an ordered list of everything needed in the product and is the single source of requirements. Acceptance criteria define when a user story is complete. Requirements in Agile are dynamic, visible to all, and the single source of truth. The document also discusses managing the backlog over time through progressive refinement and decomposition.