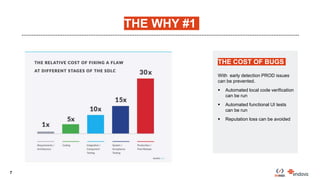
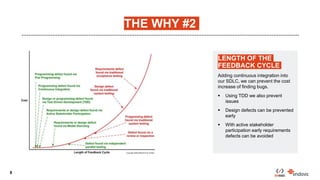
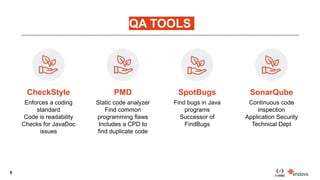
This document discusses code quality improvements made to the Client Engagement Platform. The challenges included stabilizing the risk and commercial engine, integrating continuous integration with Azure DevOps, and complying with various policies. The approach taken was to increase engine stability through automated testing, and increase quality using QA tools and continuous integration. QA tools used included CheckStyle, PMD, SpotBugs, and SonarQube. Lessons learned included not treating any tool as a silver bullet, focusing on the highest impact issues using the 80/20 rule, and creating unit tests for new code.