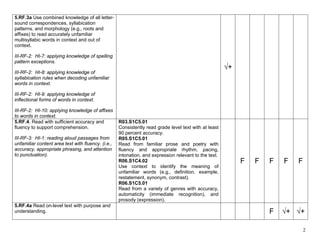
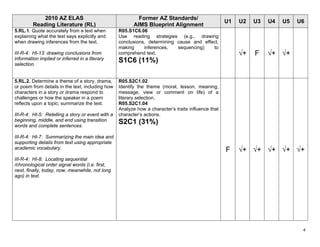
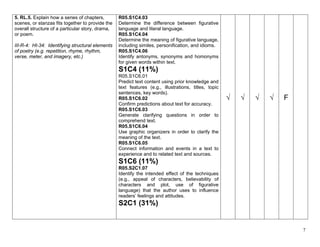
The document provides an alignment checklist for 5th grade ELAS standards and former Arizona standards. It shows the alignment of 2010 Arizona English Language Arts standards to previous Arizona standards and AIMS blueprint. Standards are organized by strands including Reading Foundations, Reading Literature, and Reading Informational Text. Cells are marked to indicate units of instruction where standards will be taught.









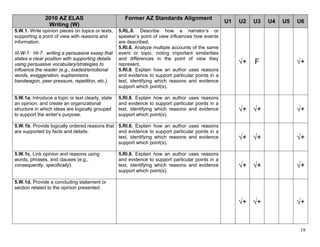




![5.W.8. Recall relevant information from 5.RI.1. Quote accurately from a text when
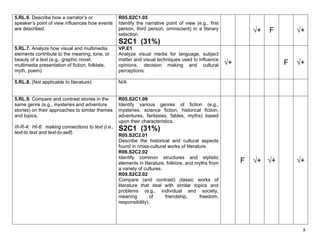
experiences or gather relevant information explaining what the text says explicitly and
from print and digital sources; summarize or when drawing inferences from the text.
paraphrase information in notes and finished 5.RI.7. Draw on information from multiple print
work, and provide a list of sources. or digital sources, demonstrating the ability to
locate an answer to a question quickly or to
(III-W-5: HI-1: recording, evaluating and solve a problem efficiently.
organizing information, observations or 5.RI.9. Integrate information from several texts √+ √+ F
questions on a topic of student interest from on the same topic in order to write or speak
two or more sources (experiment, article, about the subject knowledgeably.
textbook, guest speaker, video, Internet,
interview, podcasts, etc.) for report/research
purposes.)
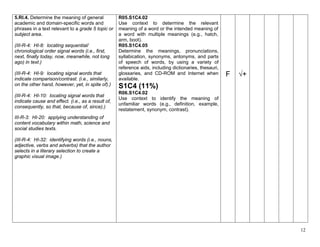
5.W.9. Draw evidence from literary or 5.RL.1. Quote accurately from a text when
informational texts to support analysis, explaining what the text says explicitly and
reflection, and research. when drawing inferences from the text.
5.RI.1. Quote accurately from a text when
explaining what the text says explicitly and
when drawing inferences from the text. √+ √+ √+ √+ √+ √+
5.RI.8. Explain how an author uses reasons
and evidence to support particular points in a
text, identifying which reasons and evidence
support which point(s).
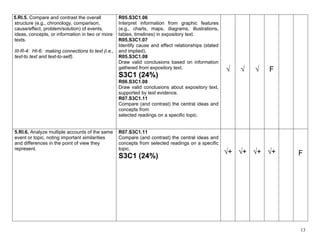
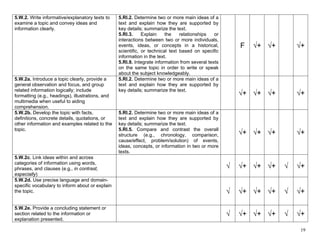
5.W.9a. Apply grade 5 Reading standards to 5.RL.1 thru 5.RL.10
literature (e.g., “Compare and contrast two or
more characters, settings, or events in a story
or a drama, drawing on specific details in the √+ √+ √+ √+ √+ √+
text [e.g., how characters interact]”).
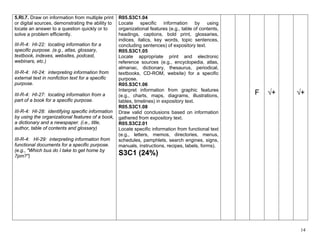
5.W.9b. Apply grade 5 Reading standards to 5.RI.1 thru 5.RI.10
informational texts (e.g., “Explain how an
author uses reasons and evidence to support
particular points in a text, identifying which √+ √+ √+ √+ √+ √+
reasons and evidence support which
point[s]”).
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5thgradechecklist-120530193654-phpapp01/85/5th-Grade-Checklist-24-320.jpg)














