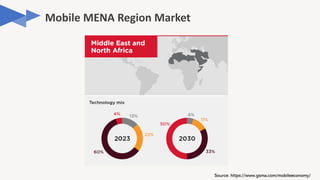
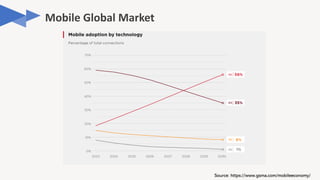
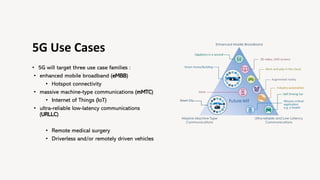
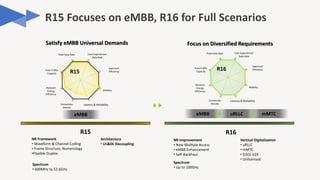
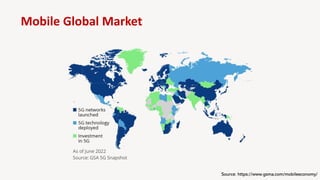
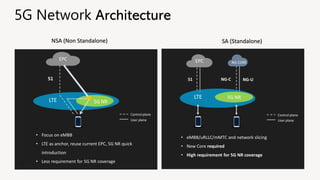
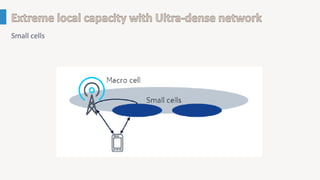
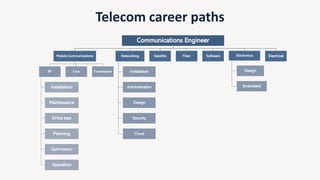
The document discusses the evolution of mobile technology, specifically the development of 5G, highlighting its major challenges, target use cases, and technical specifications. It outlines the differences between non-standalone (NSA) and standalone (SA) implementations of 5G, as well as the new radio frequencies allocated for this technology. Additionally, it emphasizes the skills required for careers in mobile communications and encourages personal development through networking and knowledge enhancement.