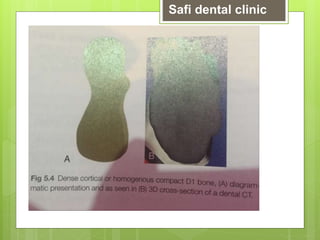
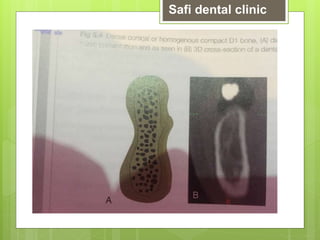
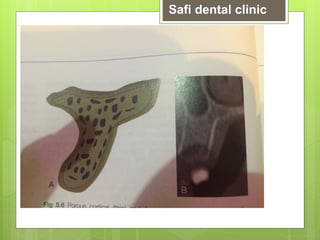
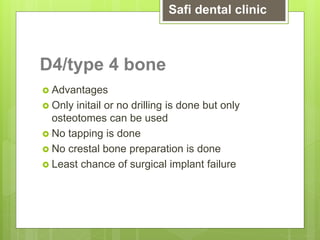
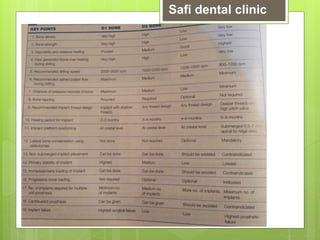
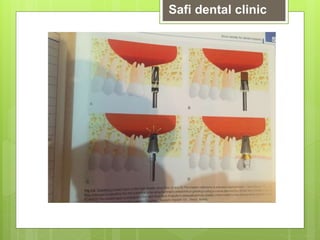
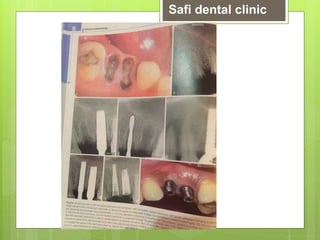
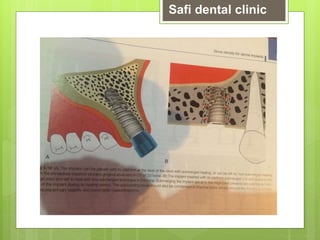
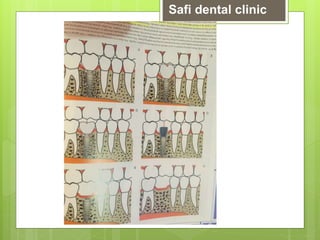
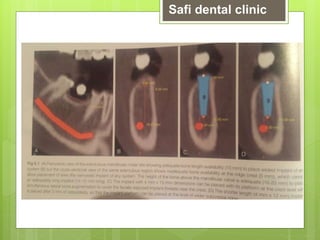
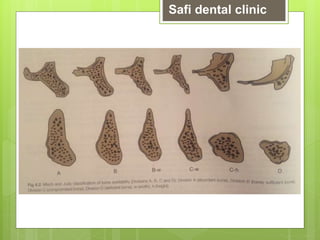
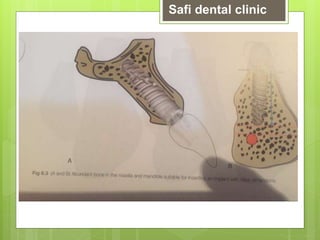
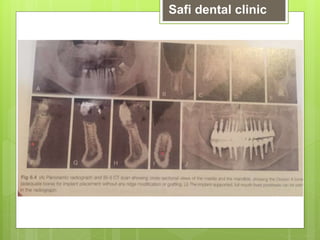
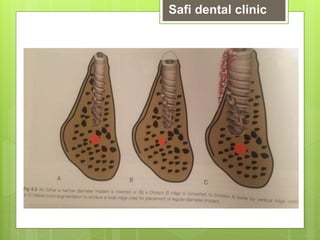
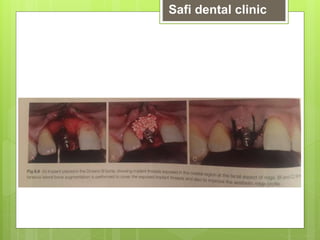
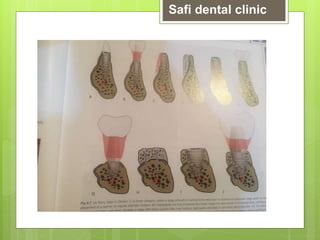
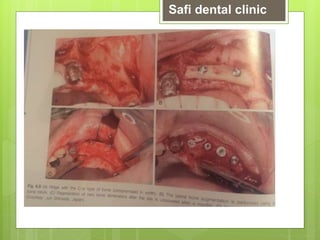
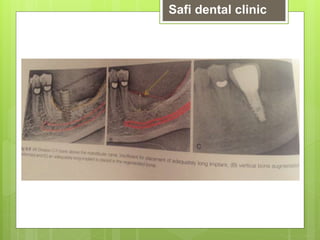
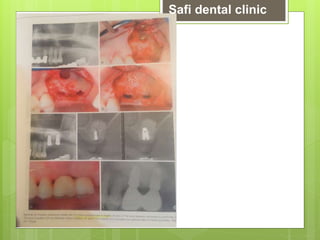
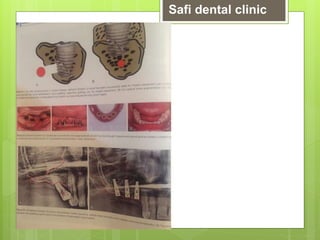
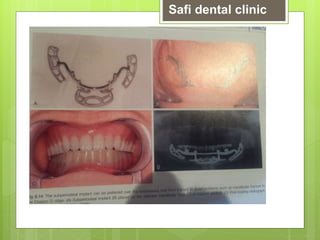
This document discusses factors related to bone density for dental implants. It describes Lekhom and Zarb's classification of jawbone quality and Misch's bone density classification. It discusses how to determine bone density using CT scans, tactile assessment, or bone gauges. The document outlines the advantages and disadvantages of different bone densities (D1-D4) for implants. It also covers Misch and Judy's classification of available bone (Divisions A-D), describing the characteristics and treatment options for each division. The overall document provides an overview of classifications for bone density and quality and how they relate to treatment planning for dental implants.