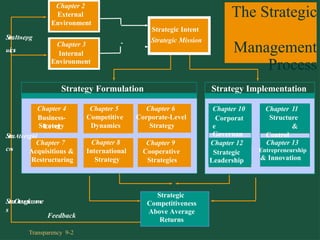
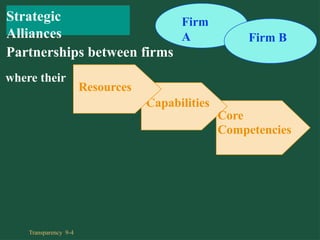
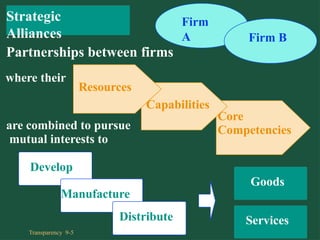
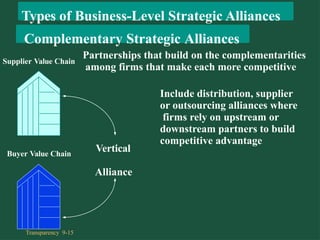
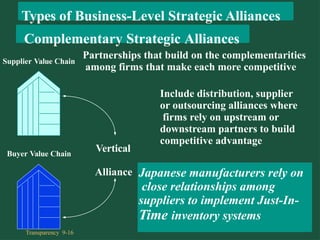
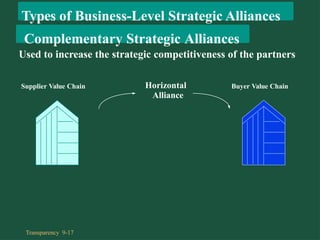
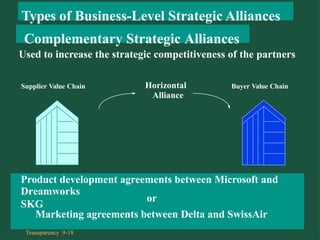
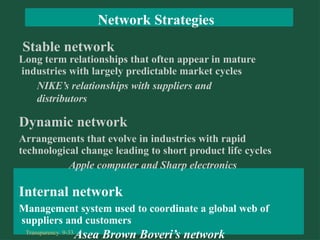
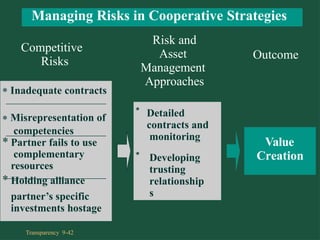
Chapter 9 discusses cooperative strategies in strategic management, outlining various types of alliances such as joint ventures, equity strategic alliances, and non-equity strategic alliances, which firms leverage to pool resources and enhance competitiveness. It elaborates on the reasons for forming these alliances, the challenges associated with managing them, and the risks involved, including misrepresentation and inadequate contracts. The chapter emphasizes the importance of understanding partners' strategic intent and creating trust to mitigate risks in cooperative arrangements.